萬字長文!一次性弄懂 Nginx 處理 HTTP 請求的 11 個階段
阿新 • • 發佈:2020-05-22
# Nginx 處理一個 HTTP 請求的全過程
前面給大家講了 [Nginx 是如何處理 HTTP請求頭部的](https://iziyang.github.io/2020/04/08/4-nginx/),接下來就到了真正處理 HTTP 請求的階段了。先看下面這張圖,這張圖是 Nginx 處理 HTTP 請求的示意圖,雖然簡單,但是卻很好的說明了整個過程。
1. Read Request Headers:解析請求頭。
2. Identify Configuration Block:識別由哪一個 location 進行處理,匹配 URL。
3. Apply Rate Limits:判斷是否限速。例如可能這個請求併發的連線數太多超過了限制,或者 QPS 太高。
4. Perform Authentication:連線控制,驗證請求。例如可能根據 Referrer 頭部做一些防盜鏈的設定,或者驗證使用者的許可權。
5. Generate Content:生成返回給使用者的響應。為了生成這個響應,做反向代理的時候可能會和上游服務(Upstream Services)進行通訊,然後這個過程中還可能會有些子請求或者重定向,那麼還會走一下這個過程(Internal redirects and subrequests)。
6. Response Filters:過濾返回給使用者的響應。比如壓縮響應,或者對圖片進行處理。
7. Log:記錄日誌。
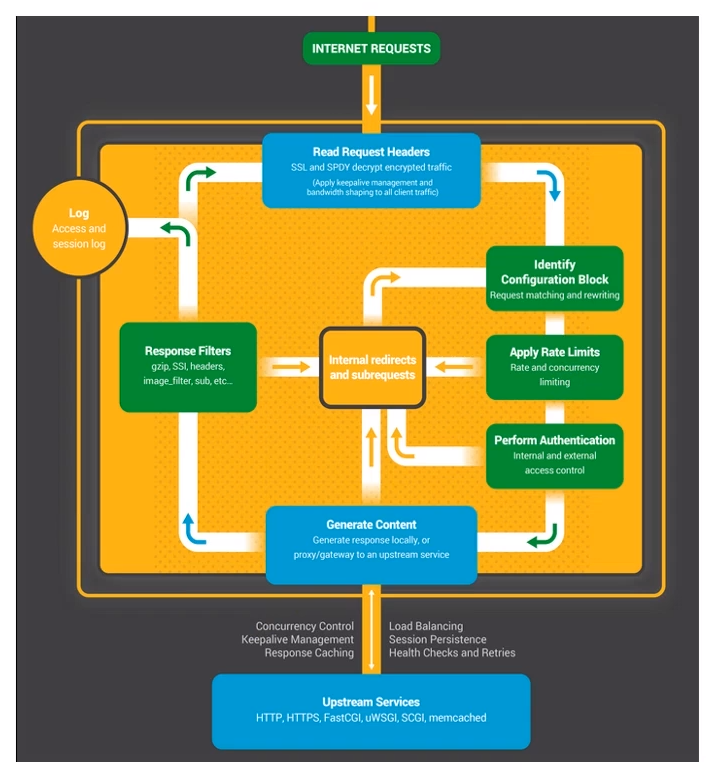
以上這七個步驟從整體上介紹了一下處理流程,下面還會再說一下實際的處理過程。
# Nginx 處理 HTTP 請求的 11 個階段
下面介紹一下詳細的 11 個階段,每個階段都可能對應著一個甚至多個 HTTP 模組,通過這樣一個模組對比,我們也能夠很好的理解這些模組具體是怎麼樣發揮作用的。

1. POST_READ:在 read 完請求的頭部之後,在沒有對頭部做任何處理之前,想要獲取到一些原始的值,就應該在這個階段進行處理。這裡面會涉及到一個 realip 模組。
2. SERVER_REWRITE:和下面的 REWRITE 階段一樣,都只有一個模組叫 rewrite 模組,一般沒有第三方模組會處理這個階段。
3. FIND_CONFIG:做 location 的匹配,暫時沒有模組會用到。
4. REWRITE:對 URL 做一些處理。
5. POST_WRITE:處於 REWRITE 之後,也是暫時沒有模組會在這個階段出現。
接下來是確認使用者訪問許可權的三個模組:
6. PREACCESS:是在 ACCESS 之前要做一些工作,例如併發連線和 QPS 需要進行限制,涉及到兩個模組:limt_conn 和 limit_req
7. ACCESS:核心要解決的是使用者能不能訪問的問題,例如 auth_basic 是使用者名稱和密碼,access 是使用者訪問 IP,auth_request 根據第三方服務返回是否可以去訪問。
8. POST_ACCESS:是在 ACCESS 之後會做一些事情,同樣暫時沒有模組會用到。
最後的三個階段處理響應和日誌:
9. PRECONTENT:在處理 CONTENT 之前會做一些事情,例如會把子請求傳送給第三方的服務去處理,try_files 模組也是在這個階段中。
10. CONTENT:這個階段涉及到的模組就非常多了,例如 index, autoindex, concat 等都是在這個階段生效的。
11. LOG:記錄日誌 access_log 模組。
以上的這些階段都是嚴格按照順序進行處理的,當然,每個階段中各個 HTTP 模組的處理順序也很重要,如果某個模組不把請求向下傳遞,後面的模組是接收不到請求的。而且每個階段中的模組也不一定所有都要執行一遍,下面就接著講一下各個階段模組之間的請求順序。
# 11 個階段的順序處理
如下圖所示,每一個模組處理之間是有序的,那麼這個順序怎麼才能得到呢?其實非常簡單,在原始碼 ngx_module.c 中,有一個數組 `ngx_module_name`,其中包含了在編譯 Nginx 的時候的 with 指令所包含的所有模組,它們之間的順序非常關鍵,在陣列中順序是相反的。
```c
char *ngx_module_names[] = {
… …
"ngx_http_static_module",
"ngx_http_autoindex_module",
"ngx_http_index_module",
"ngx_http_random_index_module",
"ngx_http_mirror_module",
"ngx_http_try_files_module",
"ngx_http_auth_request_module",
"ngx_http_auth_basic_module",
"ngx_http_access_module",
"ngx_http_limit_conn_module",
"ngx_http_limit_req_module",
"ngx_http_realip_module",
"ngx_http_referer_module",
"ngx_http_rewrite_module",
"ngx_http_concat_module",
… …
}
```
灰色部分的模組是 Nginx 的框架部分去執行處理的,第三方模組沒有機會在這裡得到處理。
在依次向下執行的過程中,也可能不按照這樣的順序。例如,在 access 階段中,有一個指令叫 satisfy,它可以指示當有一個滿足的時候就直接跳到下一個階段進行處理,例如當 access 滿足了,就直接跳到 try_files 模組進行處理,而不會再執行 auth_basic、auth_request 模組。
在 content 階段中,當 index 模組執行了,就不會再執行 auto_index 模組,而是直接跳到 log 模組。
整個 11 個階段所涉及到的模組和先後順序如下圖所示:
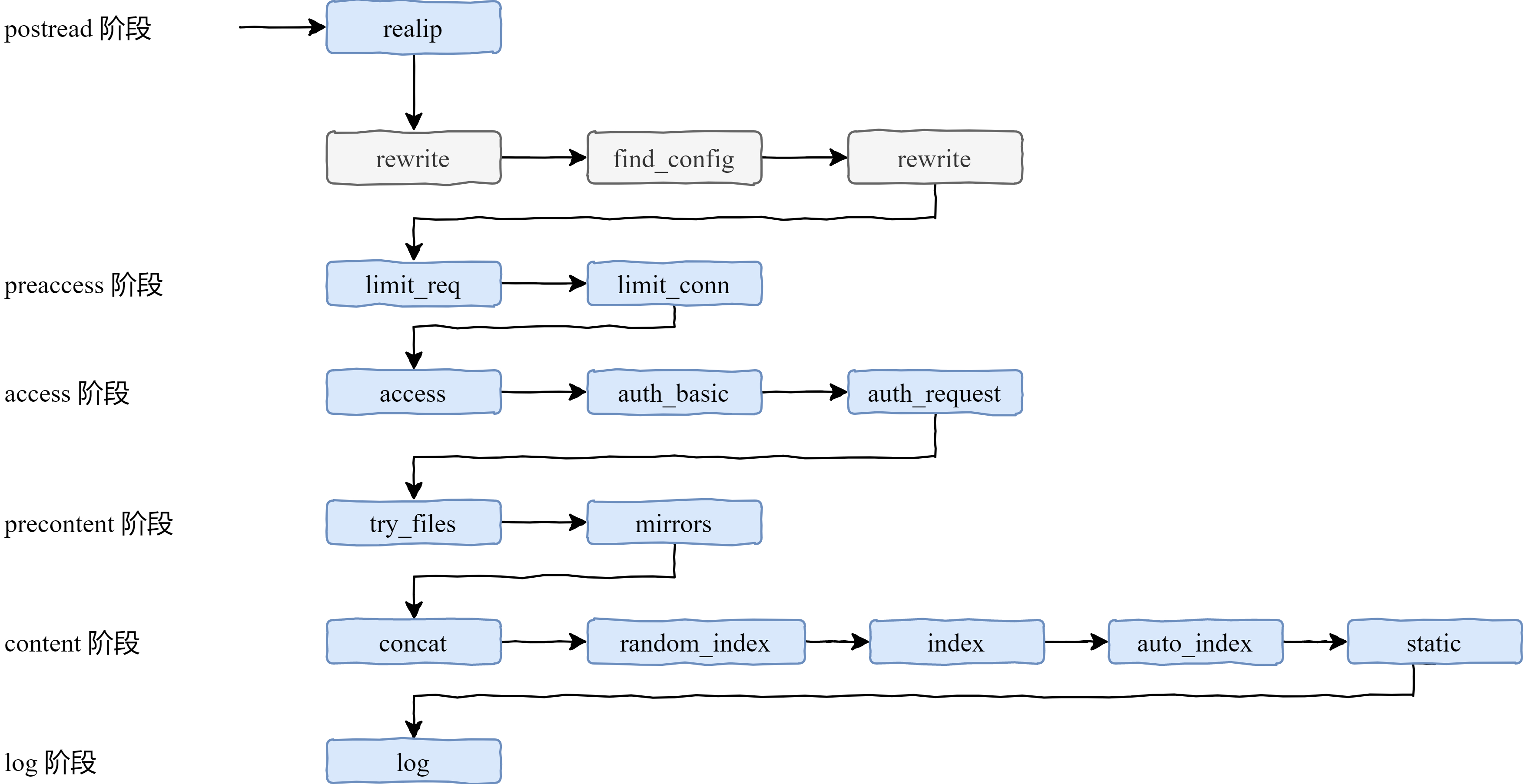
下面開始詳細講解一下各個階段。先來看下第一個階段 postread 階段,顧名思義,postread 階段是在正式處理請求之前起作用的。
# postread 階段
postread 階段,是 11 個階段的第 1 個階段,這個階段剛剛獲取到了請求的頭部,還沒有進行任何處理,我們可以拿到一些原始的資訊。例如,拿到使用者的真實 IP 地址
