Spring知識梳理
使用Spring時經常忘這忘那,然後就網上找資料浪費大部分時間,甚至只記得IOC、DI、AOP,至於其他細節早就忘記了,所以看W3Cschool和B站視訊重溫一遍加深理解,順便把學習過程記錄下來(最後會貼上二者的地址)
1. 體系結構
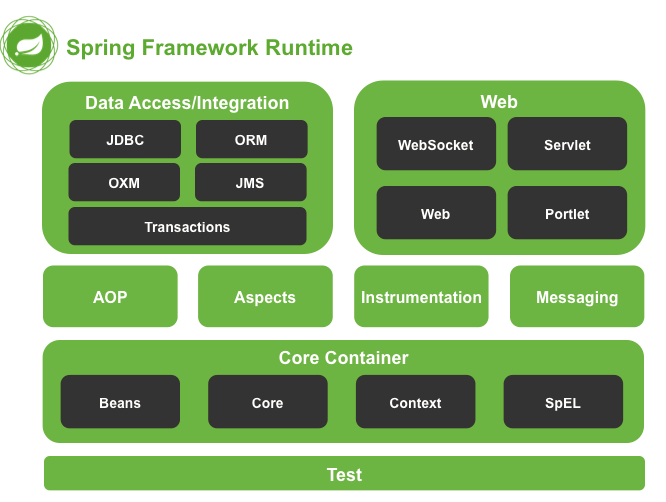
Spring是模組化的,可以選擇合適的模組來使用,其體系結構分為5個部分,分別為:
Core Container
核心容器:Spring最主要的模組,主要提供了IOC、DI、BeanFactory、Context等,列出的這些學習過Spring的同學應該都認識
Data Access/Integration
資料訪問/整合:即有JDBC的抽象層、ORM物件關係對映API、還有事務支援(重要)等
Web
Web:基礎的Web功能如Servlet、http、Web-MVC、Web-Socket等
Test
測試:支援具有Junit或TestNG框架的Spring元件測試
其他
AOP、Aspects(面向切面程式設計框架)等
2. IOC
2.1 引入耦合概念
耦合:即是類間或方法間的依賴關係,編譯時期的依賴會導致後期維護十分困難,一處的改動導致其他依賴的地方都需改動,所以要解耦
解耦:解除程式間的依賴關係,但在實際開發中我們只能做到編譯時期不依賴,執行時期才依賴即可,沒有依賴關係即沒有必要存在了
解決思路:使用Java的反射機制來避免new關鍵字(通過讀取配置檔案來獲取物件全限定類名)、使用工廠模式
2.2 IOC容器
Spring框架的核心,主要用來存放Bean物件,其中有個底層BeanFactory介面只提供最簡單的容器功能(特點延遲載入),一般不使用。常用的是其子類介面ApplicationContext介面(建立容器時立即例項化物件,繼承BeanFactory介面),提供了高階功能(訪問資源,解析檔案資訊,載入多個繼承關係的上下文,攔截器等)。
ApplicationContext介面有三個實現類:ClassPathXmlApplicationContext、FileSystemoXmlApplication、AnnotionalConfigApplication,從名字可以知道他們的區別,下面講解都將圍繞ApplicationContext介面。
容器為Map結構,鍵為id,值為Object物件。
2.2.1 Bean的建立方式
無參構造
只配了id、class標籤屬性(此時一定要有無參函式,新增有參構造時記得補回無參構造)
普通工廠建立
可能是別人寫好的類或者jar包,我們無法修改其原始碼(只有位元組碼)來提供無參建構函式,eg:
// 這是別人的jar包是使用工廠來獲取例項物件的
public class InstanceFactory {
public User getUser() {
return new User();
}
} <!-- 工廠類 -->
<bean id="UserFactory" class="com.howl.entity.UserFactory"></bean>
<!-- 指定工廠類及其生產例項物件的方法 -->
<bean id="User" factory-bean="UserFactory" factory-method="getUser"></bean>靜態工廠建立
<!-- class使用靜態工廠類,方法為靜態方法生產例項物件 -->
<bean id="User" class="com.howl.entity.UserFactory" factory-method="getUser"></bean>2.2.2 Bean標籤
該標籤在applicationContext.xml中表示一個被管理的Bean物件,Spring讀取xml配置檔案後把內容放入Spring的Bean定義登錄檔,然後根據該登錄檔來例項化Bean物件將其放入Bean快取池中,應用程式使用物件時從快取池中獲取
| 屬性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| class | 指定用來建立bean類 |
| id | 唯一的識別符號,可用 ID 或 name 屬性來指定 bean 識別符號 |
| scope | 物件的作用域,singleton(預設)/prototype |
| lazy-init | 是否懶建立 true/false |
| init-method | 初始化呼叫的方法 |
| destroy-method | x銷燬呼叫的方法 |
| autowire | 不建議使用,自動裝配byType、byName、constructor |
| factory-bean | 指定工廠類 |
| factory-method | 指定工廠方法 |
| 元素 | 描述 |
| constructor-arg | 建構函式注入 |
| properties | 屬性注入 |
| 元素的屬性 | 描述 |
| type | 按照型別注入 |
| index | 按照下標註入 |
| name | 按照名字注入,最常用 |
| value | 給基本型別和String注入 |
| ref | 給其他bean型別注入 |
| 元素的標籤 | 描述 |
<list> |
|
<Set> |
|
<Map> |
|
<props> |
2.2.3 使用
注意:預設使用無參建構函式的,若自己寫了有參構造,記得補回無參構造
XML
<bean id="User" class="com.howl.entity.User"></bean>ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
("applicationContext.xml");
User user = (User) ac.getBean("User");
user.getName();註解
前提在xml配置檔案中開啟bean掃描
<context:component-scan base-package="com.howl.entity"></context:component-scan>// 預設是類名首字母小寫
@Component(value="User")
public class User{
int id;
String name;
String eamil;
}2.2.4 生命週期
單例:與容器同生共死
多例: 使用時建立,GC回收時死亡
3. DI
Spring框架的核心功能之一就是通過依賴注入的方式來管理Bean之間的依賴關係,能注入的資料型別有三類:基本型別和String,其他Bean型別,集合型別。注入方式有:建構函式,set方法,註解
3.1 基於建構函式的注入
<!-- 把物件的建立交給Spring管理 -->
<bean id="User" class="com.howl.entity.User">
