C# 基礎知識系列- 3 集合陣列
簡單的介紹一下集合,通俗來講就是用來保管多個數據的方案。比如說我們是一個公司的倉庫管理,公司有一堆貨物需要管理,有同類的,有不同類的,總而言之就是很多、很亂。我們對照集合的概念對倉庫進行管理的話,那麼 陣列就是將一堆貨整整齊齊的碼在倉庫的某個地方,普通列表也是如此;Set就是在倉庫裡有這麼一個貨架,每種貨品只能放一個,一旦某種貨品超過一個了貨架就塌了;Dictionary字典呢,在一個貨架上隨機擺放,然後再找一個本子把每個貨品存放的位置記錄下來。
1. 主要集合
C#/.NET Framework 提供了很多很有意思的集合類,陣列、列表、連結串列、Set、字典等一系列的類。其中陣列是語言的一部分,個人認為嚴格意義上不屬於集合類這一部分。C#開發中常用的集合有陣列、 List類、Set介面、Dictionary類、Queue類、LinkedList類等,其他的出鏡率不高。
與其他(java)語言不同的一點是,C#的List
IList,但這個介面意義不大,在使用IList的時候更多的傾向於使用IEnumerable,這主要是因為IEnumerable 有 Linq的支援再者兩者的方法基本一致,能用IList的地方基本都可以用IEnumerable。
1.1 Array 陣列
陣列,集合的基礎部分,主要特點是一經初始化就無法再次對陣列本身進行增刪元素。C#雖然添加了一些修改陣列的擴充套件方法,但基本都會返回新的陣列物件。
1.1.1 初始化
陣列的初始化需要指定大小,可以顯示指定或者隱式的指定。
// 顯示指定型別與大小,具體的元素後續賦值 string[] strArr = new string[10]; //指定型別同時給元素賦值,具體大小由編譯器自動推斷 string[] strArr1 = new string[]{"1","2","3","4","5","6","7","8","9","10"}; // 型別和大小都由編譯器進行推斷 string[] strArr2 = new []{"1","2","3","4","5","6","7","8","9","10"};
1.1.2 常用方法
- 訪問和賦值
陣列可以通過下標訪問陣列中的元素,下標從0開始,表示0位。程式碼如下:
string item0 = strArr[0]; //取出 "1"
string item2 = strArr[2]; // 取出 "3"
strArr[0] = "3"; // strArr = {"3","2","3","4","5","6","7","8","9","10"}- 獲取長度
int length = strArr.Length;// 獲取一個整型的長度 //獲取一個長整型的長度,對於一個非常大的陣列且長度可能會超過int的最大值 long longLength = strArr.LongLength;
- 迴圈迭代
// 普通for 迴圈
for(int i = 0;i < strArr.Length;i++)
{
string it = strArr[i];
}
// foreach 迴圈
foreach(string it in strArr)
{
// 依次迴圈,不需要下標,操作更快一點
}1.1.3 不常用但有用的方法
CopyTo複製到public void CopyTo(Array array, int index); public void CopyTo(Array array, long index);引數說明: array 需要複製到的陣列,index 目標陣列的起始下標
方法說明:將 源陣列的元素依次複製到 array從index下標開始的位置
值得注意的是string[] strArr1 = new string[]{"1","2","3","4","5","6","7","8","9","10"}; string[] strArr3 = new string[10]; strArr1.CopyTo(strArr3, 0); //strArr3 = {"1","2","3","4",'5","6","7","8","9","10"}strArr3的長度不能 小於 index + strArr1.LengthSort排序這個方法不是陣列物件的方法,而是
Array提供的一個靜態方法。
值得注意的是,該方法是直接對陣列進行操作,所以不會返回新的陣列。int[] arr1 = new[] {1, 9, 28, 5, 3, 6, 0, 12, 44, 98, 4, 2, 13, 18, 81, 92}; Array.Sort(arr1);//0,1,2,3,4,5,6,9,12,13,18,28,44,81,92,98ToList轉成List
顧名思義,將Array物件轉成List物件。這裡需要額外注意的是,轉換成的List是不可改變長度的。
Clone()獲得一個淺拷貝的陣列物件
獲取該物件的一個淺拷貝陣列物件。
至於其他的Array類和Array物件 還有很多有意思的方法,但是平時開發的時候使用的頻率比較低。這裡就不一一介紹了,以後需要會介紹一下的。
1.2 List 列表
List列表為一個泛型類,泛型表示<T>,其中T表示列表中存放的元素型別,T代表C#中可例項化的型別。關於泛型的具體描述以後介紹,現在回過頭來繼續介紹列表。列表內部持有一個數組物件,列表有兩個私有變數:一個是列表容量,即內部陣列的大小;另一個是存放的元素數量,通過Count獲取。
List列表通過元素數量實現了Add和Remove 的操作,列表物件操作引發元素數量變動時都會導致對容量的重新計算,如果現有容量不滿足後續操作需要的話,將會對現有陣列進行擴充。
1.2.1 初始化
List<string> list = new List<string>();// 初始化一個空的列表
List<string> list1 = new List<string>{"12", "2"};//初始化一個包含兩個元素的列表
list1 = new List<string>(100);//初始化一個空的列表,並指定list的初始容量為100
list = new List<string>(list1);// 使用一個List/Array 初始化一個列表1.2.2 常用方法
Count 表示獲取一個int型別的的數量值,LongCount表示獲取一個long型別的數量值。通常情況下兩者返回的結果是一致的,但是如果列表中元素的數量超過了int允許的最大返回直接使用Count或LongCount獲取元素的數量Count獲取將會出現資料溢位的問題,這時候就需要LongCount了。訪問元素/修改元素
C#的列表操作單個元素很簡單 ,與陣列的操作方式完全一樣。
