ElasticSearch之對映常用操作
阿新 • • 發佈:2020-03-20

本文案例操作,建議先閱讀我之前的文章[《ElasticSearch之安裝及基本操作API》](https://ytao.top/2019/12/14/11-elasticsearch/)
> Mapping (對映)類似關係型資料庫中的表的結構定義。我們將資料以 JSON 格式存入到 ElasticSearch 中後,在搜尋引擎中 JSON 欄位對映對應的型別,這時需要 mapping 來定義內容的型別。
# 欄位型別
JSON 資料型別對映到 ElasticSearch 定義的型別,常用的簡單型別有:
JSON型別 | ElasticSearch 型別
:--:|:--:
文字型別 | Text/Keyword
整數型別 | long/integer
浮點型別 | float/double
時間型別 | date
布林值 | boolean
陣列 | Text/Keyword
上面要注意的是時間型別,JSON 中並沒有時間型別,這裡主要指時間格式資料的型別。
# 定義對映
在關係型資料庫中,儲存資料之前,我們會先建立表結構,給欄位指定一個存在的型別。同樣 ElasticSearch 在進行資料儲存前,也可以先定義好儲存資料的 Mapping 結構。
先定義一個簡單的 person Mapping:
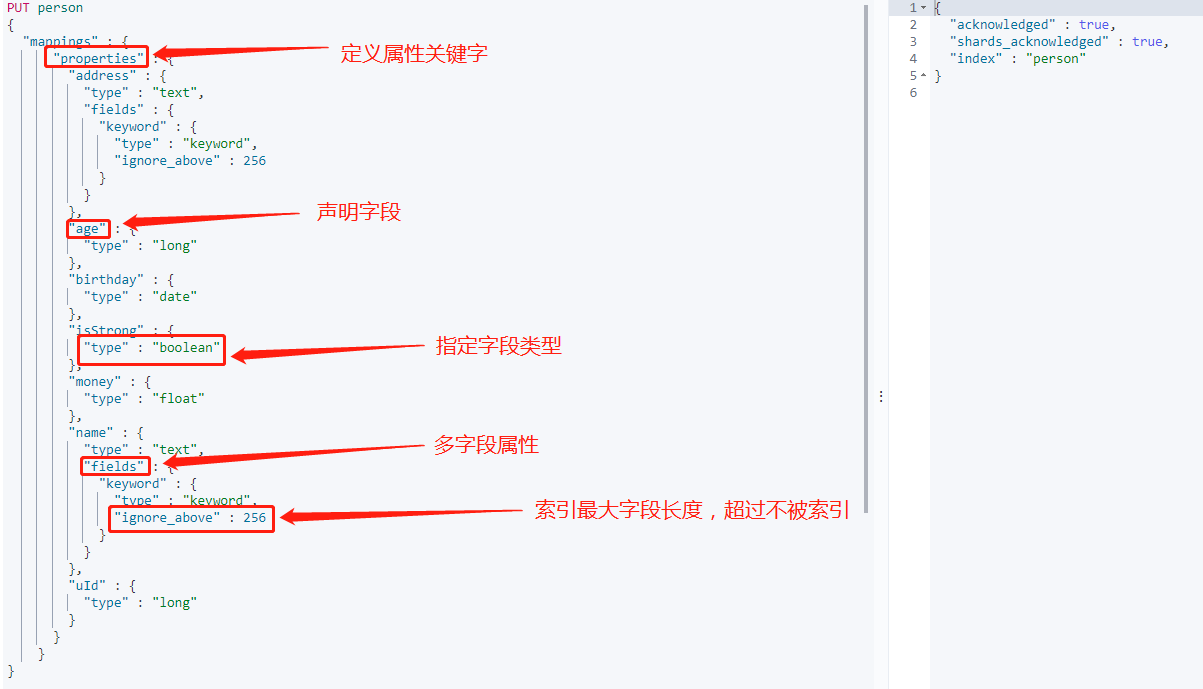