## 問題:如何拿到使用者的真實 IP 地址?
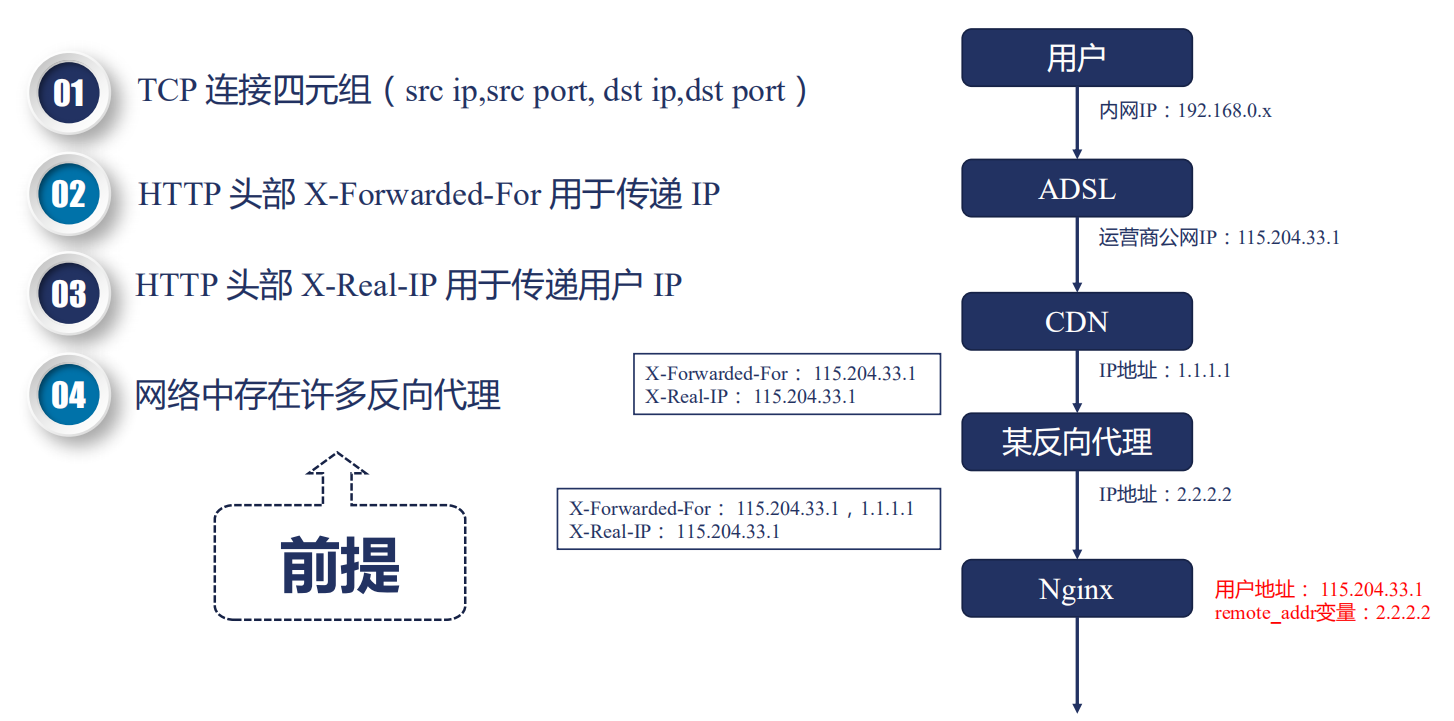
我們知道,TCP 連線是由一個四元組構成的,在四元組中,包含了源 IP 地址。而在真實的網際網路中,存在非常多的正向代理和反向代理。例如最終的使用者有自己的內網 IP 地址,運營商會分配一個公網 IP,然後訪問某個網站的時候,這個網站可能使用了 CDN 加速一些靜態檔案或圖片,如果 CDN 沒有命中,那麼就會回源,回源的時候可能還要經過一個反向代理,例如阿里雲的 SLB,然後才會到達 Nginx。
我們要拿到的地址應該是運營商給使用者分配的公網 IP 地址 115.204.33.1,對這個 IP 來進行併發連線的控制或者限速,而 Nginx 拿到的卻是 2.2.2.2,那麼怎麼才能拿到真實的使用者 IP 呢?
HTTP 協議中,有兩個頭部可以用來獲取使用者 IP:
- X-Forwardex-For 是用來傳遞 IP 的,這個頭部會把經過的節點 IP 都記錄下來
- X-Real-IP:可以記錄使用者真實的 IP 地址,只能有一個
## 拿到真實使用者 IP 後如何使用?
針對這個問題,Nginx 是基於變數來使用。
例如 binary_remote_addr、remote_addr 這樣的變數,其值就是真實的 IP,這樣做連線限制也就是 limit_conn 模組才有意義,這也說明了,limit_conn 模組只能在 preaccess 階段,而不能在 postread 階段生效。
## realip 模組
- 預設不會編譯進 Nginx
- 需要通過 `--with-http_realip_module` 啟用功能
- 變數:如果還想要使用原來的 TCP 連線中的地址和埠,需要通過這兩個變數儲存
- `realip_remote_addr`
- `realip_remote_port`
- 功能
- 修改客戶端地址
- 指令
- `set_real_ip_from`
指定可信的地址,只有從該地址建立的連線,獲取的 realip 才是可信的
- `real_ip_header`
指定從哪個頭部取真實的 IP 地址,預設從 `X-Real-IP` 中取,如果設定從 `X-Forwarded-For` 中取,會先從最後一個 IP 開始取
- `real_ip_recursive`
環回地址,預設關閉,開啟的時候,如果 `X-Forwarded-For` 最後一個地址與客戶端地址相同,會過濾掉該地址
```
Syntax: set_real_ip_from address | CIDR | unix:;
Default: —
Context: http, server, location
Syntax: real_ip_header field | X-Real-IP | X-Forwarded-For | proxy_protocol;
Default: real_ip_header X-Real-IP;
Context: http, server, location
Syntax: real_ip_recursive on | off;
Default: real_ip_recursive off;
Context: http, server, location
```
## 實戰
上面關於 `real_ip_recursive` 指令可能不太容易理解,我們來實戰練習一下,先來看 `real_ip_recursive` 預設關閉的情況:
- 重新編譯一個帶有 realip 模組的 nginx
> 關於如何編譯 Nginx,詳見:https://iziyang.github.io/2020/03/10/1-nginx/
```shell
# 下載 nginx 原始碼,在原始碼目錄下執行
./configure --prefix=自己指定的目錄 --with-http_realip_module
make
make install
```
- 然後去上一步中自己指定的 Nginx 安裝目錄
```nginx
#遮蔽預設的 nginx.conf 檔案的 server 塊內容,並新增一行
include /Users/mtdp/myproject/nginx/test_nginx/conf/example/*.conf;
```
```nginx
# 在 example 目錄下建立 realip.conf,set_real_ip_from 可以設定為自己的本機 IP
server {
listen 80;
server_name ziyang.realip.com;
error_log /Users/mtdp/myproject/nginx/nginx/logs/myerror.log debug;
set_real_ip_from 192.168.0.108;
#real_ip_header X-Real-IP;
real_ip_recursive off;
# real_ip_recursive on;
real_ip_header X-Forwarded-For;
location / {
return 200 "Client real ip: $remote_addr\n";
}
}
```
在上面的配置檔案中,我設定了可信代理地址為本機地址,`real_ip_recursive` 為預設的 off,`real_ip_header` 設為從 `X-Forwarded-For` 中取。
- 過載配置檔案
```shell
./sbin/nginx -s reload
```
- 測試響應結果
```shell
➜ test_nginx curl -H 'X-Forwarded-For: 1.1.1.1,192.168.0.108' ziyang.realip.com
Client real ip: 192.168.0.108
```
然後再來測試 `real_ip_recursive` 開啟的情況:
- 配置檔案中開啟 `real_ip_recursive`
```nginx
server {
listen 80;
server_name ziyang.realip.com;
error_log /Users/mtdp/myproject/nginx/nginx/logs/myerror.log debug;
set_real_ip_from 192.168.0.108;
#real_ip_header X-Real-IP;
#real_ip_recursive off;
real_ip_recursive on;
real_ip_header X-Forwarded-For;
location / {
return 200 "Client real ip: $remote_addr\n";
}
}
```
- 測試響應結果
```shell
➜ test_nginx curl -H 'X-Forwarded-For: 1.1.1.1,2.2.2.2,192.168.0.108' ziyang.realip.com
Client real ip: 2.2.2.2
```
所以這裡面也可看出來,如果使用 `X-Forwarded-For` 獲取 realip 的話,需要開啟 `real_ip_recursive`,並且,realip 依賴於 `set_real_ip_from` 設定的可信地址。
那麼有人可能就會問了,那直接用 `X-Real-IP` 來選取真實的 IP 地址不就好了。這是可以的,但是 `X-Real-IP` 是 Nginx 獨有的,不是 RFC 規範,如果客戶端與伺服器之間還有其他非 Nginx 軟體實現的代理,就會造成取不到 `X-Real-IP` 頭部,所以這個要根據實際情況來定。
# rewrite 階段的 rewrite 模組
下面來看一下 rewrite 模組。
首先 rewrite 階段分為兩個,一個是 server_rewrite 階段,一個是 rewrite,這兩個階段都涉及到一個 rewrite 模組,而在 rewrite 模組中,有一個 return 指令,遇到該指令就不會再向下執行,直接返回響應。


## return 指令
return 指令的語法如下:
- 返回狀態碼,後面跟上 body
- 返回狀態碼,後面跟上 URL
- 直接返回 URL
```
Syntax: return code [text];