需要注意的地方是,如果給定的下標超過了List物件的索引值範圍會報string str = list1[0];//獲取 list1 的第一個元素,即下標為0的元素 list1[2] = "233"; // 將 list1 的第三個元素設定為“233” ,即下標為2 的元素,這裡假設list1有至少三個元素ArgumentOutOfRangeException。判斷方法就是 下標>=Count,如果滿足就會越界。Add或AddRange新增到列表最後將元素新增到List的末尾,
Add新增一個,AddRange新增一組,支援陣列、列表。List<string> list = new List<string>();// 初始化一個空的列表 list.Add("12");//list = {"12"} List<string> list1 = new List<string>{"14", "2"}; list.AddRange(list1);// list = {"12","14","2"}Insert(int index, T item)或InsertRange(int index,IEnumerable<T> items)插入Insert(int index,T item)在 index 下標處插入一個元素,該下標以及該下標以後的元素依次後移InsertRange(int index,IEnumerable<T> items)在index下標處插入一組元素,該下標以及之後的元素依次後移
示例:
List<int> arr1 = new List<int>{1, 9, 28, 5, 3, 6, 0, 12, 44, 98, 4, 2, 13, 18, 81, 92}; arr1.Insert(3,37);// arr1 = 1,9,28,37,5,3,6,0,12,44,98,4,2,13,18,81,92 下標為3的元素變成了37,之後的元素依次後移了List<int> arr1 = new List<int>{1, 9, 28, 5, 3, 6, 0, 12, 44, 98, 4, 2, 13, 18, 81, 92}; List<int> arr2 = new List<int>{2,3,4,5}; arr1.InsertRange(2,arr2);//arr1= 1,9,2,3,4,5,28,5,3,6,0,12,44,98,4,2,13,18,81,92 可以明顯發現下標為2的元素髮生了變化Contains(T item)是否包含
返回一個Boolean型別的結果,如果包含則返回true,如果不包含則返回falseList<int> arr2 = new List<int>{2,3,4,5}; arr2.Contains(8);//false arr2.Contains(3);//trueRemove(T item)刪除指定元素
值得注意的是,如果刪除一個不存在的元素時,不會報錯,列表也不會發生任何改變。List<int> arr2 = new List<int>{2,3,4,5}; arr2.Remove(3);// arr2 = 2,4,5 arr2.Remove(6);//arr2 = 2,4,5RemoveAt(int index)刪除位於下標的元素
如果移除的下標超過了列表的最後一個元素的下標將會丟擲異常List<int> arr2 = new List<int>{2,3,4,5}; arr2.RemoveAt(1);//arr2 = 2,4,5RemoveRane(IEnumerable<T> items)刪除一組元素與
Remove(T item)一致,如果要刪除的元素不在列表中,則列表元素不會發生變化。List<int> arr1 = new List<int>{1, 9, 28, 5, 3, 6, 0, 12, 44, 98, 4, 2, 13, 18, 81, 92}; List<int> arr2 = new List<int>{2,3,4,5}; arr1.RemoveRange(arr2);GetRange(int index,int count)從列表中獲取一個子列表,從
index開始,獲取count個元素,如果源列表中從index開始剩餘的元素不足count個將會報錯。
1.2.3 不常用但有用的方法
將列表清空,呼叫方法之後,列表中將不包含任何元素Clear()刪除所有元素
將列表按照從尾到頭的順序進行排列Reverse()調轉順序
查詢元素在列表中的下標,如果沒找到元素,則返回-1IndexOf(T item)查詢下標Sort()排序對列表進行排序,呼叫方法後,會按照預設排序方法返回一個排序結果
1.3 Set 集合
C#沒有為Set單獨設定類,一方面是因為Set出鏡率不高,另一方面也因為Set本身的機制所致。Set集合不能包含重複元素,如果嘗試存入重複元素集合元素將不會發生任何變化。
Set集合中元素的順序與存放順序不一定相同。因為Set集合中存放對於使用者而言是亂序存放的。
我們常用的Set集合有 HashSet<T>和SortSet<T>,其他的Set相關類則屬於更加少見。至少在我5年多的開發經歷中沒有用過。
1.3.1 HashSet<T> 和SortSet<T>
HashSet俗稱 雜湊集合或者雜湊Set,內部使用Hash值作為元素的唯一性驗證,即呼叫物件的HashCode()方法作為Hash值的來源。SortSet顧名思義,排序集合,它每次在插入的時候都會對元素進行一次排序
1.3.2 共同點
初始化
兩者相同的地方就是 都有以下幾種初始化方法
Set<T> set = new HashSet<T>();// = new SortSet<T>(); 初始化一個空的集合 //使用一個集合物件初始化 Set<T> set1 = new HashSet<T>(IEnumerable<T> items);// = new SortSet<T>(IEnumerable<T> items); Set<T> set2 = new HashSet<T>(){T t1, T t2, T t3};// 與上一種一樣新增元素
set1.Add(item);// 集合只支援新增單個元素,但是可以通過集合運算的方式增加多個元素移除元素
set1.Remove(item);//刪除集合中與item判斷相等的元素訪問元素
需要注意的地方是,C#對Set沒有支援下標訪問方式獲取Set裡的元素,這是因為索引位置對於集合來說意義不大,沒有操作意義。
c# foreach (var item in set1) { // 操作 }
Set 只能通過遍歷訪問元素,不能通過Get或者下標操作訪問元素。關於foreach迴圈會在下一篇《C#基礎知識系列》裡進行介紹。集合運算
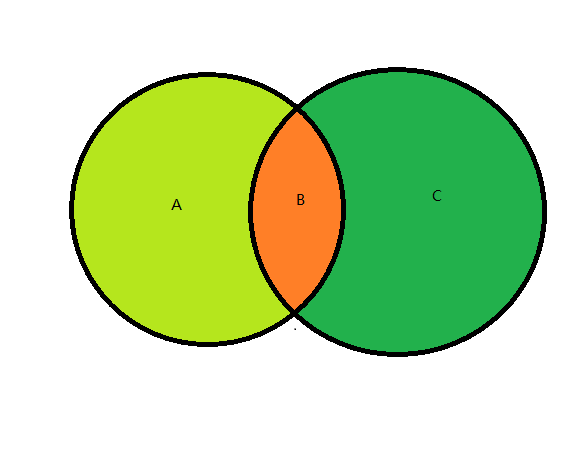
UnionWith並