上圖中就是一個 Mapping 的定義,如果是在 ElasticSearch7 之前,mappings 裡還有 _type 屬性。
# 動態對映
當沒有事先定義好 Mapping,新增資料時,ElasticSearch 會自動根據欄位進行換算出對應的型別,但是換算出來的型別並不一定是我們想要的欄位型別,還是需要人為的干預進行修改成想要的 Mapping。
# 更新對映
使用 **dynamic** 控制對映是否可以被更新。
## dynamic-true
設定 dynamic 為`true`是預設 dynamic 的預設值,新增欄位資料可以寫入,同時也可以被索引,Mapping 結構也會被更新。

新增資料,同時多新增一個沒被定義的 `gender` 欄位。
```bash
# 向 person 中新增資料
PUT person/_doc/1
{
"uId": 1,
"name": "ytao",
"age": 18,
"address": "廣東省珠海市",
"birthday": "2020-01-15T12:00:00Z",
"money": 108.2,
"isStrong": true,
"gender": "男" # Mapping 中未定義的欄位
}
```
新增成功,搜尋 `gender` 欄位:
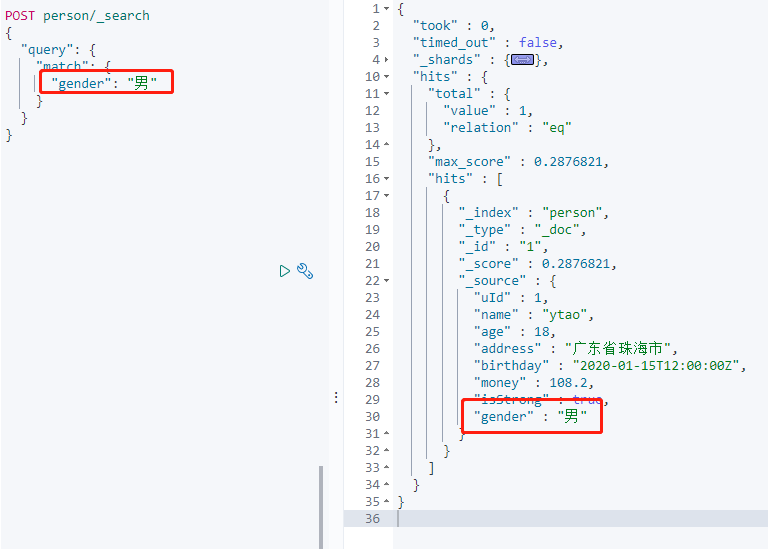
檢視 Mapping 結構:
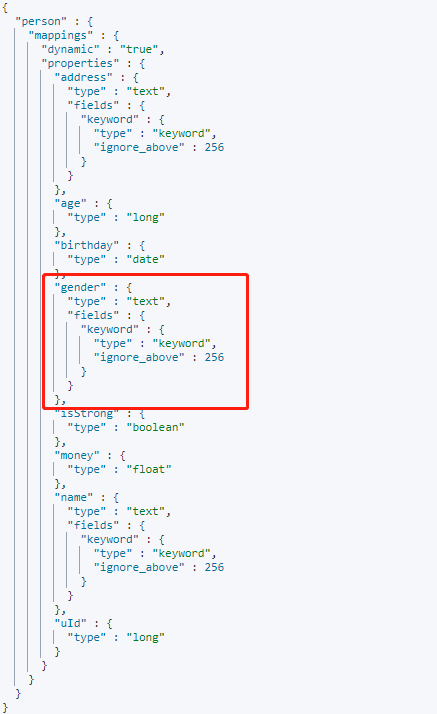
新新增的欄位值,在新增過程中 Mapping 已自動新增欄位。
## dynamic-false
設定 dynamic 為`false`時,新增欄位資料可以寫入,不可以被索引,Mapping 結構會被更新。
同樣先將 dynamic 設定為 false,然後向裡面新增資料,其他步驟和上面 true 操作一樣。定義 Mapping,新增資料。
搜尋 `gender` 欄位:

此時新增欄位資料無法被索引,但資料可以寫入。
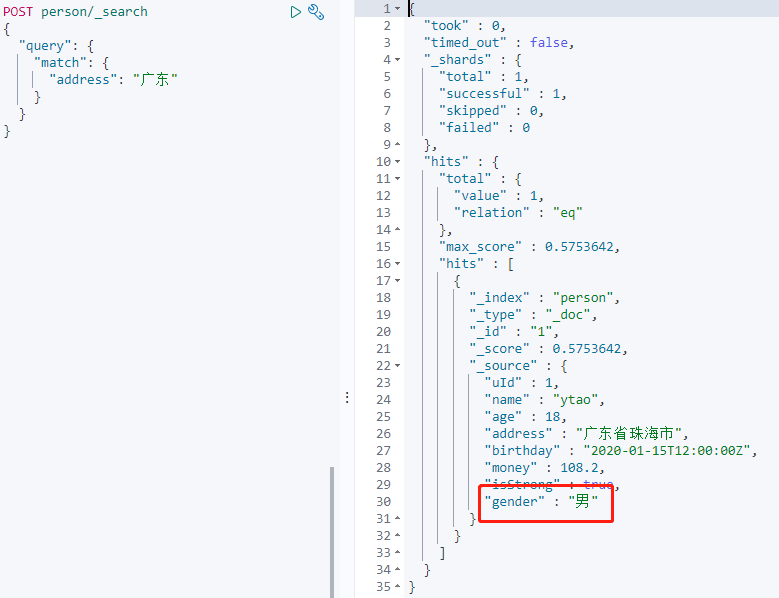
Mappnig 也不會新增新增的欄位:
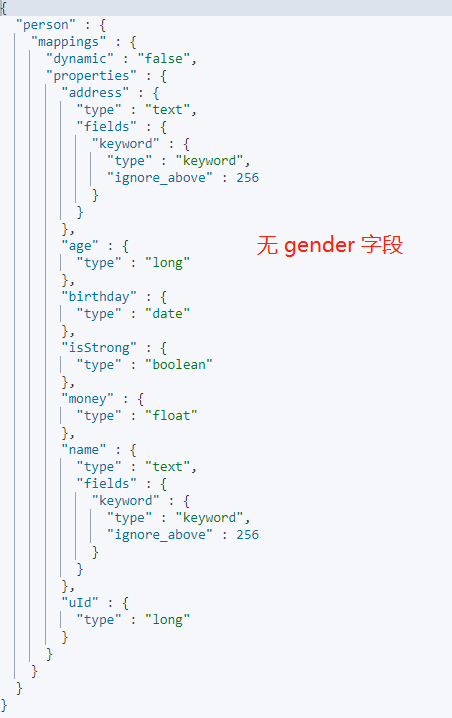
## dynamic-strict
設定 dynamic 為`strict`時,從字面上意思也可以看出,對於動態對映是較嚴格的,新增欄位資料不可以寫入,不可以被索引,Mapping 結構不會被更新。只能按照定義好的 Mapping 結構新增資料。
在新增新欄位資料時,就馬上會丟擲異常:
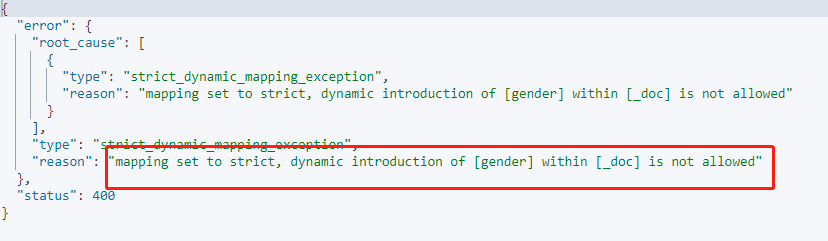
# 自動識別日期型別
上文中,當 dynamic 設定為 true 時,新增新欄位資料自動識別型別更新 Mapping,如果是日期型別的話,我們是可以指定識別的型別。