<constructor-arg type="int" value="1"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="1" value="Howl"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="email" value="[email protected]"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="birthday" ref="brithday"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="brithday" class="java.util.Date"></bean>3.2 基於setter注入(常用)
被注入的bean一定要有setter函式才可注入,而且其不關心屬性叫什麼名字,只關心setter叫什麼名字
<bean id="User" class="com.howl.entity.User">
<property name="id" value="1"></property>
<property name="name" value="Howl"></property>
<property name="email" value="[email protected]"></property>
<property name="birthday" ref="brithday"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="brithday" class="java.util.Date"></bean>3.3 注入集合
、
<bean id="User" class="com.howl.entity.User">
<property name="addressList">
<list>
<value>INDIA</value>
<value>Pakistan</value>
<value>USA</value>
<ref bean="address2"/>
</list>
</property>
<property name="addressSet">
<set>
<value>INDIA</value>
<ref bean="address2"/>
<value>USA</value>
<value>USA</value>
</set>
</property>
<property name="addressMap">
<map>
<entry key="1" value="INDIA"/>
<entry key="2" value-ref="address1"/>
<entry key="3" value="USA"/>
</map>
</property>
<property name="addressProp">
<props>
<prop key="one">INDIA</prop>
<prop key="two">Pakistan</prop>
<prop key="three">USA</prop>
<prop key="four">USA</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>3.4 註解
@Autowired:自動按照型別注入(所以使用註解時setter方法不是必須的,可用在變數上,也可在方法上)。若容器中有唯一的一個bean物件型別和要注入的變數型別匹配就可以注入;若一個型別匹配都沒有,則報錯;若有多個型別匹配時:先匹配全部的型別,再繼續匹配id是否有一致的,有則注入,沒有則報錯
@Qualifier:在按照型別注入基礎上按id注入,給類成員變數注入時不能單獨使用,給方法引數注入時可以單獨使用
@Resource:上面二者的結合
注意:以上三個注入只能注入bean型別資料,不能注入基本型別和String,集合型別的注入只能通過XMl方式實現
@Value:注入基本型別和String資料
承接上面有個User類了
@Component(value = "oneUser")
@Scope(value = "singleton")
public class OneUser {
@Autowired // 按型別注入
User user;
@Value(value = "注入的String型別")
String str;
public void UserToString() {
System.out.println(user + str);
}
}3.5 配置類(在SpringBoot中經常會遇到)
配置類等同於aplicationContext.xml,一般配置類要配置的是需要引數注入的bean物件,不需要引數配置的直接在類上加@Component
/**
* 該類是個配置類,作用與applicationContext.xml相等
* @Configuration表示配置類
* @ComponentScan(value = {""})內容可以傳多個,表示陣列
* @Bean 表示將返回值放入容器,預設方法名為id
* @Import 匯入其他配置類
* @EnableAspectJAutoProxy 表示開啟註解
*/
@Configuration
@Import(OtherConfiguration.class)
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
@ComponentScan(value = {"com.howl.entity"})
public class SpringConfiguration {
@Bean(value = "userFactory")
@Scope(value = "prototype")
public UserFactory createUserFactory(){
// 這裡的物件容器管理不到,即不能用@Autowired,要自己new出來
User user = new User();
// 這裡是基於建構函式注入
return new UserFactory(user);
}
}@Configuration
public class OtherConfiguration {
@Bean("user")
public User createUser(){
User user = new User();
// 這裡是基於setter注入
user.setId(1);
user.setName("Howl");
return user;
}
}
4. AOP
4.1 動態代理
動態代理:基於介面(invoke)和基於子類(Enhancer的create方法),基於子類的需要第三方包cglib,這裡只說明基於介面的動態代理,筆者 動態代理的博文