通過傳入一個集合物件,將該集合設定為兩個集合的並集,也就是說取上圖 A,B,C 三個區域的和SortedSet<int> set = new SortedSet<int>{1,0,29,38,33,48,17}; set.UnionWith(new []{5,57,8,4,3,1,0,33}); // set = 0,1,3,4,5,8,17,29,33,38,48,57ExceptWith差
傳入一個集合,從set中去掉同屬於兩個集合的元素,保留只存在於set的元素,也就是取上圖中的A部分元素SortedSet<int> set = new SortedSet<int>{1,0,29,38,33,48,17}; set.ExceptWith(new []{5,57,8,4,3,1,0,33}); // set =17,29,38,48IntersectWith交
傳入一個集合,保留set與傳入集合裡相同的元素,也就是說取的是上圖中的B部分SortedSet<int> set = new SortedSet<int>{1,0,29,38,33,48,17}; set.ExceptWith(new []{5,57,8,4,3,1,0,33}); // set =0,1,33SymmetricExceptWith餘集
傳入一個集合,保留set與傳入集合兩個集合中不同的元素,也就是取上圖的A+C這兩部分。SortedSet<int> set = new SortedSet<int>{1,0,29,38,33,48,17}; set.SymmetricExceptWith(new []{5,57,8,4,3,1,0,33});//set= 3,4,5,8,17,29,38,48,57
Contains包含判斷集合中是否包含目標元素,返回true/false
SortedSet<int> set = new SortedSet<int>{1,0,29,38,33,48,17}; set.Contains(1);// true
1.3.3 不同點
- 初始化
HashSet<T>支援傳入一個自定義的相等比較器,該比較器需要返回一個 bool值;可以指定起始容量SortSet<T>支援傳入一個自定義的大小比較器,該比較器返回一個int值;不能指定起始容量
- 其他
Comparer屬性:SortSet 可以獲取大小比較器;HashSet 獲取一個相等比較器
1.4 Dictionary 字典
Dictionary 字典,正如它的名稱一樣,Dictionary 需要指定兩個型別,一個作為索引鍵,一個作為資料值。就像字典一樣,每一個詞條內容都只有一個字詞索引,但可以出現同義詞一樣。當然,作為我博大精深的中文會出現同字不同音的片語,但是一旦把音、字組合起來作為索引,那還是隻會出現一個詞條。
所以 Dictionary的使用方式也跟字典一樣,通過索引訪問和操作資料。
1.4.1 初始化
Dictionary的初始化有如下幾個方法:
Dictionary<string, int> dict = new Dictionary<string, int>();// 鍵是字串,值是int型別
Dictionary<string,int> dict1 = new Dictionary<string, int>(10);// 指定初始容量是10
Dictionary<string,int> dict2 = new Dictionary<string, int>()
{
{"1",1},
{"2",2}
};// 在大括號標記中 通過 {key,value}的寫法建立一個 字典物件,幷包含這些鍵值對
// 傳入一個字典物件,以傳入的物件為基礎建立一個字典
Dictionary<string,int> dict3 = new Dictionary<string, int>(dict2);1.4.2 常用方法
新增元素
Dictionary<string, int> dict = new Dictionary<string, int>(); // 方法一 dict.Add("1",2);//新增一個 鍵為“1”,值為2的鍵值對。 //方法二 //字典可以類似列表的形式通過下標新增或更新鍵對應的值, //不過與列表不同的是,字典的下標是字串 dict["2"] = 4;// 如果 dict中2有值,則更新為4,如果沒有,則設定2對應的值為4獲取元素
C# 的Dictionary<string, int> dict = new Dictionary<string, int>(); /* 省略資料填充階段 */ int value = dict["2"]; // value = 4 // 如果Dictionary中不存在索引為“2”的資料 // 將會丟擲 System.Collections.Generic.KeyNotFoundException 異常Dictionary還有一個TryGetValue方法可以用來嘗試獲取,他的使用方法是這樣的:
c# int obj = 0; boolean isContains = dict.TryGetValue("3", out obj); // 方法會返回 dict是否包含鍵“3”的結果,如果有 obj 則存放了dict中對應的值,如果沒有,則返回false且不改變 obj 的值Count獲取
Dictionary裡鍵值對的數量。
Dictionary沒有int count = dict.Count;LongCount屬性,因為對於Dictionary存放資料需要比對Key的相等性,如果存放巨量資料將會對資料的訪問和操作效率有影響。
獲取KeysDictionary裡所有的鍵,返回一個KeyCollection物件,不需要關心這是一個什麼型別,可以簡單的把它當做一個存放了鍵的HashSet。
是否包含鍵:通常與獲取元素一起使用,可以先判斷ContainsKey()Dictionary裡是否有這個鍵,然後再進行後續操作。Remove()刪除
Dictionary中鍵對應的元素,刪除後再次訪問會報錯。如果刪除一個不存在的元素將返回flase。
操作示例:Dictionary<string,int> dict = new Dictionary<string, int>(); //省略賦值操作 bool result = dict.Remove("2");// 如果dict裡包含鍵為“2”的元素,則result為true,否則為false另一種方法:
int value = 0; bool result = dict.Remove("2", out value); // 如果dict 裡包含鍵為“2”的元素,則result 為 false且value為對應的值
1.4.3 不常用但有用的方法
是否包含值,與ContainsValue()ContainsKey的用法一樣,只不過遍歷的是值;用處不大。Values獲取值的集合類似與
KeyValues。
2. 傳統集合(非泛型)
