Linux登入shell和非登入(互動式shell)環境變數配置
阿新 • • 發佈:2020-05-15
使用Jenkins執行shell指令碼的時候, 碰到`command not found`. 比如`java mvn`, 這些環境變數配置在`/etc/profile`
中, 但jenkins執行的時候並沒有載入.
這是因為jenkins執行的shell是非登入互動式shell, 並不會載入`/etc/profile`.
互動式shell會載入`.bashrc`, 進而會載入`/etc/bashrc`, 而`/etc/bashrc`會載入`/etc/profile.d/*.sh`.
**因此, 自定義的變數應該定義在/etc/profile.d/*.sh**
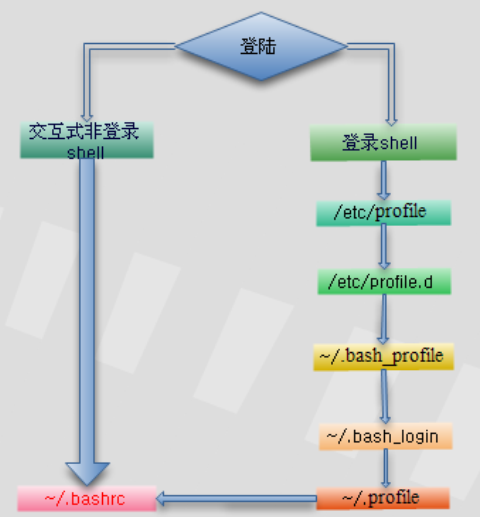
## 1.登入shell
所謂登入shell,指的是當用戶登入系統時所取的那個shell,登入shell屬於互動式shell。
登入shell將查詢4個不同的啟動檔案來處理其中的命令。 bash shell處理檔案的順序如下:
```
1:/etc/profile
2:/etc/profile.d等待配置檔案
3:$HOME/.bash_profile 會載入$HOME/.bashrc和/etc/bashrc
4:$HOME/.bash_login
5:$HOME/.profile
```
## 2. 互動式非登入shell
如果啟動了一個bash shell而沒有登入系統(如在CLI提示符中鍵入bash),
則啟動了一個互動式非登入shell.
### $HOME/.bashrc
互動式非登入shell執行~/.bashrc檔案中的命令.在每次執行shell指令碼時,都會重新讀取這個檔案,所以是最完整的。
但是萬事都不是一樣的,debain系列的是不同的,如ubuntu
/etc/profile-->/etc/environment-->$HOME/.profile.要配置java等變數時,都/etc/environment中
**.bashrc**
```
# .bashrc
# User specific aliases and functions
alias rm='rm -i'
alias cp='cp -i'
alias mv='mv -i'
# Source global definitions
if [ -f /etc/bashrc ]; then
. /etc/bashrc
fi
```
登入shell的初始化檔案(比如.bash_profile)通常會執行這個檔案。這樣,登入shell和非登入shell都可以使用.bashrc中的命令。
### /etc/bashrc
```
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/bashrc
# /etc/bashrc
# System wide functions and aliases
# Environment stuff goes in /etc/profile
# It's NOT a good idea to change this file unless you know what you
# are doing. It's much better to create a custom.sh shell script in
# /etc/profile.d/ to make custom changes to your environment, as this
# will prevent the need for merging in future updates.
# are we an interactive shell?
if [ "$PS1" ]; then
if [ -z "$PROMPT_COMMAND" ]; then
case $TERM in
xterm*|vte*)
if [ -e /etc/sysconfig/bash-prompt-xterm ]; then
PROMPT_COMMAND=/etc/sysconfig/bash-prompt-xterm
elif [ "${VTE_VERSION:-0}" -ge 3405 ]; then
PROMPT_COMMAND="__vte_prompt_command"
else
PROMPT_COMMAND='printf "\033]0;%s@%s:%s\007" "${USER}" "${HOSTNAME%%.*}" "${PWD/#$HOME/~}"'
fi
;;
screen*)
if [ -e /etc/sysconfig/bash-prompt-screen ]; then
PROMPT_COMMAND=/etc/sysconfig/bash-prompt-screen
else
PROMPT_COMMAND='printf "\033k%s@%s:%s\033\\" "${USER}" "${HOSTNAME%%.*}" "${PWD/#$HOME/~}"'
fi
;;
*)
[ -e /etc/sysconfig/bash-prompt-default ] && PROMPT_COMMAND=/etc/sysconfig/bash-prompt-default
;;
esac
fi
# Turn on parallel history
shopt -s histappend
history -a
# Turn on checkwinsize
shopt -s checkwinsize
[ "$PS1" = "\\s-\\v\\\$ " ] && PS1="[\u@\h \W]\\$ "
# You might want to have e.g. tty in prompt (e.g. more virtual machines)
# and console windows
# If you want to do so, just add e.g.
# if [ "$PS1" ]; then
# PS1="[\u@\h:\l \W]\\$ "
# fi
# to your custom modification shell script in /etc/profile.d/ directory
fi
if ! shopt -q login_shell ; then # We're not a login shell
# Need to redefine pathmunge, it get's undefined at the end of /etc/profile
pathmunge () {
case ":${PATH}:" in
*:"$1":*)
;;
*)
if [ "$2" = "after" ] ; then
PATH=$PATH:$1
else
PATH=$1:$PATH
fi
esac
}
# By default, we want umask to get set. This sets it for non-login shell.
# Current threshold for system reserved uid/gids is 200
# You could check uidgid reservation validity in
# /usr/share/doc/setup-*/uidgid file
if [ $UID -gt 199 ] && [ "`/usr/bin/id -gn`" = "`/usr/bin/id -un`" ]; then
umask 002
else
umask 022
fi
SHELL=/bin/bash
# Only display echos from profile.d scripts if we are no login shell
# and interactive - otherwise just process them to set envvars
for i in /etc/profile.d/*.sh; do
if [ -r "$i" ]; then
if [ "$PS1" ]; then
. "$i"
else
. "$i" >/dev/null
fi
fi
done
unset i
unset -f pathmunge
fi
# vim:ts=4:sw=4
```
## 參考
- https://www.cnblogs.com/woshimrf/p/shell-environment.html
- https://my.oschina.net/u/347414/blog/5