return code URL;
return URL;
Default: —
Context: server, location, if
```
返回狀態碼包括以下幾種:
- Nginx 自定義
- 444:立刻關閉連線,使用者收不到響應
- HTTP 1.0 標準
- 301:永久重定向
- 302:臨時重定向,禁止被快取
- HTTP 1.1 標準
- 303:臨時重定向,允許改變方法,禁止被快取
- 307:臨時重定向,不允許改變方法,禁止被快取
- 308:永久重定向,不允許改變方法
### return 指令與 error_page
`error_page` 的作用大家肯定經常見到。當訪問一個網站出現 404 的時候,一般不會直接出現一個 404 NOT FOUND,而是會有一個比較友好的頁面,這就是 `error_page` 的功能。
```
Syntax: error_page code ... [=[response]] uri;
Default: —
Context: http, server, location, if in location
```
我們來看幾個例子:
```nginx
1. error_page 404 /404.html;
2. error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
3. error_page 404 =200 /empty.gif;
4. error_page 404 = /404.php;
5. location / {
error_page 404 = @fallback;
}
location @fallback {
proxy_pass http://backend;
}
6. error_page 403 http://example.com/forbidden.html;
7. error_page 404 =301 http://example.com/notfound.html;
```
那麼現在就會有兩個問題,大家看下下面這個配置檔案:
```nginx
server {
server_name ziyang.return.com;
listen 80;
root html/;
error_page 404 /403.html;
#return 405;
location / {
#return 404 "find nothing!";
}
}
```
1. 當 server 下包含 error_page 且 location 下有 return 指令的時候,會執行哪一個呢?
2. return 指令同時出現在 server 塊下和同時出現在 location 塊下,它們有合併關係嗎?
這兩個問題我們通過實戰驗證一下。
### 實戰
- 將上面的配置新增到配置檔案 return.conf
- 在本機的 hosts 檔案中繫結 ziyang.return.com 為本地的 IP 地址
- 訪問一個不存在的頁面
```shell
➜ test_nginx curl ziyang.return.com/text
nginx/1.17.8
```
這個時候可以看到,是 `error_page` 生效了,返回的響應是 403。
那麼假如打開了 `location` 下 `return` 指令的註釋呢?
- 開啟 `return` 指令註釋,reload 配置檔案
- 重新訪問頁面
```
➜ test_nginx curl ziyang.return.com/text
find nothing!%
```
這時候,`return` 指令得到了執行。也就是第一個問題,當 `server` 下包含 `error_page` 且 `location` 下有 `return` 指令的時候,會執行 `return` 指令。
下面再看一下 `server` 下的 `return` 指令和 `location` 下的 `return` 指令會執行哪一個。
- 開啟 `server` 下 `return` 指令的註釋,reload 配置檔案
- 重新訪問頁面
```shell
➜ test_nginx curl ziyang.return.com/text
nginx/1.17.8
```
針對上面兩個問題也就有了答案:
1. 當 `server` 下包含 `error_page` 且 `location` 下有 `return` 指令的時候,會執行哪一個呢?
會執行 `location` 下的 `return` 指令。
2. `return` 指令同時出現在 `server` 塊下和同時出現在 `location` 塊下,它們有合併關係嗎?
沒有合併關係,先遇到哪個 `return` 指令就先執行哪一個。
## rewrite 指令
`rewrite` 指令用於修改使用者傳入 Nginx 的 URL。來看下 `rewrite` 的指令規則:
```
Syntax: rewrite regex replacement [flag];
Default: —
Context: server, location, if
```
它的功能主要有下面幾點:
- 將 `regex` 指定的 URL 替換成 `replacement` 這個新的 URL
- 可以使用正則表示式及變數提取
- 當 `replacement` 以 http:// 或者 https:// 或者 $schema 開頭,則直接返回 302 重定向
- 替換後的 URL 根據 flag 指定的方式進行處理
- last:用 `replacement` 這個 URL 進行新的 location 匹配
- break:break 指令停止當前指令碼指令的執行,等價於獨立的 break 指令
- redirect:返回 302 重定向
- permanent:返回 301 重定向
### 指令示例
現在我們有這樣的一個目錄結構:
```
html/first/
└── 1.txt
html/second/
└── 2.txt
html/third/
└── 3.txt
```
配置檔案如下所示:
```nginx
server {
listen 80;
server_name rewrite.ziyang.com;
rewrite_log on;
error_log logs/rewrite_error.log notice;
root html/;
location /first {
rewrite /first(.*) /second$1 last;
return 200 'first!\n';
}
location /second {
rewrite /second(.*) /third$1;
return 200 'second!\n';
}
location /third {
return 200 'third!\n';
}
location /redirect1 {
rewrite /redirect1(.*) $1 permanent;
}
location /redirect2 {
rewrite /redirect2(.*) $1 redirect;
}
location /redirect3 {
rewrite /redirect3(.*) http://rewrite.ziyang.com$1;
}
location /redirect4 {
rewrite /redirect4(.*) http://rewrite.ziyang.com$1 permanent;
}
}
```
那麼我們的問題是:
1. return 指令 與 rewrite 指令的順序關係?
2. 訪問 /first/3.txt,/second/3.txt,/third/3.txt 分別返回的是什麼?
3. 如果不攜帶 flag 會怎麼樣?
帶著這三個問題,我們來實際演示一下。
### 實戰
**準備工作**
- 將上面的配置新增到配置檔案 rewrite.conf
- 在本機的 hosts 檔案中繫結 rewrite.ziyang.com 為 127.0.0.1
**last flag**
首先訪問 rewrite.ziyang.com/first/3.txt,結果如下:
```shell
➜ ~ curl rewrite.ziyang.com/first/3.txt
second!