C#的傳統集合基本都存放在System.Collections名稱空間裡,詳細的可以檢視微軟官方文件。這個名稱空間裡的集合類使用都不多,不過C#的集合體系的介面規範都是在這個裡面定義的。
2.1 常見類介紹
ArrayListList的非泛型版,與List操作方法一致,不過返回值是Object型別SortedList一個排序的鍵值對集合,我沒用過,不過官方給瞭如下示例:using System; using System.Collections; public class SamplesSortedList { public static void Main() { // Creates and initializes a new SortedList. SortedList mySL = new SortedList(); mySL.Add("Third", "!"); mySL.Add("Second", "World"); mySL.Add("First", "Hello"); // Displays the properties and values of the SortedList. Console.WriteLine( "mySL" ); Console.WriteLine( " Count: {0}", mySL.Count ); Console.WriteLine( " Capacity: {0}", mySL.Capacity ); Console.WriteLine( " Keys and Values:" ); PrintKeysAndValues( mySL ); } public static void PrintKeysAndValues( SortedList myList ) { Console.WriteLine( "\t-KEY-\t-VALUE-" ); for ( int i = 0; i < myList.Count; i++ ) { Console.WriteLine( "\t{0}:\t{1}", myList.GetKey(i), myList.GetByIndex(i) ); } Console.WriteLine(); } }HashTable表示根據鍵的雜湊程式碼進行組織的鍵/值對的集合。HashTable的結構類似於Dictionary但又與其不同,它的鍵值儲存用的是Hash值。以下是官方給出的示例程式碼:using System; using System.Collections; class Example { public static void Main() { // Create a new hash table. // Hashtable openWith = new Hashtable(); // Add some elements to the hash table. There are no // duplicate keys, but some of the values are duplicates. openWith.Add("txt", "notepad.exe"); openWith.Add("bmp", "paint.exe"); openWith.Add("dib", "paint.exe"); openWith.Add("rtf", "wordpad.exe"); // The Add method throws an exception if the new key is // already in the hash table. try { openWith.Add("txt", "winword.exe"); } catch { Console.WriteLine("An element with Key = \"txt\" already exists."); } // The Item property is the default property, so you // can omit its name when accessing elements. Console.WriteLine("For key = \"rtf\", value = {0}.", openWith["rtf"]); // The default Item property can be used to change the value // associated with a key. openWith["rtf"] = "winword.exe"; Console.WriteLine("For key = \"rtf\", value = {0}.", openWith["rtf"]); // If a key does not exist, setting the default Item property // for that key adds a new key/value pair. openWith["doc"] = "winword.exe"; // ContainsKey can be used to test keys before inserting // them. if (!openWith.ContainsKey("ht")) { openWith.Add("ht", "hypertrm.exe"); Console.WriteLine("Value added for key = \"ht\": {0}", openWith["ht"]); } // When you use foreach to enumerate hash table elements, // the elements are retrieved as KeyValuePair objects. Console.WriteLine(); foreach( DictionaryEntry de in openWith ) { Console.WriteLine("Key = {0}, Value = {1}", de.Key, de.Value); } // To get the values alone, use the Values property. ICollection valueColl = openWith.Values; // The elements of the ValueCollection are strongly typed // with the type that was specified for hash table values. Console.WriteLine(); foreach( string s in valueColl ) { Console.WriteLine("Value = {0}", s); } // To get the