指定 person 的 **dynamic_date_formats** 格式:
```bash
PUT person/_mapping
{
"dynamic_date_formats": ["yyyy/MM/dd"]
}
```
這裡是可以指定多個時間格式。
向 person 新增新資料,分別是 today 和 firstDate:
```bash
PUT person/_doc/2
{
"today": "2020-01-15",
"firstDate": "2020/01/15"
}
```
新增新欄位資料後的 Mapping:
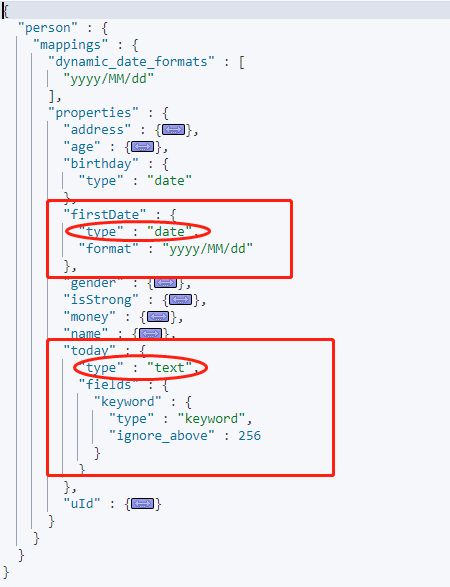
由於上面我們指定了時間格式為 `yyyy/MM/dd` 時是可以識別為時間格式,所以 today 欄位的值為 `yyyy-MM-dd` 格式無法識別為時間型別,判為 text 型別。
# 多欄位
Mapping 中可以定義 **fields** 多欄位屬性,以滿足不同場景下的實現。比如 `address` 定義為 `text` 型別,fields 裡面又有定義 `keyword` 型別,這裡主要是區分兩個不同不同使用場景。
- `text` 會建立分詞倒排索引,用於全文檢索。
- `keyword` 不會建立分詞倒排索引,用於排序和聚合。
新增資料:
```bash
# 向 person 中新增資料
PUT person/_doc/1
