欄位解析(3)
物件的定義順序和佈局順序是不一樣的。我們在寫程式碼的時候不用關心記憶體對齊問題,但是如果記憶體按照原始碼定義順序進行佈局的話,由於cpu讀取記憶體時是按暫存器(64位)大小單位載入的,如果載入的資料橫跨兩個64位,要操作該資料的話至少需要兩次讀取,加上組合移位,會產生效率問題,甚至會引發異常。比如在一些ARM處理器上,如果不按對齊要求訪問資料, 會觸發硬體異常。
在Class檔案中,欄位的定義是按照程式碼順序排列的,虛擬機器載入後會生成相應的資料結構,包含欄位的名稱,欄位在物件中的偏移等。重新佈局後,只要改變相應的偏移值即可。
獲取到fields後,下面要在ClassFileParser::parseClassFile()函式中進行變數記憶體佈局,如下:
FieldLayoutInfo info; layout_fields(class_loader, &fac, &parsed_annotations, &info, CHECK_NULL);
傳入的fac是之前介紹的FieldAllocationCount型別的變數,裡面已經儲存了各個型別變數的數量。
1、靜態變數的偏移量
程式碼如下:
int next_static_oop_offset;
int next_static_double_offset;
int next_static_word_offset;
int next_static_short_offset;
int next_static_byte_offset;
...
// Calculate the starting byte offsets
next_static_oop_offset = InstanceMirrorKlass::offset_of_static_fields();
next_static_double_offset = next_static_oop_offset + ( (fac->count[STATIC_OOP]) * heapOopSize );
if ( fac->count[STATIC_DOUBLE] &&
(
Universe::field_type_should_be_aligned(T_DOUBLE) || // 方法會返回true
Universe::field_type_should_be_aligned(T_LONG) // 方法會返回true
)
){
next_static_double_offset = align_size_up(next_static_double_offset, BytesPerLong);
}
next_static_word_offset = next_static_double_offset + ((fac->count[STATIC_DOUBLE]) * BytesPerLong);
next_static_short_offset = next_static_word_offset + ((fac->count[STATIC_WORD]) * BytesPerInt);
next_static_byte_offset = next_static_short_offset + ((fac->count[STATIC_SHORT]) * BytesPerShort);
靜態變數儲存在映象類InstanceMirrorKlass中,呼叫offset_of_static_fields()方法獲取_offset_of_static_fields屬性,也就是儲存靜態欄位的偏移量。
在計算next_static_double_offset時,因為首先佈局的是oop,所以記憶體很可能不是按8位元組對齊,需要呼叫align_size_up()方法對記憶體進行8位元組對齊,後面就不需要對齊了,因為一定是自然對齊,8位元組對齊肯定是4位元組對齊的,4位元組對齊肯定是2位元組對齊的。
呼叫InstanceMirrorKlass::offset_of_static_fields()方法會獲取到InstanceMirrorKlass類的_offset_of_static_fields屬性的值,設定_offset_of_static_fields屬性的方法如下:
static void init_offset_of_static_fields() {
// java.lang.Class類使用InstanceMirrorKlass物件來表示,而java.lang.Class物件通過Oop物件來表示,那麼imk->size_helper()獲取的就是
// Oop物件的大小,左移3位將字轉換為位元組
InstanceMirrorKlass* imk = InstanceMirrorKlass::cast(SystemDictionary::Class_klass());
_offset_of_static_fields = imk->size_helper() << LogHeapWordSize; // LogHeapWordSize=3
}
靜態欄位緊挨著儲存在java.lang.Class物件本身佔用的記憶體大小之後。
按照oop、double、word、short、byte的順序計算各個靜態變數的偏移量,next_static_xxx_offset指向的就是第一個xxx型別的靜態變數在InstanceMirrorKlass中的偏移量。可以看到,在fac中統計各個型別變數的數量就是為了方便在這裡計算偏移量。
2、非靜態變數的偏移量
計算非靜態欄位起始偏移量,在ClassFileParser::layout_fields()函式中有如下程式碼呼叫:
int nonstatic_field_size = _super_klass() == NULL ? 0 : _super_klass()->nonstatic_field_size(); ... int nonstatic_fields_start = instanceOopDesc::base_offset_in_bytes() + nonstatic_field_size * heapOopSize; next_nonstatic_field_offset = nonstatic_fields_start;
定義在instanceOop.hpp檔案中的類instanceOopDesc中實現的base_offset_in_bytes()函式的實現如下:
// If compressed, the offset of the fields of the instance may not be aligned.