keys alone, use the Keys property. ICollection keyColl = openWith.Keys; // The elements of the KeyCollection are strongly typed // with the type that was specified for hash table keys. Console.WriteLine(); foreach( string s in keyColl ) { Console.WriteLine("Key = {0}", s); } // Use the Remove method to remove a key/value pair. Console.WriteLine("\nRemove(\"doc\")"); openWith.Remove("doc"); if (!openWith.ContainsKey("doc")) { Console.WriteLine("Key \"doc\" is not found."); } } } /* This code example produces the following output: An element with Key = "txt" already exists. For key = "rtf", value = wordpad.exe. For key = "rtf", value = winword.exe. Value added for key = "ht": hypertrm.exe Key = dib, Value = paint.exe Key = txt, Value = notepad.exe Key = ht, Value = hypertrm.exe Key = bmp, Value = paint.exe Key = rtf, Value = winword.exe Key = doc, Value = winword.exe Value = paint.exe Value = notepad.exe Value = hypertrm.exe Value = paint.exe Value = winword.exe Value = winword.exe Key = dib Key = txt Key = ht Key = bmp Key = rtf Key = doc Remove("doc") Key "doc" is not found. */雖然C#框架保留了非泛型集合元素,但不建議使用非泛型集合進行開發。
3 一些不常用的集合類
除了之前所說的幾個集合類,C#還設定了一些在開發中不常用但在特定場合很有用的集合類。
3.1 Queue<T> 和 Queue
這兩個類是一對的,一個是泛型類,一個是非泛型類。該類中文名稱是佇列,如其名,佇列講究一個先進先出,所以佇列每次取元素都是從頭取,存放是放到佇列尾。
操作程式碼如下:
加入佇列
Queue queue = new Queue(); queue.Enqueue(1); queue.Enqueue("2"); Queue<string> queue1 = new Queue<string>(); queue1.Enqueue("stri");//- 讀取隊首的元素
讀取有兩種:讀取但不移除元素:
object obj= queue.Peek(); string str = queue.Peek();讀取並移除元素:
object obj = queue.Dequeue(); string str = queue.Dequeue();
- Count 獲取元素數量
3.2 LinkedList<T>
LinkedList,連結串列。與List不同的地方是,LinkedList的元素是LinkedListNode物件,該物件有四個屬性,分別是List
-指向列表物件,Previous指向前一個物件如果有的話,Next指向後一個物件如果有的話。所以根據元素的屬性可以發現連結串列的工作方式,連結串列就像一條鎖鏈一樣,一個元素分三塊,一個指向前一個元素,一個用來存放值,一個指向下一個元素,簡單如下圖所示:
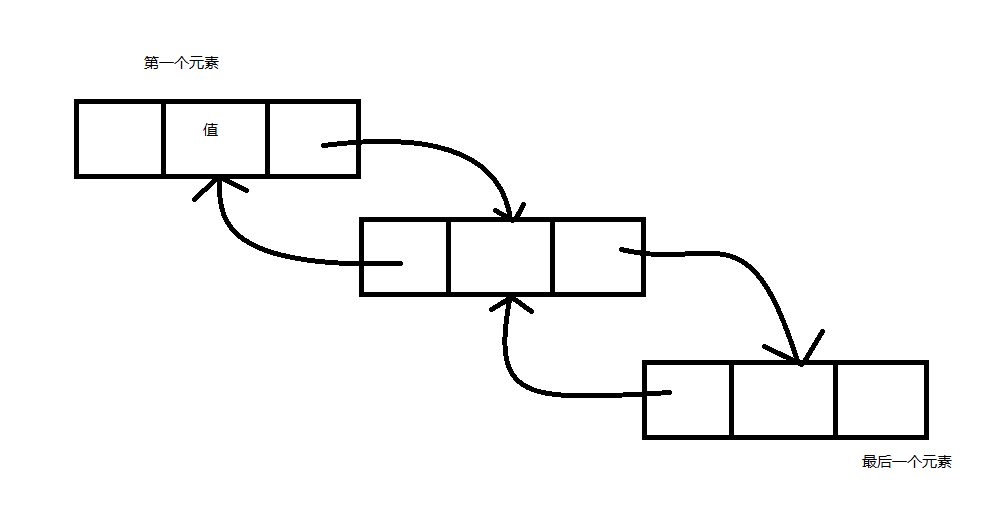
所以可以明顯的發現LinkedList在隨機插取上比一般的要快,因為它不用維護一個數組,但是在查詢和座標操作上明顯要慢很多。
LinkedList簡單介紹這麼多,可以看看它的一些常見操作:
獲取第一個元素First第一個元素
獲取最後一個元素Last最後一個元素AddAfter/AddBefore
在某個節點後/在某個節點前插入資料
支援以下引數列表:- (LinkedListNode
- (LinkedListNode
第一個引數表示要插入的節點位置,第二個表示要插入的節點/元素。第一個引數會校驗是否屬於該連結串列,如果不屬於則會丟擲一個異常。第二個可以是值,也可以是初始化好的節點物件。如果是節點物件,則判斷是否歸屬其他連結串列,如果是其他連結串列丟擲異常。
新增元素到頭或者尾,可以使用AddFirst/AddLastLinkedListNode或者新增值。
刪除,可以傳遞某個節點,或者要刪除的節點裡存放的值。RemoveRemoveFirst/RemoveLast
刪除第一個節點,刪除最後一個節點,不含引數
下面是微軟官方的一些示例
using System;
using System.Text;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class Example
{
public static void Main()
{
// Create the link list.
string[] words =
{ "the", "fox", "jumps", "over", "the", "dog" };
LinkedList<string> sentence = new LinkedList<string>(words);
Display(sentence, "The linked list values:");
Console.WriteLine("sentence.Contains(\"jumps\") = {0}",
sentence.Contains("jumps"));
// Add the word 'today' to the beginning of the linked list.
sentence.AddFirst("today");
Display(sentence, "Test 1: Add 'today' to beginning of the list:");
// Move the first node to be the last node.