```
為什麼結果是 second! 呢?應該是 third! 呀,可能有人會有這樣的疑問。實際的匹配步驟如下:
- curl rewrite.ziyang.com/first/3.txt
- 由於 `rewrite /first(.*) /second$1 last;` 這條指令的存在,last 表示使用新的 URL 進行 location 匹配,因此接下來會去匹配 second/3.txt
- 匹配到 /second 塊之後,會依次執行指令,最後返回 200
- 注意,location 塊中雖然也改寫了 URL,但是並不會去繼續匹配,因為後面沒有指定 flag。
**break flag**
下面將 `rewrite /second(.*) /third$1;` 這條指令加上 break flag,`rewrite /second(.*) /third$1 break;`
繼續訪問 rewrite.ziyang.com/first/3.txt,結果如下:
```curl
➜ ~ curl rewrite.ziyang.com/first/3.txt
test3%
```
這時候返回的是 3.txt 檔案的內容 test3。實際的匹配步驟如下:
- curl rewrite.ziyang.com/first/3.txt
- 由於 `rewrite /first(.*) /second$1 last;` 這條指令的存在,last 表示使用新的 URL 進行 location 匹配,因此接下來會去匹配 second/3.txt
- 匹配到 /second 塊之後,由於 break flag 的存在,會繼續匹配 rewrite 過後的 URL
- 匹配 /third location
因此,這個過程實際請求的 URL 是 rewrite.ziyang.com/third/3.txt,這樣自然結果就是 test3 了。你還可以試試訪問 rewrite.ziyang.com/third/2.txt 看看會返回什麼。
**redirect 和 permanent flag**
配置檔案中還有 4 個 location,你可以分別試著訪問一下,結果是這樣的:
- redirect1:返回 301
- redirect2:返回 302
- redirect3:返回 302
- redirect4:返回 301
## **rewrite** 行為記錄日誌
主要是一個指令 `rewrite_log`:
```nginx
Syntax: rewrite_log on | off;
Default: rewrite_log off;
Context: http, server, location, if
```
這個指令開啟之後,會把 rewrite 的日誌寫入 logs/rewrite_error.log 日誌檔案中,這是請求 /first/3.txt 的日誌記錄:
```
2020/05/06 06:24:05 [notice] 86959#0: *25 "/first(.*)" matches "/first/3.txt", client: 127.0.0.1, server: rewrite.ziyang.com, request: "GET /first/3.txt HTTP/1.1", host: "rewrite.ziyang.com"
2020/05/06 06:24:05 [notice] 86959#0: *25 rewritten data: "/second/3.txt", args: "", client: 127.0.0.1, server: rewrite.ziyang.com, request: "GET /first/3.txt HTTP/1.1", host: "rewrite.ziyang.com"
2020/05/06 06:24:05 [notice] 86959#0: *25 "/second(.*)" matches "/second/3.txt", client: 127.0.0.1, server: rewrite.ziyang.com, request: "GET /first/3.txt HTTP/1.1", host: "rewrite.ziyang.com"
2020/05/06 06:24:05 [notice] 86959#0: *25 rewritten data: "/third/3.txt", args: "", client: 127.0.0.1, server: rewrite.ziyang.com, request: "GET /first/3.txt HTTP/1.1", host: "rewrite.ziyang.com"
```
## if 指令
if 指令也是在 rewrite 階段生效的,它的語法如下所示:
```nginx
Syntax: if (condition) { ... }
Default: —
Context: server, location
```
它的規則是:
- 條件 condition 為真,則執行大括號內的指令;同時還遵循值指令的繼承規則(詳見我之前的文章 [Nginx 的配置指令](https://iziyang.github.io/2020/04/06/3-nginx/))
那麼 if 指令的條件表示式包含哪些內容呢?它的規則如下:
1. 檢查變數為空或者值是否為 0
2. 將變數與字串做匹配,使用 = 或 !=
3. 將變數與正則表示式做匹配
- 大小寫敏感,~ 或者 !~
- 大小寫不敏感,~* 或者 !~*
4. 檢查檔案是否存在,使用 -f 或者 !-f
5. 檢查目錄是否存在,使用 -d 或者 !-d
6. 檢查檔案、目錄、軟連結是否存在,使用 -e 或者 !-e
7. 檢查是否為可執行檔案,使用 -x 或者 !-x
下面是一些例子:
```nginx
if ($http_user_agent ~ MSIE) { # 與變數 http_user_agent 匹配
rewrite ^(.*)$ /msie/$1 break;
}
if ($http_cookie ~* "id=([^;]+)(?:;|$)") { # 與變數 http_cookie 匹配
set $id $1;
}
if ($request_method = POST) { # 與變數 request_method 匹配,獲取請求方法
return 405;
}
if ($slow) { # slow 變數在 map 模組中自定義,也可以進行匹配
limit_rate 10k;
}
if ($invalid_referer) {
return 403;
}
```
# find_config 階段
當經過 rewrite 模組,匹配到 URL 之後,就會進入 find_config 階段,開始尋找 URL 對應的 location 配置。
## location 指令
### 指令語法
還是老規矩,咱們先來看一下 location 指令的語法:
```nginx
Syntax: location [ = | ~ | ~* | ^~ ] uri { ... }
location @name { ... }
Default: —
Context: server, location
Syntax: merge_slashes on | off;
Default: merge_slashes on;
Context: http, server
```
這裡面有一個 `merge_slashes` 指令,這個指令的作用是,加入 URL 中有兩個重複的 /,那麼會合併為一個,這個指令預設是開啟的,只有當對 URL 進行 base64 之類的編碼時才需要關閉。
### 匹配規則
location 的匹配規則是僅匹配 URI,忽略引數,有下面三種大的情況:
- 字首字串
- 常規匹配
- =:精確匹配
- ^~:匹配上後則不再進行正則表示式匹配
- 正則表示式
- ~:大小寫敏感的正則匹配
- ~*:大小寫不敏感
- 使用者內部跳轉的命名 location
- @
對於這些規則剛看上去肯定是很懵的,完全不知道在說什麼,下面來實戰看幾個例子。
### 實戰
先看一下 Nginx 的配置檔案:
```nginx
server {
listen 80;
server_name location.ziyang.com;
error_log logs/error.log debug;
#root html/;
default_type text/plain;
merge_slashes off;
location ~ /Test1/$ {
return 200 'first regular expressions match!\n';
}
location ~* /Test1/(\w+)$ {
return 200 'longest regular expressions match!\n';
}
location ^~ /Test1/ {
return 200 'stop regular expressions match!\n';
}
location /Test1/Test2 {
return 200 'longest prefix string match!\n';
}
location /Test1 {
return 200 'prefix string match!\n';
}
location = /Test1 {
return 200 'exact match!\n';
}
}
```
問題就來了,訪問下面幾個 URL 會分別返回什麼內容呢?
```
/Test1
/Test1/
/Test1/Test2
/Test1/Test2/
/test1/Test2
```
例如訪問 /Test1 時,會有幾個部分都匹配上:
1. 常規字首匹配:location /Test1
2. 精確匹配:location = /Test1
訪問 /Test1/ 時,也會有幾個部分匹配上:
1. location ~ /Test1/$
2. location ^~ /Test1/
那麼究竟會匹配哪一個呢?Nginx 其實是遵循一套規則的,如下圖所示:
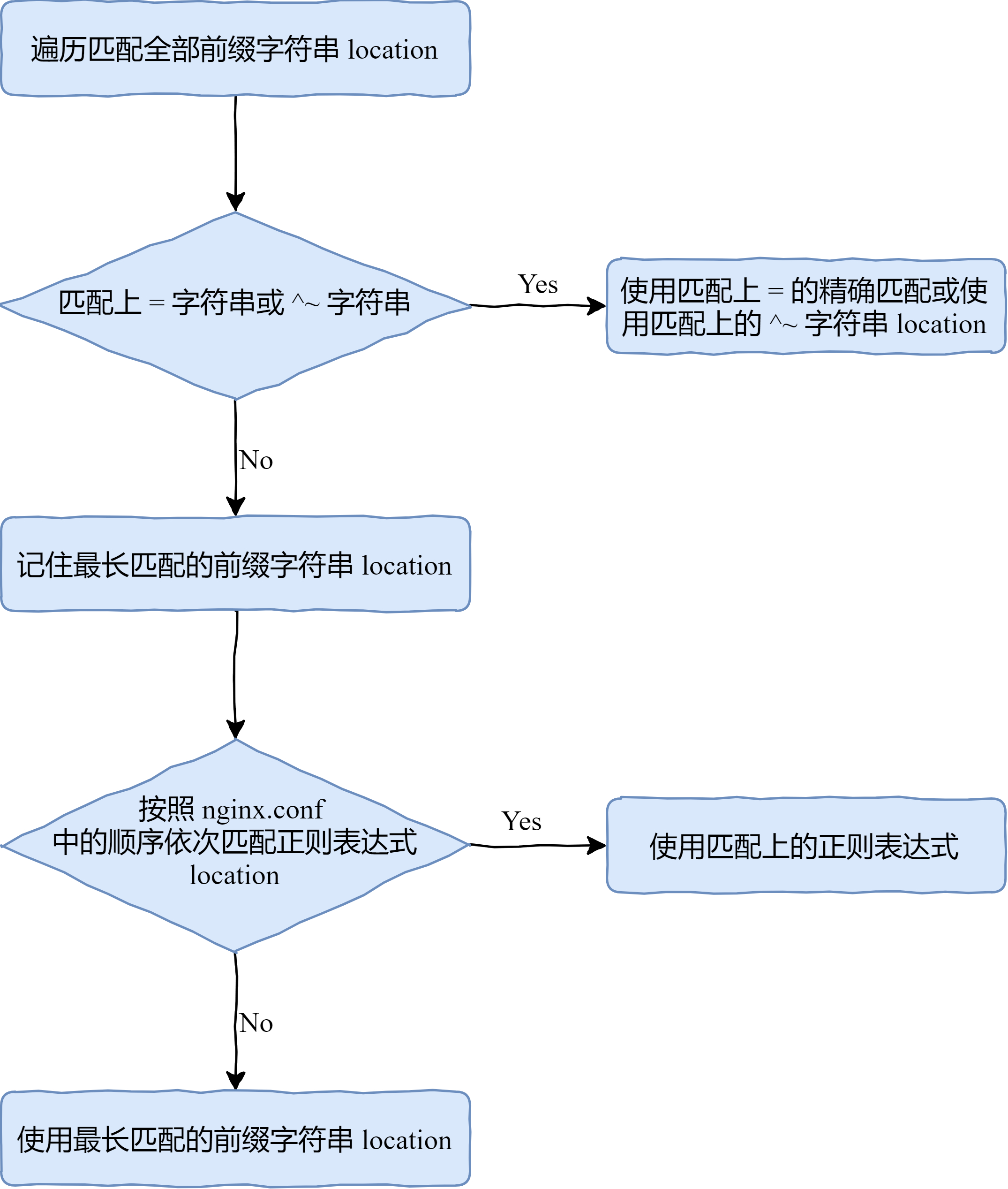
全部的字首字串是放置在一棵二叉樹中的,Nginx 會分為兩部分進行匹配:
1. 先遍歷所有的字首字串,選取最長的一個字首字串,如果這個字串是 = 的精確匹配或 ^~ 的字首匹配,會直接使用
2. 如果第一步中沒有匹配上 = 或 ^~,那麼會先記住最長匹配的字首字串 location
3. 按照 nginx.conf 檔案中的配置依次匹配正則表示式
4. 如果所有的正則表示式都沒有匹配上,那麼會使用最長匹配的字首字串
下面看下實際的響應是怎麼樣的:
```
➜ test_nginx curl location.ziyang.com/Test1
exact match!