static int base_offset_in_bytes() {
// offset computation code breaks if UseCompressedClassPointers
// only is true
return ( UseCompressedOops && UseCompressedClassPointers ) ?
klass_gap_offset_in_bytes() : // 開啟指標壓縮後計算出來的值為12
sizeof(instanceOopDesc); // 在64位上計算出來為16
}
因為非靜態變數儲存在instanceOopDesc中,並且父類變數儲存在前,所以nonstatic_fields_start變量表示的就是當前類定義的例項欄位所要儲存的起始偏移量位置。
子類會將父類中定義的所有非靜態欄位(包括private修飾的非靜態欄位)全部複製,以實現欄位繼承。所以上面在計運算元類非靜態欄位的起始偏移量時,會將父類可被繼承的欄位佔用的記憶體也考慮在內。如下圖所示。

下面在計算非靜態欄位的偏移量時還需要考慮有@Contended註解的類和欄位。對於類上的@Contended註解,需要在欄位之前填充ContendedPaddingWidth位元組,對於有@Contended註解的變數來說,需要單獨考慮佈局。相關例項變數的數量需要分別進行計算,如下程式碼所示。
// 在類上加@Contended註解的說明可參考:https://www.icode9.com/content-1-375023.html
bool is_contended_class = parsed_annotations->is_contended();
// Class is contended, pad before all the fields
if (is_contended_class) {
next_nonstatic_field_offset += ContendedPaddingWidth; // ContendedPaddingWidth=128
}
// Compute the non-contended fields count.
// The packing code below relies on these counts to determine if some field
// can be squeezed into the alignment gap. Contended fields are obviously exempt from that.
unsigned int nonstatic_double_count = fac->count[NONSTATIC_DOUBLE] - fac_contended.count[NONSTATIC_DOUBLE];
unsigned int nonstatic_word_count = fac->count[NONSTATIC_WORD] - fac_contended.count[NONSTATIC_WORD];
unsigned int nonstatic_short_count = fac->count[NONSTATIC_SHORT] - fac_contended.count[NONSTATIC_SHORT];
unsigned int nonstatic_byte_count = fac->count[NONSTATIC_BYTE] - fac_contended.count[NONSTATIC_BYTE];
unsigned int nonstatic_oop_count = fac->count[NONSTATIC_OOP] - fac_contended.count[NONSTATIC_OOP];
// Total non-static fields count, including every contended field
unsigned int nonstatic_fields_count = fac->count[NONSTATIC_DOUBLE] +
fac->count[NONSTATIC_WORD] +
fac->count[NONSTATIC_SHORT] +
fac->count[NONSTATIC_BYTE] +
fac->count[NONSTATIC_OOP];
這裡涉及到了對有@Contended註解的例項變數的處理,為了避免偽共享的問題,可能需要在2個變數的儲存佈局之間填充一些資料或空白。這個問題在前一篇已經介紹過,這裡不再介紹。
如果類上有@Contended註解,最終的相關變數更新後指向如下:
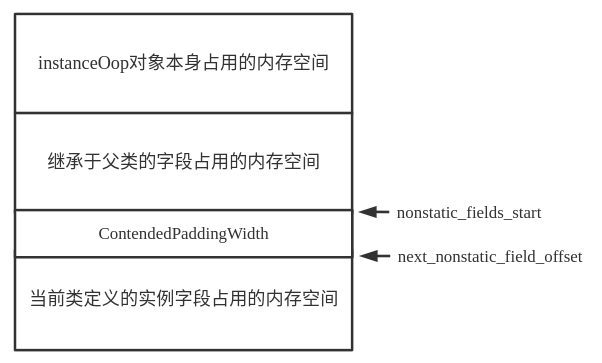
在HotSpot中,物件佈局有三種模式,如下:
- allocation_style=0,欄位排列順序為oops、longs/doubles、ints、shorts/chars、bytes,最後是填充欄位,以滿足對齊要求;
- allocation_style=1,欄位排列順序為longs/doubles、ints、shorts/chars、bytes、oops,最後是填充欄位,以滿足對齊要求;
- allocation_style=2,JVM在佈局時會盡量使父類oops和子類oops挨在一起。
另外,由於填充會形成空隙,比如使用壓縮指標時,頭佔12位元組,後面如果是long型別變數的話,long的對齊要求是8位元組,中間會有4個位元組的空隙,為了提高記憶體利用率, 可以把int/short/byte等相對記憶體佔用比較小的物件塞進去,與此同時JVM提供了-XX:+/-CompactFields命令控制該特性,預設開啟。
bool compact_fields = CompactFields; // 預設值為true
int allocation_style = FieldsAllocationStyle; // 預設的佈局為1
// ...