{
"uId": 1,
"name": "ytao",
"age": 18,
"address": "廣東省珠海市",
"birthday": "2020-01-15T12:00:00Z",
"money": 108.2,
"isStrong": true
}
```
查詢`address`資料。

查詢`address.keyword`資料。
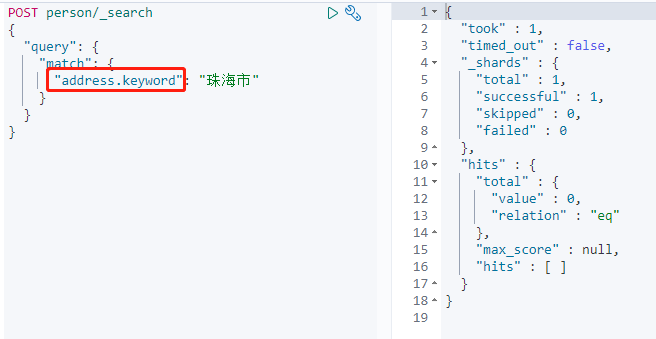
通過`keyword`檢索時,由於不會建立分詞索引,並沒有獲取到資料。
# 控制索引
在欄位中使用 **index** 指定當前欄位索引是否能被搜尋到。指定型別為 boolean 型別,false 為不可搜尋到,true 為可以搜尋到。
先刪除之前的 Mapping:
```bash
DELETE person
```
建立 Mapping,設定`name`屬性的 `index` 為 false。
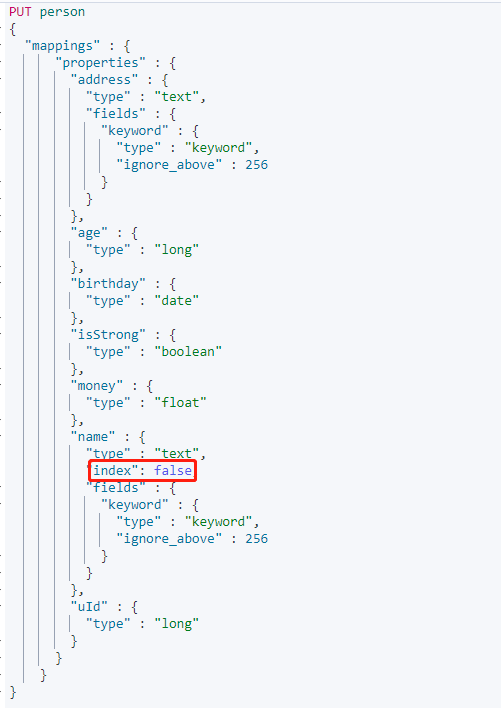
再次新增上面的資料後搜尋`name`欄位:
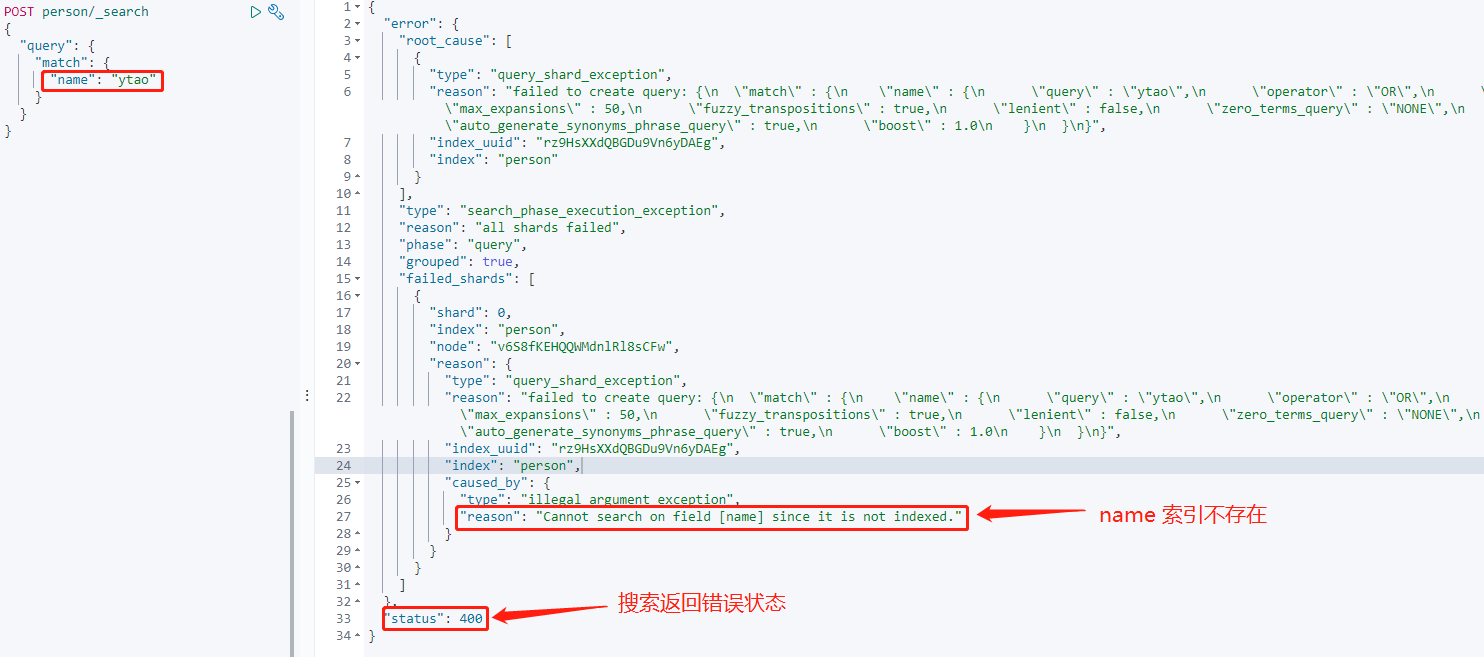
欄位 index 設定 false 後,由於沒有被索引,所以搜尋無法獲取到索引。
# 空值處理
現在向 ElasticSearch 中新增一條 address 為空的資料:
```bash
PUT person/_doc/2
