動態追蹤技術之SystemTap
阿新 • • 發佈:2020-06-27
# SystemTap
SystemTap是一個深入檢查Linux系統活動的工具,使用該工具編寫一些簡單的程式碼就可以輕鬆的提取應用或核心的執行資料,以診斷複雜的效能或者功能問題。有了它,開發者不再需要重編譯、安裝新核心、重啟動等煩人的步驟,應用程式同理。
配合火焰圖的視覺化,對程式的效能分析極其有利。
## 原理
SystemTap 基本思想是命名事件,併為它們提供處理程式。每當發生指定的事件時,核心都會將處理程式視為子例程執行,然後繼續執行。有一系列的事件,例如進入或退出函式,計時器到期或整個SystemTap會話的開始和停止。處理程式是一系列指令碼語言語句,用於指定事件發生時要完成的工作。這項工作通常包含從事件上下文中提取資料,將其儲存到內部變數或列印結果。
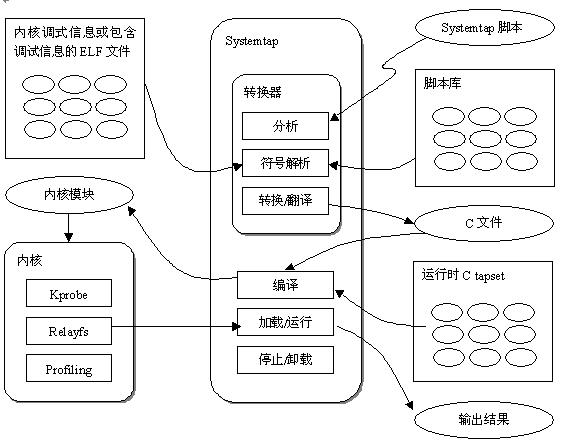
SystemTap 的工作原理是將指令碼翻譯成C語言,執行C編譯器建立一個核心模組。當模組被載入後,通過掛載到核心來啟用所有的探測事件。然後,當事件發生再任何處理器上時,編譯後的處理程式就執行,最終,SystemTap繪畫停止,Hook取消,核心模組被移除,整個過程由命令列程式stap驅動。
原理圖如下:
## 安裝
需要核心級別的支援,依賴了三個rpm[下載連結](#rpm_addr),
1. kernel-debuginfo-common
2. kernel-debuginfo
3. kernel-devel
這三個包的版本必須匹配當前核心的版本,比如我自己的核心版本是 `3.10.0-327`, 那麼以上三個包版本都必須保持一致。
安裝 SystemTap:
> $ yum install systemtap
測試是否成功安裝:
> $ stap -ve 'probe begin{printf("Hello, World\n"); exit();}'
正常的話會輸出 Hello, World,但是不出意外會出現版本不一致的情況:
```sh
ERROR: module version mismatch (#1 SMP Fri Nov 20 11:12:42 CST 2015 vs #1 SMP Thu Nov 19 22:10:57 UTC 2015), release 3.10.0-327.el7.x86_64
```
出現這個的情況是版本相同但是打包事件不相同的情況,修改這個時間和uname -a 中的時間保持一致。
```sh
$ rpm -ql kernel-devel | xargs grep UTS_VERSION 2>/dev/null
/usr/src/kernels/3.10.0-327.el7.x86_64/include/generated/compile.h:#define UTS_VERSION "#1 SMP Fri Nov 20 11:12:42 CST 2015"
```
再次執行那個hello測試,出現快取的錯誤,刪除快取檔案
1. /root/.systemtap/cache/34/stap_34443d4ad1fe1d37c0352b7b8c691aee_975.c
2. /root/.systemtap/cache/34/stap_34443d4ad1fe1d37c0352b7b8c691aee_975.ko
## 追蹤
最簡單的探測型別就是跟蹤事件。Systemtap支援許多內建事件,所有的事件家族見 `tapset`
可以探測的的常用事件:
- begin, systemtap 會話開始
- end, systemtap 會話結束
- kernel.function("sys_xxx"), 系統呼叫xx的入口
- kernel.function("sys_xxx").return, 系統呼叫xx的返回
- timer.ms(300), 每300毫秒的定時器
- timer.profile, 每個CPU上週期觸發的定時器
- process("a.out").function("foo*"), a.out 中函式名字首為foo的函式資訊
- process("a.out").statement("*@main.c:200"), a.out中檔案main.c 200行處的狀態
常用的可列印值(具體見 tapset):
- tid(), 當前執行緒id
- pid(), 當前程序id
- uid(), 當前使用者id
- execname(), 當前程序名稱
- cpu(), 當前cpu編號
- gettimeofday_s(), 秒時間戳
- get_cycles(), 硬體週期計數器快照
- pp(), 探測點事件名稱
- ppfunc(), 探測點觸發的函式名稱
- `$$var`, 上下文中存在 `$var`,可以使用該變數
- print_backtrace(), 列印核心棧
- print_ubacktrace(), 列印使用者空間棧
## SystemTap 指令碼
stap 指令碼簡單,語法類似C;
- 註釋
```c
# fuck
// fuck
/* fuck */
```
- 函式
```lua
function foo() {
// exit(); // 退出 systemtap 會話
}
```
- 基本的 if/else/while/for 控制結構
```lua
function if_expr() {
i = 0
if (i == 1)
printf("[if] i = %d\n", i);
else
printf("[else] i = %d\n", i);
}
function while_expr() {
i = 0;
while (i != 2)
printf("[while] i = %d\n", i++);
}
function for_expr() {
for (i = 0; i < 2; i++)
printf("[for] i = %d\n", i);
}
```
- 字串比較,拼接,轉換
```lua
function str() {
uid = uid();