➜ test_nginx curl location.ziyang.com/Test1/
stop regular expressions match!
➜ test_nginx curl location.ziyang.com/Test1/Test2
longest regular expressions match!
➜ test_nginx curl location.ziyang.com/Test1/Test2/
longest prefix string match!
➜ test_nginx curl location.ziyang.com/Test1/Test3
stop regular expressions match!
```
- /Test1 匹配 location = /Test1
- /Test1/ 匹配 location ^~ /Test1/
- /Test1/Test2 匹配 location ~* /Test1/(\w+)$
- /Test1/Test2/ 匹配 location /Test1/Test2
- /Test1/Test3 匹配 location ^~ /Test1/
這裡面重點解釋一下 /Test1/Test3 的匹配過程:
1. 遍歷所有可以匹配上的字首字串,總共有兩個
- ^~ /Test1/
- /Test1
2. 選取最長的字首字串 /Test1/,由於前面有 ^~ 禁止正則表示式匹配,因此直接使用 location ^~ /Test1/ 的規則
3. 返回 `stop regular expressions match!`
# preaccess 階段
下面就來到了 preaccess 階段。我們經常會遇到一個問題,就是如何限制每個客戶端的併發連線數?如何限制訪問頻率?這些就是在 preaccess 階段處理完成的,顧名思義,preaccess 就是在連線之前。先來看下 limit_conn 模組。
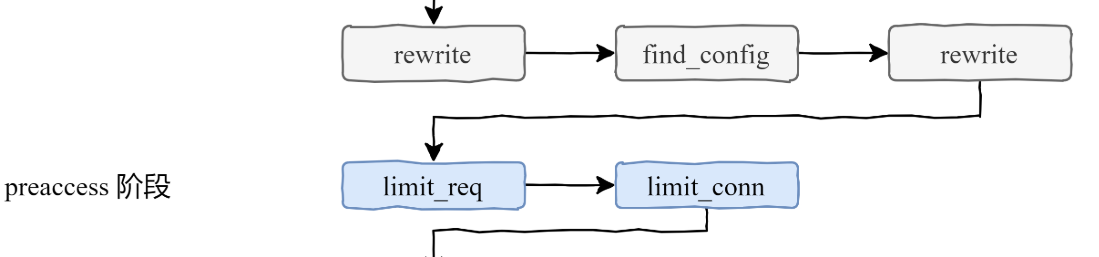
## limit_conn 模組
這裡面涉及到的模組是 `ngx_http_limit_conn_module`,它的基本特性如下:
- 生效階段:`NGX_HTTP_PREACCESS_PHASE` 階段
- 模組:`http_limit_conn_module`
- 預設編譯進 Nginx,通過 `--without-http_limit_conn_module` 禁用
- 生效範圍
- 全部 worker 程序(基於共享記憶體)
- 進入 preaccess 階段前不生效
- 限制的有效性取決於 key 的設計:依賴 postread 階段的 realip 模組取到真實 IP
這裡面有一點需要注意,就是 limit_conn key 的設計,所謂的 key 指的就是對哪個變數進行限制,通常我們取的都是使用者的真實 IP。
說完了 limit_conn 的模組,再來說一下指令語法。
### 指令語法
- 定義共享記憶體(包括大小),以及 key 關鍵字
```nginx
Syntax: limit_conn_zone key zone=name:size;
Default: —
Context: http
```
- 限制併發連線數
```
Syntax: limit_conn zone number;
Default: —
Context: http, server, location
```
- 限制發生時的日誌級別
```nginx
Syntax: limit_conn_log_level info | notice | warn | error;
Default: limit_conn_log_level error;
Context: http, server, location
```
- 限制發生時向客戶端返回的錯誤碼
```nginx
Syntax: limit_conn_status code;
Default: limit_conn_status 503;
Context: http, server, location
```
### 實戰
下面又到了實戰的環節了,通過一個實際的例子來看一下以上的幾個指令是怎麼起作用的。
老規矩,先上配置檔案:
```nginx
limit_conn_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=addr:10m;
#limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=one:10m rate=2r/m;
server {
listen 80;
server_name limit.ziyang.com;
root html/;
error_log logs/myerror.log info;
location /{
limit_conn_status 500;
limit_conn_log_level warn;
limit_rate 50;
limit_conn addr 1;
#limit_req zone=one burst=3 nodelay;
#limit_req zone=one;
}
}
```
- 在本地的 hosts 檔案中新增 limit.ziyang.com 為本機 IP
在這個配置檔案中,做了兩條限制,一個是 `limit_rate` 限制為 50 個位元組,併發連線數 `limit_conn` 限制為 1。
```shell
➜ test_nginx curl limit.ziyang.com
```
這時候訪問 limit.ziyang.com 這個站點,會發現速度非常慢,因為每秒鐘只有 50 個位元組。
如果再同時訪問這個站點的話,則會返回 500。
我在另一個終端裡面同時訪問:
```shell
➜ ~ curl limit.ziyang.com
nginx/1.17.8
```
可以看到,Nginx 直接返回了 500。
## limit_req 模組
在本節開頭我們就提出了兩個問題:
- 如何限制每個客戶端的併發連線數?
- 如何限制訪問頻率?
第一個問題限制併發連線數的問題已經解決了,下面來看第二個問題。
這裡面生效的模組是 `ngx_http_limit_req_module`,它的基本特性如下:
- 生效階段:`NGX_HTTP_PREACCESS_PHASE` 階段
- 模組:`http_limit_req_module`
- 預設編譯進 Nginx,通過 `--without-http_limit_req_module` 禁用
- 生效演算法:leaky bucket 演算法
- 生效範圍
- 全部 worker 程序(基於共享記憶體)
- 進入 preaccess 階段前不生效
### leaky bucket 演算法
leaky bucket 叫漏桶演算法,其他用來限制請求速率的還有令牌環演算法等,這裡面不展開講。
漏桶演算法的原理是,先定義一個桶的大小,所有進入桶內的請求都會以恆定的速率被處理,如果請求太多超出了桶的容量,那麼就會立刻返回錯誤。用一張圖解釋一下。
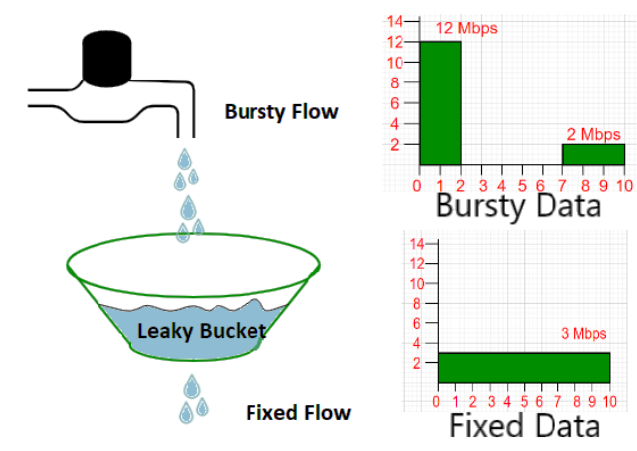
這張圖裡面,水龍頭在不停地滴水,就像使用者發來的請求,所有的水滴都會以恆定的速率流出去,也就是被處理。漏桶演算法對於突發流量有很好的限制作用,會將所有的請求平滑的處理掉。
### 指令語法
- 定義共享記憶體(包括大小),以及 key 關鍵字和限制速率
```
Syntax: limit_req_zone key zone=name:size rate=rate ;
Default: —
Context: http
```
> rate 單位為 r/s 或者 r/m(每分鐘或者每秒處理多少個請求)
- 限制併發連線數
```
Syntax: limit_req zone=name [burst=number] [nodelay];
Default: —
Context: http, server, location
```
> - burst 預設為 0
> - nodelay,如果設定了這個引數,那麼對於漏桶中的請求也會立刻返回錯誤
- 限制發生時的日誌級別
```nginx
Syntax: limit_req_log_level info | notice | warn | error;
Default: limit_req_log_level error;
Context: http, server, location
```
- 限制發生時向客戶端返回的錯誤碼
```nginx
Syntax: limit_req_status code;
Default: limit_req_status 503;
Context: http, server, location
```
### 實戰
在實際驗證之前呢,需要注意兩個問題:
- limit_req 與 limit_conn 配置同時生效時,哪個優先順序高?
- nodelay 新增與否,有什麼不同?