{
"uId": 2,
"name": "Jack",
"age": 22,
"address": null,
"birthday": "2020-01-15T12:00:00Z",
"money": 68.7,
"isStrong": true
}
```
搜尋 address.keyword 為空的資料:
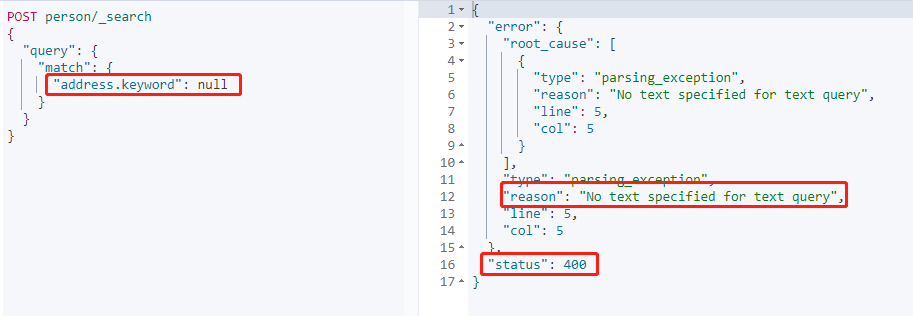
搜尋返回異常,預設是不被允許搜尋 NUll。
這是需要在 Mapping 指定 **null_value** 屬性,並且不能在`text`型別中宣告。
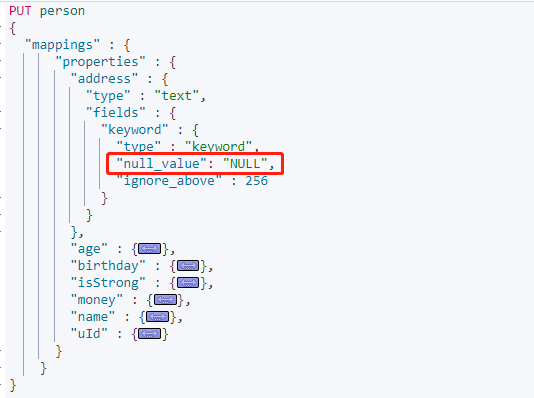
搜尋 address.keyword 為空的資料:
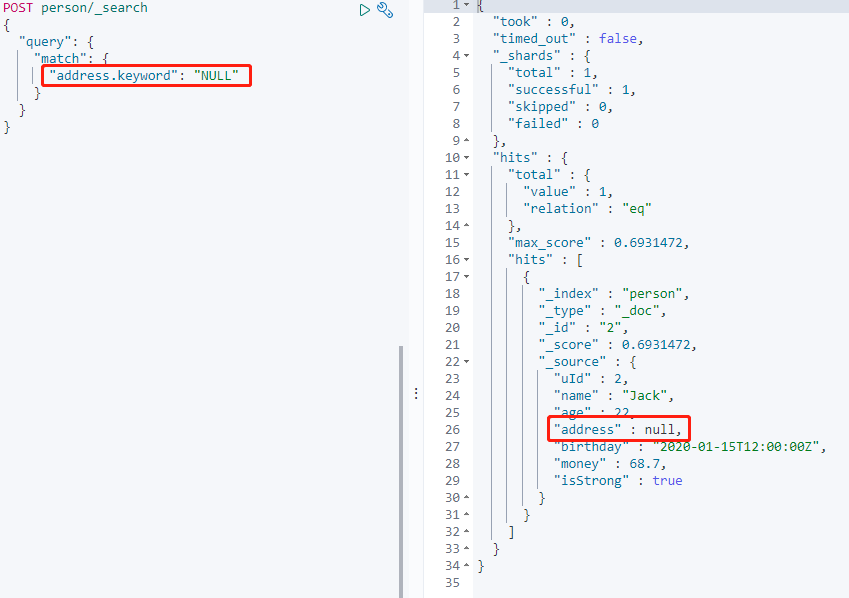
設定 `"null_value": "NULL"` 後,空值可以處理搜尋。
# 聚合多個欄位
聚合多個欄位放到一個索引中,使用 **copy_to** 進行聚合。例如我們在多欄位查詢中,這是不需要對每個欄位進行過濾篩選,只需對聚合欄位即可。
在使用 copy_to 時,是通過指定聚合的名稱實現。
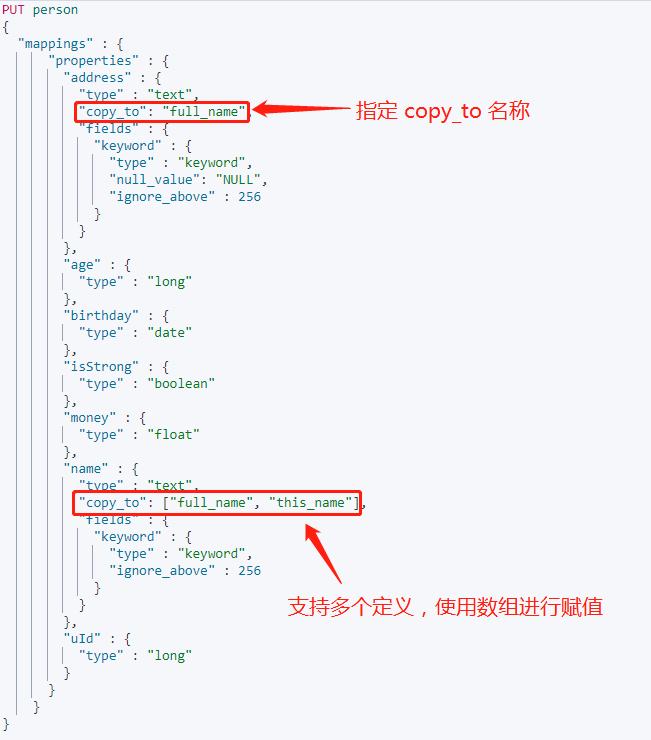
實際上,copy_to 不使用陣列格式新增名稱,也會自動轉換成資料格式。
新增兩條資料,待校驗搜尋:
```bash