LinkedListNode<string> mark1 = sentence.First;
sentence.RemoveFirst();
sentence.AddLast(mark1);
Display(sentence, "Test 2: Move first node to be last node:");
// Change the last node to 'yesterday'.
sentence.RemoveLast();
sentence.AddLast("yesterday");
Display(sentence, "Test 3: Change the last node to 'yesterday':");
// Move the last node to be the first node.
mark1 = sentence.Last;
sentence.RemoveLast();
sentence.AddFirst(mark1);
Display(sentence, "Test 4: Move last node to be first node:");
// Indicate the last occurence of 'the'.
sentence.RemoveFirst();
LinkedListNode<string> current = sentence.FindLast("the");
IndicateNode(current, "Test 5: Indicate last occurence of 'the':");
// Add 'lazy' and 'old' after 'the' (the LinkedListNode named current).
sentence.AddAfter(current, "old");
sentence.AddAfter(current, "lazy");
IndicateNode(current, "Test 6: Add 'lazy' and 'old' after 'the':");
// Indicate 'fox' node.
current = sentence.Find("fox");
IndicateNode(current, "Test 7: Indicate the 'fox' node:");
// Add 'quick' and 'brown' before 'fox':
sentence.AddBefore(current, "quick");
sentence.AddBefore(current, "brown");
IndicateNode(current, "Test 8: Add 'quick' and 'brown' before 'fox':");
// Keep a reference to the current node, 'fox',
// and to the previous node in the list. Indicate the 'dog' node.
mark1 = current;
LinkedListNode<string> mark2 = current.Previous;
current = sentence.Find("dog");
IndicateNode(current, "Test 9: Indicate the 'dog' node:");
// The AddBefore method throws an InvalidOperationException
// if you try to add a node that already belongs to a list.
Console.WriteLine("Test 10: Throw exception by adding node (fox) already in the list:");
try
{
sentence.AddBefore(current, mark1);
}
catch (InvalidOperationException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("Exception message: {0}", ex.Message);
}
Console.WriteLine();
// Remove the node referred to by mark1, and then add it
// before the node referred to by current.
// Indicate the node referred to by current.
sentence.Remove(mark1);
sentence.AddBefore(current, mark1);
IndicateNode(current, "Test 11: Move a referenced node (fox) before the current node (dog):");
// Remove the node referred to by current.
sentence.Remove(current);
IndicateNode(current, "Test 12: Remove current node (dog) and attempt to indicate it:");
// Add the node after the node referred to by mark2.
sentence.AddAfter(mark2, current);
IndicateNode(current, "Test 13: Add node removed in test 11 after a referenced node (brown):");
// The Remove method finds and removes the
// first node that that has the specified value.
sentence.Remove("old");
Display(sentence, "Test 14: Remove node that has the value 'old':");
// When the linked list is cast to ICollection(Of String),
// the Add method adds a node to the end of the list.
sentence.RemoveLast();
ICollection<string> icoll = sentence;
icoll.Add("rhinoceros");
Display(sentence, "Test 15: Remove last node, cast to ICollection, and add 'rhinoceros':");
Console.WriteLine("Test 16: Copy the list to an array:");
// Create an array with the same number of
// elements as the inked list.
string[] sArray = new string[sentence.Count];
sentence.CopyTo(sArray, 0);
foreach (string s in sArray)
{
Console.WriteLine(s);
}
// Release all the nodes.
sentence.Clear();
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Test 17: Clear linked list. Contains 'jumps' = {0}",
sentence.Contains("jumps"));
Console.ReadLine();
}
private static void Display(LinkedList<string> words, string test)
{
Console.WriteLine(test);
foreach (string word in words)
{
Console.Write(word + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine();
}
private static void IndicateNode(LinkedListNode<string> node, string test)
{
Console.WriteLine(test);
if (node.List == null)
{
Console.WriteLine("Node '{0}' is not in the list.\n",
node.Value);
return;
}
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder("(" + node.Value + ")");
LinkedListNode<string> nodeP = node.Previous;
while (nodeP != null)
{
result.Insert(0, nodeP.Value + " ");
nodeP = nodeP.Previous;
}
node = node.Next;
while (node != null)
{
result.Append(" " + node.Value);
node = node.Next;
}
Console.WriteLine(result);
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
//This code example produces the following output:
//
//The linked list values:
//the fox jumps over the dog
//Test 1: Add 'today' to beginning of the list:
//today the fox jumps over the dog
//Test 2: Move first node to be last node:
//the fox jumps over the dog today
//Test 3: Change the last node to 'yesterday':
//the fox jumps over the dog yesterday
//Test 4: Move last node to be first node:
//yesterday the fox jumps over the dog
//Test 5: Indicate last occurence of 'the':
//the fox jumps over (the) dog
//Test 6: Add 'lazy' and 'old' after 'the':
//the fox jumps over (the) lazy old dog
//Test 7: Indicate the 'fox' node:
//the (fox) jumps over the lazy old dog
//Test 8: Add 'quick' and 'brown' before 'fox':
//the quick brown (fox) jumps over the lazy old dog
//Test 9: Indicate the 'dog' node:
//the quick brown fox jumps over the lazy old (dog)
//Test 10: Throw exception by adding node (fox) already in the list:
//Exception message: The LinkedList node belongs a LinkedList.