新增配置檔案,這個配置檔案與上一節的配置檔案其實是相同的只不過需要註釋一下:
```nginx
limit_conn_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=addr:10m;
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=one:10m rate=2r/m;
server {
listen 80;
server_name limit.ziyang.com;
root html/;
error_log logs/myerror.log info;
location /{
limit_conn_status 500;
limit_conn_log_level warn;
#limit_rate 50;
#limit_conn addr 1;
#limit_req zone=one burst=3 nodelay;
limit_req zone=one;
}
}
```
結論:在 `limit_req zone=one` 指令下,超出每分鐘處理的請求數後就會立刻返回 503。
```shell
➜ test_nginx curl limit.ziyang.com
nginx/1.17.8
```
改變一下注釋的指令:
```nginx
limit_req zone=one burst=3;
#limit_req zone=one;
```
在沒有新增 burst 引數時,會立刻返回錯誤,而加上之後,不會返回錯誤,而是等待請求限制解除,直到可以處理請求時再返回。
再來看一下 nodelay 引數:
```nginx
limit_req zone=one burst=3 nodelay;
```
添加了 nodelay 之後,請求在沒有達到 burst 限制之前都可以立刻被處理並返回,超出了 burst 限制之後,才會返回 503。
現在可以回答一下剛開始提出的兩個問題:
- limit_req 與 limit_conn 配置同時生效時,哪個優先順序高?
- limit_req 在 limit_conn 處理之前,因此是 limit_req 會生效
- nodelay 新增與否,有什麼不同?
- 不新增 nodelay,請求會等待,直到能夠處理請求;新增 nodelay,在不超出 burst 的限制的情況下會立刻處理並返回,超出限制則會返回 503。
# access 階段
經過 preaccess 階段對使用者的限流之後,就到了 access 階段。
## access 模組
這裡面涉及到的模組是 `ngx_http_access_module`,它的基本特性如下:
- 生效階段:`NGX_HTTP_ACCESS_PHASE` 階段
- 模組:`http_access_module`
- 預設編譯進 Nginx,通過 `--without-http_access_module` 禁用
- 生效範圍
- 進入 access 階段前不生效
### 指令語法
```nginx
Syntax: allow address | CIDR | unix: | all;
Default: —
Context: http, server, location, limit_except
Syntax: deny address | CIDR | unix: | all;
Default: —
Context: http, server, location, limit_except
```
access 模組提供了兩條指令 `allow` 和 `deny`,來看幾個例子:
```nginx
location / {
deny 192.168.1.1;
allow 192.168.1.0/24;
allow 10.1.1.0/16;
allow 2001:0db8::/32;
deny all;
}
```
對於使用者訪問來說,這些指令是順序執行的,當滿足了一條之後,就不會再向下執行。這個模組比較簡單,我們這裡不做實戰演練了。
## auth_basic 模組
auth_basic 模組是用作使用者認證的,當開啟了這個模組之後,我們通過瀏覽器訪問網站時,就會返回一個 401 Unauthorized,當然這個 401 使用者不會看見,瀏覽器會彈出一個對話方塊要求輸入使用者名稱和密碼。這個模組使用的是 RFC2617 中的定義。
### 指令語法
- 基於 HTTP Basic Authutication 協議進行使用者密碼的認證
- 預設編譯進 Nginx
- --without-http_auth_basic_module
- disable ngx_http_auth_basic_module
```nginx
Syntax: auth_basic string | off;
Default: auth_basic off;
Context: http, server, location, limit_except
Syntax: auth_basic_user_file file;
Default: —
Context: http, server, location, limit_except
```
這裡面我們會用到一個工具叫 htpasswd,這個工具可以用來生成密碼檔案,而 `auth_basic_user_file` 就依賴這個密碼檔案。
> htpasswd 依賴安裝包 httpd-tools
生成密碼的命令為:
```shell
htpasswd –c file –b user pass
```
生成的密碼檔案的格式為:
```
# comment
name1:password1
name2:password2:comment
name3:password3
```
### 實戰
- 在 example 目錄下生成密碼檔案 auth.pass
```
htpasswd -bc auth.pass ziyang 123456
```
- 新增配置檔案
```nginx
server {
server_name access.ziyang.com;
listen 80;
error_log logs/error.log debug;
default_type text/plain;
location /auth_basic {
satisfy any;
auth_basic "test auth_basic";
auth_basic_user_file example/auth.pass;
deny all;
}
}
```
- 過載 Nginx 配置檔案
- 在 /etc/hosts 檔案中新增 access.ziyang.com
這時候訪問 access.ziyang.com 就會彈出對話方塊,提示輸入密碼:

## auth_request 模組
- 功能:向上遊的服務轉發請求,若上游服務返回的響應碼是 2xx,則繼續執行,若上游服務返回的響應碼是 2xx,則繼續執行,若上游服務返回的是 401 或者 403,則將響應返回給客戶端
- 原理:收到請求後,生成子請求,通過反向代理技術把請求傳遞給上游服務
- 預設未編譯進 Nginx,需要通過 --with-http_auth_request_module 編譯進去
### 指令語法
```nginx
Syntax: auth_request uri | off;
Default: auth_request off;
Context: http, server, location
Syntax: auth_request_set $variable value;
Default: —
Context: http, server, location
```
### 實戰
- 在上一個配置檔案中新增以下內容
```nginx
server {
server_name access.ziyang.com;
listen 80;
error_log logs/error.log debug;
#root html/;
default_type text/plain;
location /auth_basic {
satisfy any;
auth_basic "test auth_basic";
auth_basic_user_file example/auth.pass;
deny all;
}
location / {
auth_request /test_auth;
}
location = /test_auth {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8090/auth_upstream;
proxy_pass_request_body off;
proxy_set_header Content-Length "";
proxy_set_header X-Original-URI $request_uri;
}
}
```
- 這個配置檔案中,/ 路徑下會將請求轉發到另外一個服務中去,可以用 nginx 再搭建一個服務
- 如果這個服務返回 2xx,那麼鑑權成功,如果返回 401 或 403 則鑑權失敗
## 限制所有 access 階段模組的 satisfy 指令
### 指令語法
```nginx
Syntax: satisfy all | any;
Default: satisfy all;
Context: http, server, location
```
`satisfy` 指令有兩個值一個是 all,一個是 any,這個模組對 acces 階段的三個模組都生效:
- access 模組
- auth_basic 模組
- auth_request 模組
- 其他模組
如果 `satisfy` 指令的值是 all 的話,就表示必須所有 access 階段的模組都要執行,都通過了才會放行;值是 any 的話,表示有任意一個模組得到執行即可。
下面有幾個問題可以加深一下理解:
1. 如果有 return 指令,access 階段會生效嗎?
return 指令屬於 rewrite 階段,在 access 階段之前,因此不會生效。
2. 多個 access 模組的順序有影響嗎?
```
ngx_http_auth_request_module,
ngx_http_auth_basic_module,
ngx_http_access_module,
```
有影響
3. 輸對密碼,下面可以訪問到檔案嗎?
```nginx
location /{
satisfy any;
auth_basic "test auth_basic";
auth_basic_user_file examples/auth.pass;
deny all;
}
```
可以訪問到,因為 `satisfy` 的值是 any,因此只要有模組滿足,即可放行。
4. 如果把 deny all 提到 auth_basic 之前呢?
依然可以,因為各個模組執行順序和指令的順序無關。
5. 如果改為 allow all,有機會輸入密碼嗎?
沒有機會,因為 allow all 是 access 模組,先於 auth_basic 模組執行。
# precontent 階段
講到了這裡,我們再來回顧一下 Nginx 處理 HTTP 請求的 11 個階段:

現在我們已經來到了 precontent 階段,這個階段只有 try_files 這一個指令。
## try_files 模組
### 指令語法
```nginx
Syntax: try_files file ... uri;
try_files file ... =code;
Default: —
Context: server, location
```
- 模組:`ngx_http_try_files_module` 模組
- 依次試圖訪問多個 URL 對應的檔案(由 root 或者 alias 指令指定),當檔案存在時,直接返回檔案內容,如果所有檔案都不存在,則按照最後一個 URL 結果或者 code 返回
### 實戰
下面我們實際看一個例子:
```nginx
server {
server_name tryfiles.ziyang.com;
listen 80;
error_log logs/myerror.log info;
root html/;
default_type text/plain;
location /first {
try_files /system/maintenance.html
$uri $uri/index.html $uri.html
@lasturl;
}
location @lasturl {
return 200 'lasturl!\n';
}
location /second {
try_files $uri $uri/index.html $uri.html =404;
}
}
```
結果如下:
- 訪問 /first 實際上到了 lasturl,然後返回 200
- 訪問 /second 則返回了 404
這兩個結果都與配置檔案是一致的。
```shell
➜ test_nginx curl tryfiles.ziyang.com/second
nginx/1.17.8
➜ test_nginx curl tryfiles.ziyang.com/first
lasturl!