// Rearrange fields for a given allocation style
if( allocation_style == 0 ) {
// Fields order: oops, longs/doubles, ints, shorts/chars, bytes, padded fields
next_nonstatic_oop_offset = next_nonstatic_field_offset; // 首先佈局oop型別的變數
next_nonstatic_double_offset = next_nonstatic_oop_offset + (nonstatic_oop_count * heapOopSize);
}
else if( allocation_style == 1 ) {
// Fields order: longs/doubles, ints, shorts/chars, bytes, oops, padded fields
next_nonstatic_double_offset = next_nonstatic_field_offset; // 首先佈局long/double型別的變數
}
else if( allocation_style == 2 ) {
// Fields allocation: oops fields in super and sub classes are together.
if(
nonstatic_field_size > 0 && // nonstatic_field_size指的是父類的非靜態變數佔用的大小
_super_klass() != NULL &&
_super_klass->nonstatic_oop_map_size() > 0
){
unsigned int map_count = _super_klass->nonstatic_oop_map_count();
OopMapBlock* first_map = _super_klass->start_of_nonstatic_oop_maps();
OopMapBlock* last_map = first_map + map_count - 1;
int next_offset = last_map->offset() + (last_map->count() * heapOopSize);
if (next_offset == next_nonstatic_field_offset) {
allocation_style = 0; // allocate oops first
next_nonstatic_oop_offset = next_nonstatic_field_offset;
next_nonstatic_double_offset = next_nonstatic_oop_offset + (nonstatic_oop_count * heapOopSize);
}
}
if( allocation_style == 2 ) {
allocation_style = 1; // allocate oops last
next_nonstatic_double_offset = next_nonstatic_field_offset;
}
}
else {
ShouldNotReachHere();
}
對於allocation_style屬性的值為0與為1時的邏輯非常好理解,當為2時,如果父類有OopMapBlock,那麼_super_klass->nonstatic_oop_map_size()大於0,並且父類將oop佈局在末尾時,此時可使用allocation_style=0來佈局,這樣子類會首先將自己的oop佈局在開始,正好和父類的oop連在一起,有利於GC掃描處理引用。剩下的其它情況都是按allocation_style屬性的值為1來佈局的,也就是oop在末尾。後面在介紹了OopMapBlock後就會對allocation_style等於2時的程式碼邏輯有更充分的理解。
選定了佈局策略allocation_style後,首先要向空隙中填充屬性,如下:
// count
int nonstatic_oop_space_count = 0;
int nonstatic_word_space_count = 0;
int nonstatic_short_space_count = 0;
int nonstatic_byte_space_count = 0;
// offset
int nonstatic_oop_space_offset;
int nonstatic_word_space_offset;
int nonstatic_short_space_offset;
int nonstatic_byte_space_offset;
// Try to squeeze some of the fields into the gaps due to long/double alignment.
// 向補白空隙中填充欄位,填充的順序為int、short、byte、oopmap
if( nonstatic_double_count > 0 ) { // 當有long/double型別的例項變數存在時,可能存在空隙
int offset = next_nonstatic_double_offset;
next_nonstatic_double_offset = align_size_up(offset, BytesPerLong);
// 只有開啟了-XX:+CompactFields命令時才會進行空白填充
if( compact_fields && offset != next_nonstatic_double_offset ) {
// Allocate available fields into the gap before double field.