//Test 11: Move a referenced node (fox) before the current node (dog):
//the quick brown jumps over the lazy old fox (dog)
//Test 12: Remove current node (dog) and attempt to indicate it:
//Node 'dog' is not in the list.
//Test 13: Add node removed in test 11 after a referenced node (brown):
//the quick brown (dog) jumps over the lazy old fox
//Test 14: Remove node that has the value 'old':
//the quick brown dog jumps over the lazy fox
//Test 15: Remove last node, cast to ICollection, and add 'rhinoceros':
//the quick brown dog jumps over the lazy rhinoceros
//Test 16: Copy the list to an array:
//the
//quick
//brown
//dog
//jumps
//over
//the
//lazy
//rhinoceros
//Test 17: Clear linked list. Contains 'jumps' = False
//3.3 Stack<T> 和 Stack
Stack廣泛的翻譯是棧,是一種後進先出的集合。在一些特殊場景裡,使用十分廣泛。
Stack有兩個很重要的方法Pop 和Push,出/進。Pop 獲取最後一個元素,並退出棧,Push 向棧推入一個元素。
具體可以參照官方文件
4 集合相關名稱空間
C# 的集合還有其他的一些名稱空間裡藏著寶貝,不過在實際開發中使用頻率並不大,可以按需檢視。
4.1 System.Collections.Concurrent 執行緒安全
這個名稱空間,提供了一系列執行緒安全的集合類,當出現多執行緒操作集合的時候,應當使用這個名稱空間的集合。名稱和常用的類是一一對應的,不過只提供了ConcurrentDictionary<TKey,TValue>、ConcurrentQueue<T>、ConcurrentStack<T>等幾個集合類。具體可以檢視官方文件
4.2 System.Collections.Immutable 不可變集合
名稱空間包含用於定義不可變集合的介面和類,如果需要使用這個名稱空間,則需要使用NuGet下載。
- 共享集合,使其使用者可以確保集合永遠不會發生更改。
- 提供多執行緒應用程式中的隱式執行緒安全(無需鎖來訪問集合)。
- 遵循函式程式設計做法。
- 在列舉過程中修改集合,同時確保該原始集合不會更改。
更多內容煩請關注我的部落格

相關推薦
C# 基礎知識系列- 3 集合陣列
簡單的介紹一下集合,通俗來講就是用來保管多個數據的方案。比如說我們是一個公司的倉庫管理,公司有一堆貨物需要管理,有同類的,有不同類的,總而言之就是很多、很亂。我們對照集合的概念對倉庫進行管理的話,那麼 陣列就是將一堆貨整整齊齊的碼在倉庫的某個地方,普通列表也是如此;Set就是在倉庫裡有這麼一個貨架,每種貨品
[C# 基礎知識系列] 專題十五:全面解析擴充套件方法
引言: C# 3中所有特性的提出都是更好地為Linq服務的, 充分理解這些基礎特性後。對於更深層次地去理解Linq的架構方面會更加簡單,從而就可以自己去實現一個簡單的ORM框架的,對於Linq的學習在下一個專題中將會簡單和大家介紹下,這個專題還是先來介紹服務於Li
[C#基礎知識系列]專題十:全面解析可空型別
引言: C# 2.0 中還引入了可空型別,可空型別也是值型別,只是可空型別是包括null的值型別的,下面就介紹下C#2.0中對可空型別的支援具體有哪些內容(最近一直都在思考如何來分享這篇文章的,因為剛開始覺得可空型別使用過程中比較簡單,覺得沒有講的必要,但是考慮到這
[C#基礎知識系列]專題十二:迭代器
引言: 在C# 1.0中我們經常使用foreach來遍歷一個集合中的元素,然而一個型別要能夠使用foreach關鍵字來對其進行遍歷必須實現IEnumerable或IEnumerable<T>介面,(之所以來必須要實現IEnumerable這個介面,是因
C# 基礎知識系列- 4 面向物件
# 面向物件 面向物件是一個抽象的概念,其本質就是對事物以抽象的方式建立對應的模型。 簡單來講,比如我有一隻鋼筆,那麼我就可以通過分析,可以得到 這隻鋼筆的材第是塑料,品牌是個雜牌 ,裡面裝的墨是黑色的,可以用。這時候就能建立一個鋼筆的模型,它在這裡應該有這些屬性: 
0. 前言 上一篇文章介紹了字串自身的一些方法,就是物件方法。在字串體系中,還有一些是string類提供的靜態方法。這兩部分構成了字串體系,當然還有一些三方庫為字串提供了擴充套件方法。 這裡簡單的介紹一下string類的靜態方法。 1. 玩轉建立字串 1.1 Create一個字串 通過呼叫string.Cre
C# 基礎知識系列- 10 反射和泛型(二)
0. 前言 這篇文章延續《C# 基礎知識系列- 5 反射和泛型》,繼續介紹C#在反射所開發的功能和做的努力。上一篇文章大概介紹了一下泛型和反射的一些基本內容,主要是通過獲取物件的型別,然後通過這個型別物件操作物件。這一篇介紹一個在反射中很重要的內容:特性,以及上一篇未完成的內容——泛型在反射中的引用。 1.