s_uid = sprint(uid);
f_uid = "fuck" . s_uid
printf("uid: %d-%s-%s\n", uid, s_uid); // uid: 0-0-fuck0
// exit();
}
```
- 元組
```c
global t; // 宣告元組
global tpl[400]; // 宣告一個400容量的元組
t["fuck"]++; // t["fuck"] 初始值預設為0, ++ 變成 1
t["fuck"] = 4396; // 賦值為4396
tpl["fuck", pid()]++; // 兩個元素
tpl["shit", tid()]++;
```
- 聚集統計
```c
// 包含4個維度 @count @avg @min @max
global t;
t["fuck", tid()] <<< 1
t["fuck", pid()] <<< 1
t[execname(), tid()] <<< 1
t["fuck", 5487] <<< 2
t["fuck", 5487] <<< 3
t["fuck", 5487] <<< 1
具體結構如下:
t["fuck",5487] @count=3 @min=1 @max=3 @sum=6 @avg=2
t["fuck",26060] @count=2 @min=1 @max=1 @sum=2 @avg=1
t["stapio",26060] @count=1 @min=1 @max=1 @sum=1 @avg=1
// 遍歷(升序), 限制5次迴圈
foreach([key, value] in t+ limit 5)
printf("%s: %d\n", key, value)
// 結果
stapio: 2571
fuck: 2571
fuck: 5487
```
## 應用
### stap 常用命令
```sh
Usage: stap [options] FILE Run script in file.
or: stap [options] -e SCRIPT Run given script.
or: stap [options] -l PROBE List matching probes.
or: stap [options] -L PROBE List matching probes and local variables.
[options]
-T TIME terminate the script after TIME seconds
```
除了直接執行指令碼檔案外,另外一個比較有用的功能 `-L` `-l` 現象,列出可探測點及區域性變數
- 列出程式中的可探測點
```sh
// 擷取部分~
[root@localhost stp]# stap -l 'process("/tmp/limlog/build/tests/LogTest").function("*")'
process("/tmp/limlog/build/tests/LogTest").function("write@/tmp/limlog/limlog/Log.cpp:107")
process("/tmp/limlog/build/tests/LogTest").function("~LimLog@/tmp/limlog/limlog/Log.cpp:213")
process("/tmp/limlog/build/tests/LogTest").function("~LogLine@/tmp/limlog/limlog/Log.cpp:341")
process("/tmp/limlog/build/tests/LogTest").function("~LogSink@/tmp/limlog/limlog/Log.cpp:59")
process("/tmp/limlog/build/tests/LogTest").function("~_Impl@/usr/include/c++/4.8.2/thread:107")
process("/tmp/limlog/build/tests/LogTest").function("~_Impl_base@/usr/include/c++/4.8.2/thread:97")
```
- 列出程式中的可探測點及區域性變數(字首為`$`)
```sh
[root@localhost stp]# stap -L 'process("/tmp/limlog/build/tests/LogTest").function("*")'
process("/tmp/limlog/build/tests/LogTest").function("id@/usr/include/c++/4.8.2/thread:73") $this:class id* const
process("/tmp/limlog/build/tests/LogTest").function("incConsumable@/tmp/limlog/limlog/Log.cpp:313") $this:class LimLog* const $n:uint32_t
process("/tmp/limlog/build/tests/LogTest").function("incConsumablePos@/tmp/limlog/limlog/Log.cpp:135") $this:class BlockingBuffer* const $n:uint32_t
process("/tmp/limlog/build/tests/LogTest").function("incConsumablePos@/tmp/limlog/limlog/Log.cpp:460") $n:uint32_t
process("/tmp/limlog/build/tests/LogTest").function("insert@/usr/include/c++/4.8.2/bits/basic_string.h:1319") $__c:char $__n:size_type $__pos:size_type $this:class basi