int length = next_nonstatic_double_offset - offset;
assert(length == BytesPerInt, "");
// nonstatic_word_count記錄了word的總數,由於這個gap算一個特殊位置,故把放入這裡的word從正常情況刪除,
// 並加入特殊的nonstatic_word_space_count中。
nonstatic_word_space_offset = offset;
if( nonstatic_word_count > 0 ) { // 由於long/double是8位元組對齊,所以最多隻能有7個位元組的空隙,最多隻能填充一個word型別的變數
nonstatic_word_count -= 1;
nonstatic_word_space_count = 1; // Only one will fit
length -= BytesPerInt;
offset += BytesPerInt;
}
nonstatic_short_space_offset = offset;
while( length >= BytesPerShort && nonstatic_short_count > 0 ) {
nonstatic_short_count -= 1;
nonstatic_short_space_count += 1;
length -= BytesPerShort;
offset += BytesPerShort;
}
nonstatic_byte_space_offset = offset;
while( length > 0 && nonstatic_byte_count > 0 ) {
nonstatic_byte_count -= 1;
nonstatic_byte_space_count += 1;
length -= 1;
}
// Allocate oop field in the gap if there are no other fields for that.
nonstatic_oop_space_offset = offset;
// when oop fields not first
// heapOopSize在開啟指標壓縮時為4,否則為8,所以一個oop佔用的位元組數要看heapOopSize的大小,理論上空隙也最多
// 只能存放一個oop物件
// allocation_style必須不等於0,因為等於0時,oop要分配到開始的位置,和父類的oop進行連續儲存,不能
// 進行空隙填充
if( length >= heapOopSize && nonstatic_oop_count > 0 && allocation_style != 0 ) {
nonstatic_oop_count -= 1;
nonstatic_oop_space_count = 1; // Only one will fit
length -= heapOopSize;
offset += heapOopSize;
}
}
}
long/double型別佔用8位元組,對齊時,最多可能留下7位元組的空白。Java資料型別與JVM內部定義的5種資料型別的對應關係如下表所示。
| Java資料型別 | JVM內部資料型別 | 資料寬度 |
| reference | oop | 4位元組(指標壓縮)/8位元組 |
| boolean/byte | byte | 1位元組 |
| char/short | short | 2位元組 |
| int/float | word | 4位元組 |
| long/double | double | 8位元組 |
有可能對齊後會有最多7位元組的空隙,這樣就可按順序填充int/float、char/short、boolean/byte及引用型別,充分利用了記憶體空間。
下面開始計算非靜態變數的偏移量,如下:
next_nonstatic_word_offset = next_nonstatic_double_offset + (nonstatic_double_count * BytesPerLong);
next_nonstatic_short_offset = next_nonstatic_word_offset + (nonstatic_word_count * BytesPerInt);
next_nonstatic_byte_offset = next_nonstatic_short_offset + (nonstatic_short_count * BytesPerShort);
next_nonstatic_padded_offset = next_nonstatic_byte_offset + nonstatic_byte_count;
// let oops jump before padding with this allocation style
// 為1時的佈局為: // Fields order: longs/doubles, ints, shorts/chars, bytes, oops, padded fields
if( allocation_style == 1 ) {
next_nonstatic_oop_offset = next_nonstatic_padded_offset;
if( nonstatic_oop_count > 0 ) {
next_nonstatic_oop_offset = align_size_up(next_nonstatic_oop_offset, heapOopSize);
}
next_nonstatic_padded_offset = next_nonstatic_oop_offset + (nonstatic_oop_count * heapOopSize);
}
將各個型別的變數在instanceOop中的偏移量計算好後,下面就是計算每個變數的實際偏移量了。
3、計算每個變數的偏移量
程式碼如下:
// Iterate over fields again and compute correct offsets.
// The field allocation type was temporarily stored in the offset slot.
// oop fields are located before non-oop fields (static and non-static).