Object ob = Proxy.newProxyInstance(mydog.getClass().getClassLoader(), mydog.getClass().getInterfaces(),new InvocationHandler(){
// 引數依次為:被代理類一般不使用、使用的方法、引數的陣列
// 返回值為建立的代理物件
// 該方法會攔截類的所有方法,並在每個方法內注入invoke內容
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 只增強eat方法
if(method.getName().equals("eat")){
System.out.println("吃肉前洗手");
method.invoke(mydog, args);
}else{
method.invoke(mydog, args);
}
return proxy;
}
})4.2 AOP
相關術語:
連線點:這裡指被攔截的方法(Spring只支援方法)
通知:攔截到連線點要執行的任務
切入點:攔截中要被增強的方法
織入:增強方法的過程
代理物件:增強功能後返回的物件
切面:整體的結合,什麼時候,如何增強方法
xml配置
<!-- 需要額外的jar包,aspectjweaver表示式需要 -->
<!-- 被切入的方法 -->
<bean id="accountServiceImpl" class="com.howl.interfaces.impl.AccountServiceImpl"></bean>
<!-- 通知bean也交給容器管理 -->
<bean id="logger" class="com.howl.util.Logger"></bean>
<!-- 配置aop -->
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="pt1" expression="execution(* com.howl.interfaces..*(..))"/>
<aop:aspect id="logAdvice" ref="logger">
<aop:before method="beforeLog" pointcut-ref="pt1"></aop:before>
<aop:after-returning method="afterReturningLog" pointcut-ref="pt1"></aop:after-returning>
<aop:after-throwing method="afterThrowingLog" pointcut-ref="pt1"></aop:after-throwing>
<aop:after method="afterLog" pointcut="execution(* com.howl.interfaces..*(..))"></aop:after>
<!-- 配置環繞通知,測試時請把上面四個註釋掉,排除干擾 -->
<aop:around method="aroundLog" pointcut-ref="pt1"></aop:around>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
<!-- 切入表示式 -->
<!-- 訪問修飾符 . 返回值 . 包名 . 包名 . 包名。。。 . 類名 . 方法名(引數列表) -->
<!-- public void com.howl.Service.UserService.deleteUser() -->
<!-- 訪問修飾符可以省略 -->
<!-- * 表示通配,可用於修飾符,返回值,包名,方法名 -->
<!-- .. 標誌當前包及其子包 -->
<!-- ..可以表示有無引數,*表示有引數 -->
<!-- * com.howl.service.*(..) -->
<!-- 環繞通知是手動編碼方式實現增強方法合適執行的方式,類似於invoke? -->即環繞通知是手動配置切入方法的,且Spring框架提供了ProceedingJoinPoint,該介面有一個proceed()和getArgs()方法。此方法就明確相當於呼叫切入點方法和獲取引數。在程式執行時,spring框架會為我們提供該介面的實現類供我們使用
// 抽取了公共的程式碼(日誌)
public class Logger {
public void beforeLog(){
System.out.println("前置通知");
}
public void afterReturningLog(){
System.out.println("後置通知");
}
public void afterThrowingLog(){
System.out.println("異常通知");
}
public void afterLog(){
System.out.println("最終通知");
}
// 這裡就是環繞通知
public Object aroundLog(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp){
Object rtValue = null;
try {
// 獲取方法引數
Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();
System.out.println("前置通知");
// 呼叫業務層方法
rtValue = pjp.proceed();
System.out.println("後置通知");
} catch (Throwable t) {
System.out.println("異常通知");
t.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println("最終通知");
}
return rtValue;
}
}基於註解的AOP
<!-- 配置Spring建立容器時要掃描的包,主要掃描被切入的類,以及切面類 -->
<context:compinent-scan base-package="com.howl.*"></context:compinent-scan>
<!-- 這二者的類上要註解 @Compinent / @Service -->
<!-- 開啟AOP註解支援 -->
<aop:aspectj:autoproxy></aop:aspectj:autoproxy>>注意要在切面類上加上註解表示是個切面類,四個通知在註解中通知順序是不能決定的且亂序,不建議使用,不過可用環繞通知代替 。即註解中建議使用環繞通知來代替其他四個通知
// 抽取了公共的日誌
@Component(value = "logger")
@Aspect
public class Logger {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.howl.interfaces..*(..))")
