C++11 隨機數生成器
阿新 • • 發佈:2020-09-22
# 背景
考試想造浮點數然後發現不會
正好下午被虎哥茶話會
談到了一些不會的問題balabala的
被告知$C++11$有些神奇特性(哦豁)
然後就學習了一手看上去沒什麼用的隨機數生成器$QwQ$
# 函式
## random_device
標準庫提供了一個非確定性隨機數生成裝置
在$Linux$的實現中,是讀取$/dev/urandom$裝置
random_device提供()操作符,用來返回一個min()到max()之間的一個數字
如果是$Linux(Unix Like或者Unix)$下,都可以使用這個來產生高質量的隨機數,可以理解為**真隨機數**
(以上都是廢話,其實和最原始的c++的rand()用法一樣,不過**真隨機數**好評)
```
#include
#include
using namespace std;
signed main(){
random_device rand;
cout << rand() << endl;
return 0;
}
```
## default_random_engine
一個隨機化的前置引擎
給後面要用到的函式生成一個隨機節點(時間戳balabala隨便理解一下就好,並沒有什麼卵用,就是讓後面的函式隨機化更強)
和上面提到的random_device不同的是,這個需要提供時間種子,看上去和rand也沒什麼區別。。。
```cpp
#include
#include
using namespace std;
signed main(){
default_random_engine rand(time(NULL));
cout << rand() << endl;
return 0;
}
```
## uniform_int_distribution
好了乾貨來了
該函式的作用是生成一個[a,b]範圍內的整數
定義的時候傳進去相應的引數(資料範圍即可)
```cpp
uniform_int_distribution rand1(-100, 100);
```
呼叫的時候給時間種子(就是上面device寫的rand函式)
```cpp
cout << rand1(rand) << " ";
```
## uniform_real_distribution
最有用的東西還是這個實數域的隨機生成器
用法和上述int一樣
```cpp
uniform_real_distribution rand2(0.0, 1.0);
cout << rand2(rand) << endl;
```
# 正態分佈normal_distribution
再來說一個常用的
正態分佈
正態分佈$N(μ,σ^2)$呈現經典的”鐘形曲線”的形狀,其中中心峰的$x$座標由$μ$給出,峰的寬度受$σ$控制。
正態分佈由兩個引數控制,$μ∈R$和$σ∈(0,∞)$
分佈的標準差用$σ$表示,方差用$σ^2$表示
使用方法,第一個引數是$μ$,第二個是$σ$
```cpp
normal_distribution N(10.0, 5.0);
```
為了方便直觀的看出資料分佈,把每次生成的資料出現次數+1,測試的時候輸出了資料分佈圖像
```cpp
for(register int i = 0; i < 10000; i++){
double num = nor(rand);
if ((num >= 0.0) && (num < 20.0)) ++p[int(num)];
}
for (int i = 0; i < 20; ++i) {
cout << i << "-" << (i + 1) << ": ";
cout << string(p[i] * 100 / 10000, '*') << endl;
}
```
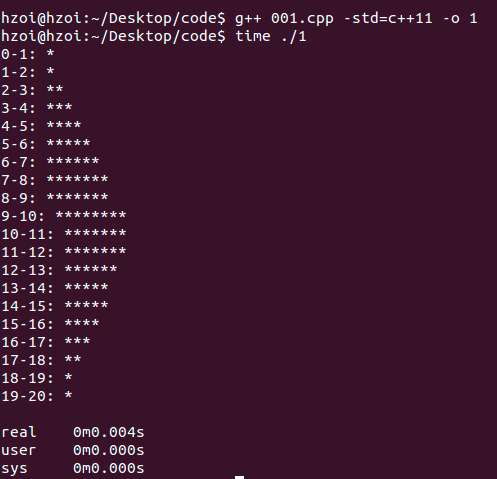
具體要求按照具體題目要求,修改引數即可
# Code
最後把程式碼貼上一下,有需要自取就好
```cpp
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int p[1000];
signed main(){
default_random_engine rand(time(NULL));
uniform_int_distribution rand1(-100, 100);
uniform_real_distribution rand2(0.0, 1.0);
cout << rand() << " ";
cout << rand1(rand) << " ";
cout << rand2(rand) << endl;
normal_distribution nor(10.0, 5.0);
for(register int i = 0; i < 10000; i++){
double num = nor(rand);
if ((num >= 0.0) && (num < 20.0)) ++p[int(num)];
}
for (int i = 0; i < 20; ++i) {
cout << i << "-" << (i + 1) << ": ";
cout << std::string(p[i] * 100 / 10000, '*') << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
```
# 小結
目前常用的這些
如果後續再有需求再補充吧
哦對了
編譯命令
```cpp
g++ 001.cpp -std=c++11 -o 1
```