for (AllFieldStream fs(_fields, _cp); !fs.done(); fs.next()) {
// skip already laid out fields
if (fs.is_offset_set())
continue;
// contended instance fields are handled below
if (fs.is_contended() && !fs.access_flags().is_static()){
continue; // 這個迴圈邏輯不處理有@Contended註解的例項變數
}
int real_offset;
FieldAllocationType atype = (FieldAllocationType) fs.allocation_type();
// pack the rest of the fields
switch (atype) {
case STATIC_OOP:
real_offset = next_static_oop_offset;
next_static_oop_offset += heapOopSize;
break;
case STATIC_BYTE:
real_offset = next_static_byte_offset;
next_static_byte_offset += 1;
break;
case STATIC_SHORT:
real_offset = next_static_short_offset;
next_static_short_offset += BytesPerShort;
break;
case STATIC_WORD:
real_offset = next_static_word_offset;
next_static_word_offset += BytesPerInt;
break;
case STATIC_DOUBLE:
real_offset = next_static_double_offset;
next_static_double_offset += BytesPerLong;
break;
case NONSTATIC_OOP:
if( nonstatic_oop_space_count > 0 ) {
real_offset = nonstatic_oop_space_offset;
nonstatic_oop_space_offset += heapOopSize;
nonstatic_oop_space_count -= 1;
} else {
real_offset = next_nonstatic_oop_offset;
next_nonstatic_oop_offset += heapOopSize;
}
// Update oop maps
if(
nonstatic_oop_map_count > 0 &&
nonstatic_oop_offsets[nonstatic_oop_map_count - 1] ==
real_offset - int(nonstatic_oop_counts[nonstatic_oop_map_count - 1]) * heapOopSize
){
// Extend current oop map
nonstatic_oop_counts[nonstatic_oop_map_count - 1] += 1;
} else {
// Create new oop map
nonstatic_oop_offsets[nonstatic_oop_map_count] = real_offset;
nonstatic_oop_counts [nonstatic_oop_map_count] = 1;
nonstatic_oop_map_count += 1;
if( first_nonstatic_oop_offset == 0 ) { // Undefined
first_nonstatic_oop_offset = real_offset;
}
}
break;
case NONSTATIC_BYTE:
if( nonstatic_byte_space_count > 0 ) {
real_offset = nonstatic_byte_space_offset;
nonstatic_byte_space_offset += 1;
nonstatic_byte_space_count -= 1;
} else {
real_offset = next_nonstatic_byte_offset;
next_nonstatic_byte_offset += 1;
}
break;
case NONSTATIC_SHORT:
if( nonstatic_short_space_count > 0 ) {
real_offset = nonstatic_short_space_offset;
nonstatic_short_space_offset += BytesPerShort;
nonstatic_short_space_count -= 1;
} else {
real_offset = next_nonstatic_short_offset;
next_nonstatic_short_offset += BytesPerShort;
}
break;
case NONSTATIC_WORD:
if( nonstatic_word_space_count > 0 ) {
real_offset = nonstatic_word_space_offset;
nonstatic_word_space_offset += BytesPerInt;
nonstatic_word_space_count -= 1;
} else {
real_offset = next_nonstatic_word_offset;
next_nonstatic_word_offset += BytesPerInt;
}
break;
case NONSTATIC_DOUBLE:
real_offset = next_nonstatic_double_offset;
next_nonstatic_double_offset += BytesPerLong;
break;
default:
ShouldNotReachHere();
} // end switch
fs.set_offset(real_offset); // 設定真正的偏移量
} // end for
由於第一個變數的偏移量已經計算好,所以接下來就按順序進行連續儲存即可。不過由於例項變數會填充到空隙中,所以還需要考慮這一部分的變數,剩下的同樣是通過計算出來的偏移量連續儲存即可。最終算出來的每個變數的偏移量要呼叫fs.set_offset()儲存起來,這樣就能快速找到這些變數的儲存位置了。
對於NONSTATIC_OOP型別的變數來說,會涉及到OopMapBlock,這個知識點在下一篇中將詳細介紹。
4、@Contended變數的偏移量
實現程式碼如下:
// Handle the contended cases.
//
// Each contended field should not intersect the cache line with another contended field.
// In the absence of alignment information, we end up with pessimistically separating
// the fields with full-width padding.
//
// Additionally, this should not break alignment for the fields, so we round the alignment up
// for each field.