private void pt1(){}
@Before("pt1()")
public void beforeLog(){
System.out.println("前置通知");
}
@AfterReturning("pt1()")
public void afterReturningLog(){
System.out.println("後置通知");
}
@AfterThrowing("pt1()")
public void afterThrowingLog(){
System.out.println("異常通知");
}
@After("pt1()")
public void afterLog(){
System.out.println("最終通知");
}
@Around("pt1()")
public Object aroundLog(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp){
Object rtValue = null;
try {
// 獲取方法引數
Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();
System.out.println("前置通知");
// 呼叫業務層方法
rtValue = pjp.proceed();
System.out.println("後置通知");
} catch (Throwable t) {
System.out.println("異常通知");
t.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println("最終通知");
}
return rtValue;
}
}
5. 事務
Spring提供了宣告式事務和程式設計式事務,後者難於使用而選擇放棄,Spring提供的事務在業務層,是基於AOP的
5.1 宣告式事務
從業務程式碼中分離事務管理,僅僅使用註釋或 XML 配置來管理事務,Spring 把事務抽象成介面 org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager ,其內容如下,重要的是其只是個介面,真正實現類是:org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager
public interface PlatformTransactionManager {
// 根據定義建立或獲取當前事務
TransactionStatus getTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition);
void commit(TransactionStatus status);
void rollback(TransactionStatus status);
}TransactionDefinition事務定義資訊
public interface TransactionDefinition {
int getPropagationBehavior();
int getIsolationLevel();
String getName();
int getTimeout();
boolean isReadOnly();
}因為不熟悉所以把過程全部貼下來
5.2 xml配置
建表
CREATE TABLE `account` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`money` int(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=3 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;entity
public class Account {
private int id;
private int money;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(int money) {
this.money = money;
}
public Account(int id, int money) {
this.id = id;
this.money = money;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account{" +
"id=" + id +
", money=" + money +
'}';
}
}Dao層
public interface AccountDao {
// 查詢賬戶
public Account selectAccountById(int id);
// 更新賬戶
public void updateAccountById(@Param(value = "id") int id, @Param(value = "money") int money);
}Mapper層
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.howl.dao.AccountDao">
<select id="selectAccountById" resultType="com.howl.entity.Account">
SELECT * FROM account WHERE id = #{id};
</select>
<update id="updateAccountById">
UPDATE account SET money = #{money} WHERE id = #{id}
</update>
</mapper>Service層
public interface AccountService {
public Account selectAccountById(int id);
public void transfer(int fid,int sid,int money);
}Service層Impl
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao;
public Account selectAccountById(int id) {
return accountDao.selectAccountById(id);
}
// 這裡只考慮事務,不關心錢額是否充足
public void transfer(int fid, int sid, int money) {
Account sourceAccount = accountDao.selectAccountById(fid);
Account targetAccount = accountDao.selectAccountById(sid);
accountDao.updateAccountById(fid, sourceAccount.getMoney() - money);
// 異常
int i = 1 / 0;
accountDao.updateAccountById(sid, targetAccount.getMoney() + money);
}
}applicationContext.xml配置
<!-- 配置資料來源,spring自帶的沒有連線池功能 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/spring"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value=""></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置sqlSessionFactory工廠 -->
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis-config.xml"></property>
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 業務層bean -->