```
## mirror 模組
mirror 模組可以實時拷貝流量,這對於需要同時訪問多個環境的請求是非常有用的。
### 指令語法
- 模組:`ngx_http_mirror_module` 模組,預設編譯進 Nginx
- 通過 --without-http_mirror_module 移除模組
- 功能:處理請求時,生成子請求訪問其他服務,對子請求的返回值不做處理
```nginx
Syntax: mirror uri | off;
Default: mirror off;
Context: http, server, location
Syntax: mirror_request_body on | off;
Default: mirror_request_body on;
Context: http, server, location
```
### 實戰
- 配置檔案如下所示,需要再開啟另外一個 Nginx 來接收請求
```nginx
server {
server_name mirror.ziyang.com;
listen 8001;
error_log logs/error_log debug;
location / {
mirror /mirror;
mirror_request_body off;
}
location = /mirror {
internal;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:10020$request_uri;
proxy_pass_request_body off;
proxy_set_header Content-Length "";
proxy_set_header X-Original-URI $request_uri;
}
}
```
- 在 access.log 檔案中可以看到有請求記錄日誌
# content 階段
下面開始就到了 content 階段,先來看 content 階段的 static 模組,雖然這是位於 content 階段的最後一個處理模組,但是這裡先來介紹它。

## static 模組
### root 和 alias 指令
先來一下 root 和 alias 這兩個指令,這兩個指令都是用來對映檔案路徑的。
```nginx
Syntax: alias path;
Default: —
Context: location
```
```nginx
Syntax: root path;
Default: root html;
Context: http, server, location, if in location
```
- 功能:將 URL 對映為檔案路徑,以返回靜態檔案內容
- 差別:root 會將完整 URL 對映進檔案路徑中,alias 只會將 location 後的 URL 對映到檔案路徑
### 實戰
下面來看一個問題:
現在有一個檔案路徑:
```shell
html/first/
└── 1.txt
```
配置檔案如下所示:
```nginx
server {
server_name static.ziyang.com;
listen 80;
error_log logs/myerror.log info;
location /root {
root html;
}
location /alias {
alias html;
}
location ~ /root/(\w+\.txt) {
root html/first/$1;
}
location ~ /alias/(\w+\.txt) {
alias html/first/$1;
}
location /RealPath/ {
alias html/realpath/;
return 200 '$request_filename:$document_root:$realpath_root\n';
}
}
```
那麼訪問以下 URL 會得到什麼響應呢?
```
/root
/alias
/root/1.txt
/alias/1.txt
```
```shell
➜ test_nginx curl static.ziyang.com/alias/1.txt
test1%
➜ test_nginx curl static.ziyang.com/alias/
...
➜ test_nginx curl static.ziyang.com/root/
nginx/1.17.8
➜ test_nginx curl static.ziyang.com/root/1.txt
nginx/1.17.8
```
訪問這四個路徑分別得到的結果是:
- /root:404
- /alias:200
- /root/1.txt:404
- /alias/1.txt:200
這是為什麼呢?是因為,root 在對映 URL 時,會把 location 中的路徑也加進去,也就是:
- `static.ziyang.com/root/` 實際訪問的是 `html/root/`
- `static.ziyang.com/root/1.txt` 實際是 `html/first/1.txt/root/1.txt`
- `static.ziyang.com/alias/` 實際上是正確訪問到了 `html` 資料夾,由於後面有 `/` 的存在,因此實際訪問的是 `html/index.html`
- `static.ziyang.com/alias/1.txt` 實際訪問的是 `html/first/1.txt`,檔案存在
### 三個相關變數
還是上面的配置檔案:
```nginx
location /RealPath/ {
alias html/realpath/;
return 200 '$request_filename:$document_root:$realpath_root\n';
}
```
這裡有一個問題,在訪問 `/RealPath/1.txt` 時,這三個變數的值各為多少?
為了解答這個問題,我們先來解釋三個變數:
- request_filename:待訪問檔案的完整路徑
- document_root:由 URI 和 root/alias 指令生成的資料夾路徑(可能包含軟連結的路徑)
- realpath_root:將 document_root 中的軟連結替換成真實路徑
為了驗證這三個變數,在 html 目錄下建立一個軟連結指向 first 資料夾:
```shell
ln -s first realpath
```
```
➜ html curl static.ziyang.com/realpath/1.txt
/Users/mtdp/myproject/nginx/test_nginx/html/realpath/1.txt:/Users/mtdp/myproject/nginx/test_nginx/html/realpath/:/Users/mtdp/myproject/nginx/test_nginx/html/first
```
可以看出來,三個路徑分別是:
- /Users/mtdp/myproject/nginx/test_nginx/html/realpath/1.txt
- /Users/mtdp/myproject/nginx/test_nginx/html/realpath/
- /Users/mtdp/myproject/nginx/test_nginx/html/first
還有其他的一些配置指令,例如:
**靜態檔案返回時的 Content-Type**
```nginx
Syntax: types { ... }
Default: types { text/html html; image/gif gif; image/jpeg jpg; }
Context: http, server, location
Syntax: default_type mime-type;
Default: default_type text/plain;
Context: http, server, location
Syntax: types_hash_bucket_size size;
Default: types_hash_bucket_size 64;
Context: http, server, location
Syntax: types_hash_max_size size;
Default: types_hash_max_size 1024;
Context: http, server, location
```
**未找到檔案時的錯誤日誌**
```nginx
Syntax: log_not_found on | off;
Default: log_not_found on;
Context: http, server, location
```
在生產環境中,經常可能會有找不到檔案的情況,錯誤日誌中就會打印出來:
```
[error] 10156#0: *10723 open() "/html/first/2.txt/root/2.txt" failed (2: No such file or directory)
```
如果不想記錄日誌,可以關掉。
### 重定向跳轉的域名
現在有另外一個問題,當我們訪問目錄時最後沒有帶 `/`,static 模組會返回 301 重定向,那麼這個規則是怎麼定義的呢,看下面三個指令:
```nginx
# 該指令決定重定向時的域名,可以決定返回哪個域名
Syntax: server_name_in_redirect on | off;
Default: server_name_in_redirect off;
Context: http, server, location
# 該指令決定重定向時的埠
Syntax: port_in_redirect on | off;
Default: port_in_redirect on;
Context: http, server, location
# 該指令決定是否填域名,預設是開啟的,也就是返回絕對路徑
Syntax: absolute_redirect on | off;
Default: absolute_redirect on;
Context: http, server, location
```
這三個指令的實際用法來實戰演示一下,先來看配置檔案:
```nginx
server {
server_name return.ziyang.com dir.ziyang.com;
server_name_in_redirect on;
listen 8088;
port_in_redirect on;
absolute_redirect off;
root html/;
}
```
`absolute_redirect` 預設是開啟的,我們把它關閉了,看下是怎麼返回的:
```
➜ test_nginx curl localhost:8088/first -I
HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently
Server: nginx/1.17.8
Date: Tue, 12 May 2020 00:31:36 GMT
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: 169
Connection: keep-alive
Location: /first/
```
這個時候看到返回的頭部 `Location` 中沒有加上域名。
下面再把 `absolute_redirect` 開啟(預設是開啟的,因此註釋掉就行了),看下返回什麼:
- `absolute_redirect on`
- `server_name_in_redirect on`
- `port_in_redirect on`
```shell