if (nonstatic_contended_count > 0) { // 標註有@Contended註解的欄位數量
// if there is at least one contended field, we need to have pre-padding for them
next_nonstatic_padded_offset += ContendedPaddingWidth;
// collect all contended groups
BitMap bm(_cp->size());
for (AllFieldStream fs(_fields, _cp); !fs.done(); fs.next()) {
// skip already laid out fields
if (fs.is_offset_set()){
continue;
}
if (fs.is_contended()) {
bm.set_bit(fs.contended_group());
}
}
// 將同一組的@Contended變數佈局在一起
int current_group = -1;
while ((current_group = (int)bm.get_next_one_offset(current_group + 1)) != (int)bm.size()) {
for (AllFieldStream fs(_fields, _cp); !fs.done(); fs.next()) {
// skip already laid out fields
if (fs.is_offset_set())
continue;
// skip non-contended fields and fields from different group
if (!fs.is_contended() || (fs.contended_group() != current_group))
continue;
// handle statics below
if (fs.access_flags().is_static())
continue;
int real_offset;
FieldAllocationType atype = (FieldAllocationType) fs.allocation_type();
switch (atype) {
case NONSTATIC_BYTE:
next_nonstatic_padded_offset = align_size_up(next_nonstatic_padded_offset, 1);
real_offset = next_nonstatic_padded_offset;
next_nonstatic_padded_offset += 1;
break;
case NONSTATIC_SHORT:
next_nonstatic_padded_offset = align_size_up(next_nonstatic_padded_offset, BytesPerShort);
real_offset = next_nonstatic_padded_offset;
next_nonstatic_padded_offset += BytesPerShort;
break;
case NONSTATIC_WORD:
next_nonstatic_padded_offset = align_size_up(next_nonstatic_padded_offset, BytesPerInt);
real_offset = next_nonstatic_padded_offset;
next_nonstatic_padded_offset += BytesPerInt;
break;
case NONSTATIC_DOUBLE:
next_nonstatic_padded_offset = align_size_up(next_nonstatic_padded_offset, BytesPerLong);
real_offset = next_nonstatic_padded_offset;
next_nonstatic_padded_offset += BytesPerLong;
break;
case NONSTATIC_OOP:
next_nonstatic_padded_offset = align_size_up(next_nonstatic_padded_offset, heapOopSize);
real_offset = next_nonstatic_padded_offset;
next_nonstatic_padded_offset += heapOopSize;
// Create new oop map
assert(nonstatic_oop_map_count < max_nonstatic_oop_maps, "range check");
nonstatic_oop_offsets[nonstatic_oop_map_count] = real_offset;
nonstatic_oop_counts [nonstatic_oop_map_count] = 1;
nonstatic_oop_map_count += 1;
if( first_nonstatic_oop_offset == 0 ) { // Undefined
first_nonstatic_oop_offset = real_offset;
}
break;
default:
ShouldNotReachHere();
}
if (fs.contended_group() == 0) {
// Contended group defines the equivalence class over the fields:
// the fields within the same contended group are not inter-padded.
// The only exception is default group, which does not incur the
// equivalence, and so requires intra-padding.
next_nonstatic_padded_offset += ContendedPaddingWidth;
}
fs.set_offset(real_offset);
} // end for
// Start laying out the next group.
// Note that this will effectively pad the last group in the back;
// this is expected to alleviate memory contention effects for
// subclass fields and/or adjacent object.
// If this was the default group, the padding is already in place.
if (current_group != 0) {
next_nonstatic_padded_offset += ContendedPaddingWidth;
}
} // end while
// handle static fields
}
同為一組的、有@Contended註解的變數要佈局在一起。同一組的變數可能型別不同,並且也不會遵循之前介紹的對例項變數的佈局策略,所以要在每次開始之前呼叫align_size_up()進行對齊操作。在佈局完一組後要填充ontendedPaddingWidth個位元組,然後使用相同的邏輯佈局下一組的變數。最終的變數偏移量同樣會呼叫fs.set_offset()儲存起來,以方便後續進行偏移查詢。
相關文章的連結如下:
1、在Ubuntu 16.04上編譯OpenJDK8的原始碼
2、除錯HotSpot原始碼
3、HotSpot專案結構
4、HotSpot的啟動過程
5、HotSpot二分模型(1)
6、HotSpot的類模型(2)
7、HotSpot的類模型(3)
8、HotSpot的類模型(4)
9、HotSpot的物件模型(5)
10、HotSpot的物件模型(6)
11、操作控制代碼Handle(7)
12、控制代碼Handle的釋放(8)
13、類載入器
14、類的雙親委派機制
15、核心類的預裝載
16、Java主類的裝載
17、觸發類的裝載
18、類檔案介紹
19、檔案流
20、解析Class檔案
21、常量池解析(1)
22、常量池解析(2)
23、欄位解析(1)
24、欄位解析之偽共享(2)
作者持續維護的個人部落格classloading.com。
關注公眾號,有HotSpot原始碼剖析系列文章!

參考文章:
(1)成員變數重排序
&n