<bean id="accountServiceImpl" class="com.howl.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl" lazy-init="true">
<property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 事務管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置事務通知,可以理解為Logger -->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<!-- 配置事務的屬性
isolation:隔離界別,預設使用資料庫的
propagation:轉播行為,預設REQUIRED
read-only:只有查詢方法才需要設定true
timeout:預設-1永不超時
no-rollback-for
rollback-for
-->
<tx:attributes>
<!-- name中是選擇匹配的方法 -->
<tx:method name="select*" propagation="SUPPORTS" read-only="true"></tx:method>
<tx:method name="*" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"></tx:method>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!-- 配置AOP -->
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="pt1" expression="execution(* com.howl.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl.transfer(..))"/>
<!-- 建立切入點表示式與事務通知的對應關係 -->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="pt1"></aop:advisor>
</aop:config>測試
public class UI {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
AccountService accountService = (AccountService) ac.getBean("accountServiceImpl");
Account account = accountService.selectAccountById(1);
System.out.println(account);
accountService.transfer(1,2,100);
}
}正常或發生異常都完美執行個人覺得重點在於配置事務管理器(而像資料來源這樣是日常需要)
事務管理器:管理獲取的資料庫連線
事務通知:根據事務管理器來配置所需要的通知(類似於前後置通知)
上面兩個可以認為是合一起配一個通知,而下面的配置方法與通知的對映關係
AOP配置:用特有的<aop:advisor>標籤來說明這是一個事務,需要在哪些地方切入
5.3 註解事務
- 配置事務管理器(和xml一樣必須的)
- 開啟Spring事務註解支援
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"></tx:annotation-driven> - 在需要註解的地方使用@Transaction
- 不需要AOP,是因為@Transaction註解放在了哪個類上就說明哪個類需要切入,裡面所有方法都是切入點,對映關係已經存在了
在AccountServiceImpl中簡化成,xml中可以選擇方法匹配,註解不可,只能這樣配
@Service(value = "accountServiceImpl")
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.SUPPORTS, readOnly = true)
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
// 這裡為了獲取Dao層
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao;
// 業務正式開始
public Account selectAccountById(int id) {
return accountDao.selectAccountById(id);
}
// 這裡只考慮事務,不關心錢額是否充足
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED,readOnly = false)
public void transfer(int fid, int sid, int money) {
Account sourceAccount = accountDao.selectAccountById(fid);
Account targetAccount = accountDao.selectAccountById(sid);
accountDao.updateAccountById(fid, sourceAccount.getMoney() - money);
// 異常
// int i = 1 / 0;
accountDao.updateAccountById(sid, targetAccount.getMoney() + money);
}
}
6. Test
應用程式的入口是main方法,而JUnit單元測試中,沒有main方法也能執行,因為其內部集成了一個main方法,該方法會自動判斷當前測試類哪些方法有@Test註解,有就執行。
JUnit不會知道我們是否用了Spring框架,所以在執行測試方法時,不會為我們讀取Spring的配置檔案來建立核心容器,所以不能使用@Autowired來注入依賴。
解決方法:
- 匯入JUnit包
- 匯入Spring整合JUnit的包
- 替換Running,@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
- 加入配置檔案,@ContextConfiguration
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = SpringConfiguration.class)
//@ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class UITest {
@Autowired
UserFactory userFactory;
@Test
public void User(){
System.out.println(userFactory.getUser().toString());
}
}
7. 註解總覽
@Component
@Controller
@Service
@Repository
@Autowired
@Qualifier
@Resource
@Value
@Scope
@Configuration
@ComponentScan
@Bean
@Import
@PropertySource()
@RunWith
@ContextConfiguration
@Transactional
8. 總結
學完Spring之後感覺有什麼優勢呢?
IOC、DI:方便降耦
AOP:重複的功能形成元件,在需要處切入,切入出只需關心自身業務甚至不知道有元件切入,也可把切入的元件放到開發的最後才完成
宣告式事務的支援
- 最小侵入性:不用繼承或實現他們的類和介面,沒有綁定了程式設計,Spring儘可能不讓自身API弄亂開發者程式碼
整合測試
方便整合其他框架
參考
W3Cschool
B站視訊
<