➜ test_nginx curl localhost:8088/first -I
HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently
Server: nginx/1.17.8
Date: Tue, 12 May 2020 00:35:49 GMT
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: 169
Location: http://return.ziyang.com:8088/first/
Connection: keep-alive
```
可以看到,這時候就返回了域名,而且返回的是我們配置的主域名加埠號,這是因為,`server_name_in_redirect` 和 `port_in_redirect` 這兩個指令打開了,如果關閉掉這兩個指令,看下返回什麼:
- `absolute_redirect on`
- `server_name_in_redirect off`
- `port_in_redirect off`
```shell
➜ test_nginx curl localhost:8088/first -I
HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently
Server: nginx/1.17.8
Date: Tue, 12 May 2020 00:39:31 GMT
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: 169
Location: http://localhost/first/
Connection: keep-alive
```
這兩個指令都設定為 `off` 之後,會發現返回的不再是主域名加埠號,而是我們請求的域名和埠號,如果在請求頭中加上 `Host`,那麼就會用 `Host` 請求頭中的域名。
## index 模組
- 模組:`ngx_http_index_module`
- 功能:指定 `/` 結尾的目錄訪問時,返回 index 檔案內容
- 語法:
```nginx
Syntax: index file ...;
Default: index index.html;
Context: http, server, location
```
- 先於 autoindex 模組執行
這個模組,當我們訪問以 `/` 結尾的目錄時,會去找 root 或 alias 指令的資料夾下的 index.html,如果有這個檔案,就會把檔案內容返回,也可以指定其他檔案。
## autoindex 模組
- 模組:`ngx_http_autoindex_module`,預設編譯進 Nginx,使用 `--without-http_autoindex_module` 取消
- 功能:當 URL 以 `/` 結尾時,嘗試以 html/xml/json/jsonp 等格式返回 root/alias 中指向目錄的目錄結構
- 語法:
```nginx
# 開啟或關閉
Syntax: autoindex on | off;
Default: autoindex off;
Context: http, server, location
# 當以 HTML 格式輸出時,控制是否轉換為 KB/MB/GB
Syntax: autoindex_exact_size on | off;
Default: autoindex_exact_size on;
Context: http, server, location
# 控制以哪種格式輸出
Syntax: autoindex_format html | xml | json | jsonp;
Default: autoindex_format html;
Context: http, server, location
# 控制是否以本地時間格式顯示還是 UTC 格式
Syntax: autoindex_localtime on | off;
Default: autoindex_localtime off;
Context: http, server, location
```
### 實戰
- 配置檔案如下:
```nginx
server {
server_name autoindex.ziyang.com;
listen 8080;
location / {
alias html/;
autoindex on;
#index b.html;
autoindex_exact_size on;
autoindex_format html;
autoindex_localtime on;
}
}
```
這裡我把 `index b.html` 這條指令給註釋掉了,而 index 模組是預設編譯進 Nginx 的,且預設指令是 `index index.html`,因此,會去找是否有 index.html 這個檔案。
- 開啟瀏覽器,訪問 autoindex.ziyang.com:8080,html 目錄下預設是有 index.html 檔案的,因此顯示結果為:
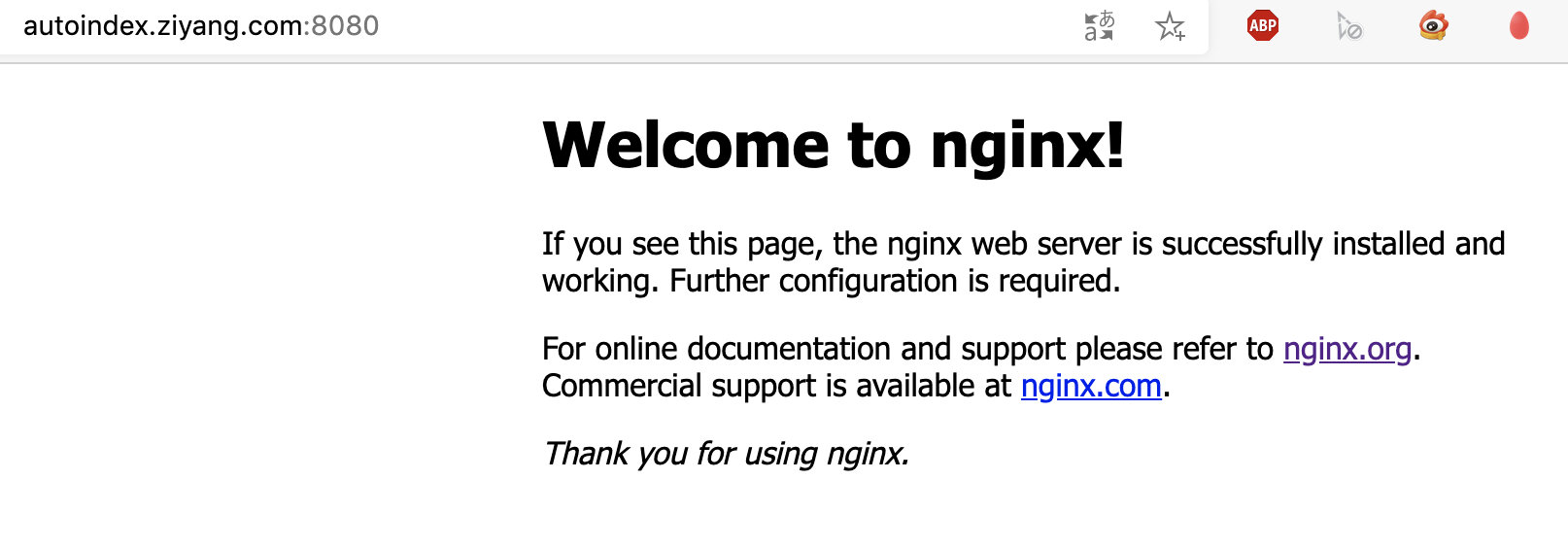
- 開啟 `index b.html` 指令註釋。由於 html 資料夾下並不存在 b.html 這個檔案,所以請求會走到 autoindex 模組,顯示目錄:
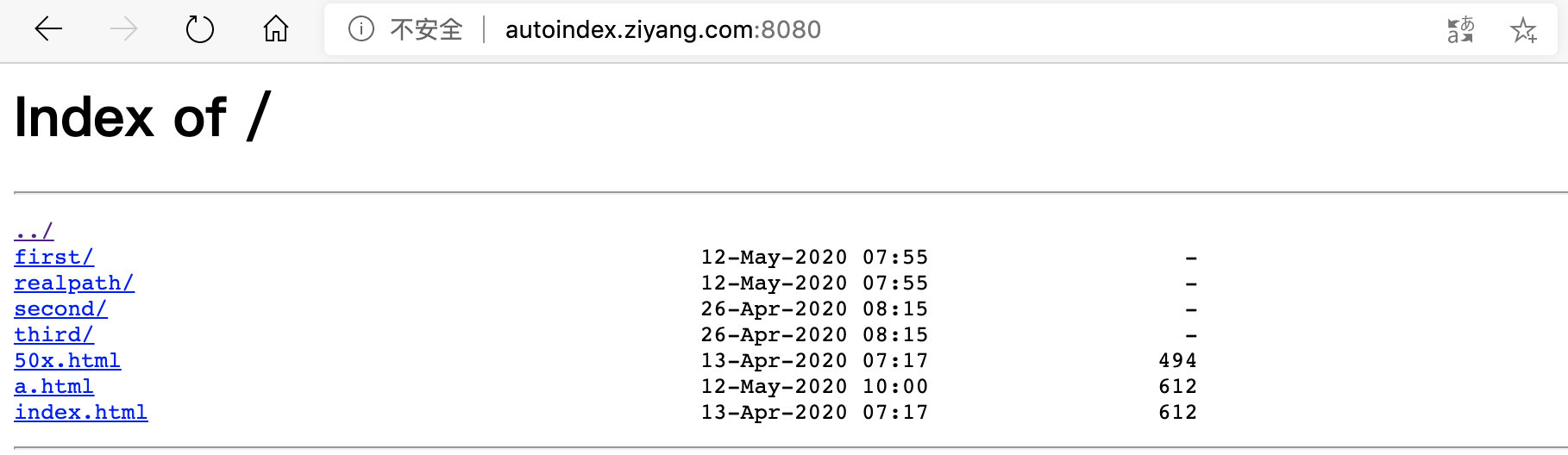
後面的檔案大小顯示格式就是由 `autoindex_exact_size on;` 這條指令決定的。
## concat模組
下面介紹一個可以提升小檔案效能的模組,這個模組是由阿里巴巴開發的,在淘寶網中有廣泛應用。
- 模組:ngx_http_concat_module
- 模組開發者:Tengine(https://github.com/alibaba/nginx-http-concat) --add-module=../nginx-http-concat/
- 功能:合併多個小檔案請求,可以明顯提升 HTTP 請求的效能
- 指令:
```nginx
#在 URI 後面加上 ??,通過 ”,“ 分割檔案,如果還有引數,則在最後通過 ? 新增引數
concat on | off
default concat off
Context http, server, location
concat_types MIME types
Default concat_types: text/css application/x-javascript
Context http, server, location
concat_unique on | off
Default concat_unique on
Context http, server, location
concat_max_files numberp
Default concat_max_files 10
Context http, server, location
concat_delimiter string
Default NONE
Context http, server, locatione
concat_ignore_file_error on | off
Default off
Context http, server, location
```
開啟淘寶主頁,會發現小檔案都是通過這個模組來提高效能的:

這裡就不做實戰了,感興趣的同學可以自己去編譯一下這個模組,做一下實驗,我把配置檔案放在這裡:
```nginx
server {
server_name concat.ziyang.com;
error_log logs/myerror.log debug;
concat on;
root html;
location /concat {
concat_max_files 20;
concat_types text/plain;
concat_unique on;
concat_delimiter ':::';
concat_ignore_file_error on;
}
}
```
# log 階段
下面終於來到了 11 個階段的最後一個階段,記錄請求訪問日誌的 log 模組。
- 功能:將 HTTP 請求相關資訊記錄到日誌
- 模組:`ngx_http_log_module`,無法禁用
## access 日誌格式
```nginx
Syntax: log_format name [escape=default|json|none] string ...;
Default: log_format combined "...";
Context: http
```
預設的 combined 日誌格式:
```nginx
log_format combined '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] '
'"$request" $status $body_bytes_sent ' '"$http_referer"
"$http_user_agent"';
```
## 配置日誌檔案路徑
```nginx
Syntax: access_log path [format [buffer=size] [gzip[=level]] [flush=time] [if=condition]];
access_log off;
Default: access_log logs/access.log combined;
Context: http, server, location, if in location, limit_except
```
- path 路徑可以包含變數:不開啟 cache 時每記錄一條日誌都需要開啟、關閉日誌檔案
- if 通過變數值控制請求日誌是否記錄
- 日誌快取
- 功能:批量將記憶體中的日誌寫入磁碟
- 寫入磁碟的條件:
所有待寫入磁碟的日誌大小超出快取大小;
達到 flush 指定的過期時間;
worker 程序執行 reopen 命令,或者正在關閉。
- 日誌壓縮
- 功能:批量壓縮記憶體中的日誌,再寫入磁碟
- buffer 大小預設為 64KB
- 壓縮級別預設為 1(1最快壓縮率最低,9最慢壓縮率最高)
- 開啟日誌壓縮時,預設開啟日誌快取功能
## 對日誌檔名包含變數時的優化
```nginx
Syntax: open_log_file_cache max=N [inactive=time] [min_uses=N] [valid=time];
open_log_file_cache off;
Default: open_log_file_cache off;
Context: http, server, location
```
- max:快取內的最大檔案控制代碼數,超出後用 LRU 演算法淘汰
- inactive:檔案訪問完後在這段時間內不會被關閉。預設 10 秒
- min_uses:在 inactive 時間內使用次數超過 min_uses 才會繼續存在記憶體中。預設 1
- valid:超出 valid 時間後,將對快取的日誌檔案檢查是否存在。預設 60 秒
- off:關閉快取功能
日誌模組沒有實戰。
-----
到了這裡,我們已經將 Nginx 處理 HTTP 請求的 11 個階段全部梳理了一遍,每個階段基本都有對應的模組。相信對於這樣一個全流程的解析,大家都能夠看懂 Nginx 的配置了,在此之上,還能夠按照需求靈活配置出自己想要的配置,這樣就真正的掌握了 11 個階段。
最後,歡迎大家關注我的個人部落格:[iziyang.github.io](https://iziyang.github.io)
---
本文首發於我的個人部落格:[iziyang.github.io](https://iziyang.gi