C# 基礎知識系列- 12 任務和多執行緒
0. 前言 照例一份前言,在介紹任務和多執行緒之前,先介紹一下非同步和同步的概念。我們之間介紹的知識點都是在同步執行,所謂的同步就是一行程式碼一行程式碼的執行,就像是我們日常乘坐地鐵通過安檢通道一樣,想象我們每個人都是一行程式碼,我們依次通過安檢儀器的時候就是同步。 那麼,什麼是非同步呢?有一個時間利用率的故
C# 基礎知識系列- 13 常見類庫介紹(一)
0. 前言 每篇一個前言,介紹一下這一篇的內容。之前的內容都是針對某些知識點進行的介紹,這篇內容介紹一下實際開發中常用的一些類和名稱空間。這一篇是個連續劇,大概有個三四集。嗯,就是這樣。 1. System 名稱空間 System空間,是C#的基礎名稱空間,裡面定義了常用值和資料型別以及各種型別的基類,當然也
C# 基礎知識系列- 13 常見類庫介紹(二)日期時間類
# 0. 前言 上一篇內容介紹了Console類和Math類,這篇內容著重介紹一下C#中時間日期的處理方式。 > 上一篇勘誤: 上一篇中關於靜態類沒有建構函式,這一表述有誤。正確的說法是C#中靜態類不包含常規建構函式,但可以新增一個靜態建構函式。 > 靜態建構函式與普通普通建構函式的區別是,靜態
C# 基礎知識系列- 14 IO篇 檔案的操作
> 本篇繼續前兩篇內容,跟大家介紹一下Path類以及FileSystemInfo這個類的主要方法和屬性。 > > 上文提到,在《C# 基礎知識系列-IO篇》之檔案相關的內容完結之後,會帶領大家開發一個小工具-快速檢索檔案所在目錄。 ## 1.3. Path Path的中文名稱有路徑的
C# 基礎知識系列- 14 IO篇 流的使用
# 0. 前言 繼續之前的C# IO流,在前幾篇小短片中我們大概看了下C# 的基礎IO也對檔案、目錄和路徑的操作有了一定的瞭解。這一篇開始,給大家演示一下流的各種操作。以檔案流為例,一起來看看如何操作吧。 > 注:之前更新了一篇《Spring Cloud 實戰日記》,這是一個新的系列,有興趣的小夥伴
C# 基礎知識系列- 17 實戰篇 編寫一個小工具(1)
# 0. 前言 這是對C# 基礎系列的一個總結,現在我們利用之前學到的知識做一個小小的工具來給我們使用。 如果有看過IO篇的小夥伴,應該有印象。當時我提過一個場景描述,我們在平時使用系統的時候,經常會為了找某個檔案的位置而煩惱。那麼我們現在嘗試寫一個控制檯程式來幫助我們找檔案的具體位置。 # 1. 分析
C# 基礎知識系列- 17 小工具優化
# 0. 前言 不知道有沒有動手能力強的小夥伴照著上一篇的內容寫過程式呢?如果有的話,應該會在使用的時候發現以下幾個問題: 1. 每次啟動都需要經過漫長的時間去遍歷磁盤裡的檔案目錄 2. 因為資料是用的字典儲存的,所以會消耗大量的記憶體空間 3. 不能多次查詢 現在我們就針對這些問題,讓我們的小工具實用
Linux-C基礎知識學習:C語言作業-輸入m、n,並把m~n之間的不能被3整除的數輸出
Linux基礎知識學習 C語言作業:輸入m、n,並把m~n之間的不能被3整除的數輸出 //輸入m、n,並把m~n之間的不能被3整除的數輸出 #include <stdio.h> ma
C++基礎知識複習--結構體類陣列作為函式引數
//結構體陣列,類陣列,普通陣列,作為函式引數 #include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; class C
C#基礎知識-函數的定義和調用(五)
返回 {0} string 訪問修飾符 容器 列表 rdquo 所有 func 函數也可以稱為方法,可以很方便的把一些行為封裝到函數裏面,當調用這一函數時會把函數塊裏面的代碼按照順序執行,方法可以有多種形式,有無參數,有無返回值等。 1. 函數的定義 函數定
C#基礎知識-流程控制的應用(四)
相關 ats 循環 nbsp 使用 logs 嘗試 exc 設置斷點 流程控制我們在編程中運用到的地方非常的多,在上篇中僅僅只是簡單的介紹每一種的使用,並沒有運用到實例中,很難去理解它真正的作用。下面我們將實際的運用流程控制的代碼寫一些實例相關的程序,加深對流程控制的理解,
C#基礎知識-引用類型和值類型的區別(六)
值類型 type 調用 執行 new 內存堆 ada ont 不同類 在第一篇中我們介紹了C#中基本的15種數據類型,這15種數據類型中又分為兩大類,一種是值類型,一種是引用類型。值類型有sbyte、short、long、int、byte、ushort、uint、u
C#基礎知識-面向對象思想之繼承(八)
添加 電視劇 一中 一段 public bsp 更多 cnblogs tin 上一篇的標題編程思想我覺得不是很符合主題,因為編程思想的範圍太大了,不僅僅是封裝 繼承 多態,所以比較符合主題的應該是面向對象思想。這一篇中將繼續敘述面向對象思想中的繼承。 從字面來看繼承表達的意