# 向 person 中新增資料
PUT person/_doc/1
{
"uId": 1,
"name": "ytao",
"age": 18,
"address": "廣東省珠海市",
"birthday": "2020-01-15T12:00:00Z",
"money": 108.2,
"isStrong": true
}
PUT person/_doc/2
{
"uId": 2,
"name": "楊廣東",
"age": 22,
"address": null,
"birthday": "2020-01-15T12:00:00Z",
"money": 68.7,
"isStrong": true
}
```
查詢 `full_name` 的值,會返回 name 和 address 相關的值的物件。
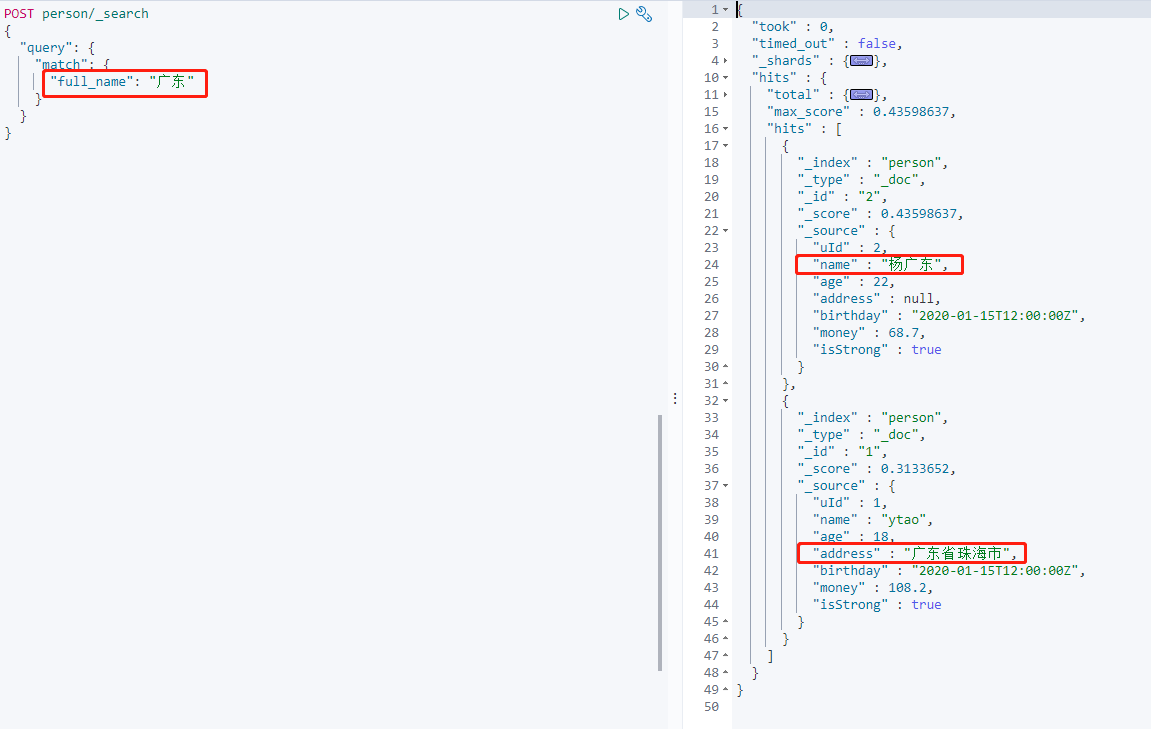
從上面返回結果看到,_source 中的欄位沒有增加相應的 copy_to 欄位名,所以 copy_to 只會拷貝欄位內容至索引,並不會改變包含的欄位。
# 總結
> 通過本文對建立 Mapping 檔案的常用並且實用的操作介紹,也基本能掌握這些日常的使用。瞭解 Mapping 的功能操作,相信對儲存時的設計也有一定幫助。
個人部落格: [https://ytao.top](https://ytao.top)
關注公眾號 【ytao】,更多原創好文
