redis原始碼學習之slowlog 阿新 • • 發佈:2020-11-22 [toc] ##背景 redis雖說是一個基於記憶體的KV資料庫,以高效能著稱,但是依然存在一些耗時比較高的命令,比如keys *,lrem等,更有甚者會在lua中寫一些比較耗時的操作,比如大迴圈裡面執行命令等,鑑於此,本篇將從原始碼角度分析redis慢日誌的記錄原理,並給出一些自己的看法。 ##環境說明 win10+redis v2.8.9,對本地除錯redis原始碼感興趣的可以參考我另一篇文章[redis原始碼學習之工作流程初探](https://www.cnblogs.com/chopper-poet/p/13207546.html)。 ##redis執行命令流程 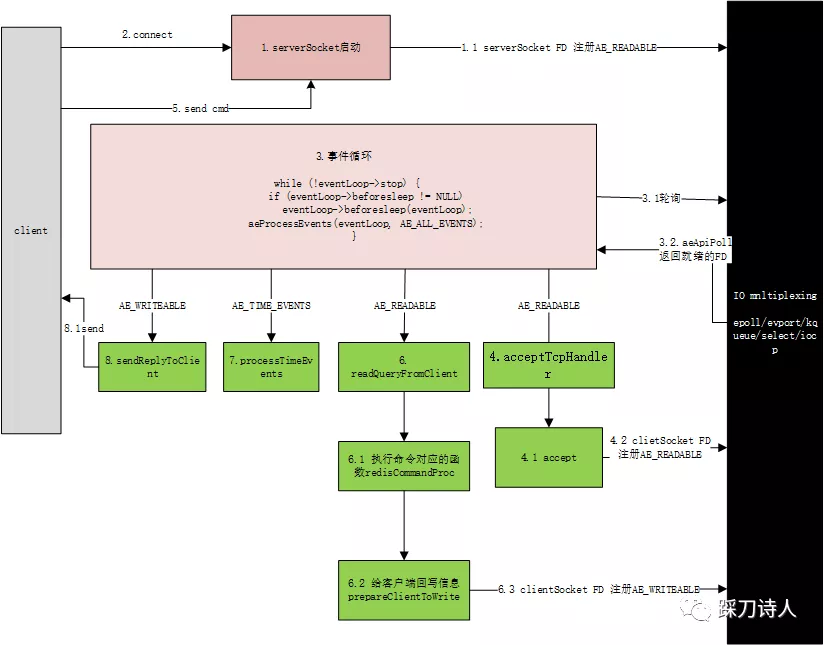 在這裡就不重複redis的執行流程了,不清楚的可以參考我之前的文章[redis原始碼學習之工作流程初探](https://www.cnblogs.com/chopper-poet/p/13207546.html),這裡重點說一下6.1,這一步是真實執行redis命令的地方,redis記錄慢日誌也是這一步實現的。 ##記錄slowlog原始碼分析 1.執行redis 命令之前獲取當前時間; 2.執行redis 命令之後計算耗時; 3.如果開啟了記錄slowlog而且耗時大於設定的閾值就將slowlog記錄下來; 4.如果slowlog數目大於了設定的最大記錄數,就移除最早插入的slowlog; ``` redis.c /* Call() is the core of Redis execution of a command */ void call(redisClient *c, int flags) { ... /* Call the command. */ c->flags &= ~(REDIS_FORCE_AOF|REDIS_FORCE_REPL); redisOpArrayInit(&server.also_propagate); dirty = server.dirty; //執行命令前獲取當前時間 start = ustime(); //執行命令對應的commandProc c->cmd->proc(c); //命令執行完成計算耗時,單位為ms duration = ustime()-start; dirty = server.dirty-dirty; //記錄slowlog if (flags & REDIS_CALL_SLOWLOG && c->cmd->proc != execCommand) slowlogPushEntryIfNeeded(c->argv,c->argc,duration); } ``` ``` slowlog.c /* Push a new entry into the slow log. * This function will make sure to trim the slow log accordingly to the * configured max length. */ void slowlogPushEntryIfNeeded(robj **argv, int argc, long long duration) { //如果slowlog_log_slower_than 小於0,說明不需要記錄 if (server.slowlog_log_slower_than < 0) return; /* Slowlog disabled */ //耗時大於 slowlog_log_slower_than,說明需要記錄, //slowlog_log_slower_than預設為10ms if (duration >= server.slowlog_log_slower_than) listAddNodeHead(server.slowlog,slowlogCreateEntry(argv,argc,duration)); //slowlog記錄數大於slowlog_max_len,就移除最早的那條slowlog /* Remove old entries if needed. */ while (listLength(server.slowlog) > server.slowlog_max_len) listDelNode(server.slowlog,listLast(server.slowlog)); } /* Create a new slowlog entry. * Incrementing the ref count of all the objects retained is up to * this function. */ slowlogEntry *slowlogCreateEntry(robj **argv, int argc, long long duration) { slowlogEntry *se = zmalloc(sizeof(*se)); int j, slargc = argc; if (slargc > SLOWLOG_ENTRY_MAX_ARGC) slargc = SLOWLOG_ENTRY_MAX_ARGC; //引數數量 se->argc = slargc; //具體引數 se->argv = zmalloc(sizeof(robj*)*slargc); for (j = 0; j < slargc; j++) { /* Logging too many arguments is a useless memory waste, so we stop * at SLOWLOG_ENTRY_MAX_ARGC, but use the last argument to specify * how many remaining arguments there were in the original command. */ if (slargc != argc && j == slargc-1) { se->argv[j] = createObject(REDIS_STRING, sdscatprintf(sdsempty(),"... (%d more arguments)", argc-slargc+1)); } else { /* Trim too long strings as well... */ if (argv[j]->type == REDIS_STRING && argv[j]->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_RAW && sdslen(argv[j]->ptr) > SLOWLOG_ENTRY_MAX_STRING) { sds s = sdsnewlen(argv[j]->ptr, SLOWLOG_ENTRY_MAX_STRING); s = sdscatprintf(s,"... (%lu more bytes)", (unsigned long) sdslen(argv[j]->ptr) - SLOWLOG_ENTRY_MAX_STRING); se->argv[j] = createObject(REDIS_STRING,s); } else { se->argv[j] = argv[j]; incrRefCount(argv[j]); } } } //發生時間 se->time = time(NULL); //耗時 se->duration = duration; //slowlog id,server.slowlog_entry_id自增 se->id = server.slowlog_entry_id++; return se; } ``` ##製造一條slowlog 為了講解方便我使用斷點的方式製造一條slowlog,方式如下: 1.連線redis,執行get 1; 2.ide 斷點在redis.c 的Call函式c->cmd->proc處 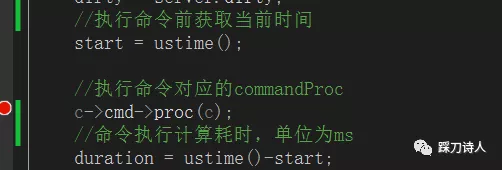 3.等待10s+以後繼續執行,即可產生一條例slowlog; 4.檢視slowlog 127.0.0.1:6379> slowlog get 1) 1) (integer) 0 #slowlog 標識,從0開始遞增 2) (integer) 1606033532 #slowlog產生時間,unix時間戳格式 3) (integer) 28049157 #執行命令耗時 4) 1) "get" # 執行的命令 2) "1" ##slowlog分析 通過前面的章節對slowlog的寫入過程有了一個初步的瞭解,其中有這麼幾點我要重點提一下: ###1.slowlog如何開啟 slowlog預設情況下是開啟的,主要受限於slowlog-log-slower-than的設定,如果其大於0意味著開始slowlog,預設值為10ms,可以通過修改redis配置檔案或者使用CONFIG SET這種方式,單位為微秒; ###2.slowlog數量限制 預設情況下只會儲存128條記錄,超過128會丟棄最早的那條記錄,可以通過修改redis配置檔案或者使用CONFIG SET slowlog-max-len這種方式; ###3.slowlog中的耗時的含義 耗時只包括執行命令的時間,不包括等待、網路傳輸的時間,這個不難理解,從redis的工作模型可知,redis執行命令採用單執行緒方式,所以內部有排隊機制,如果之前的命令非常耗時,只會影響redis整體的吞吐量,但不一定會影響當前命令的執行時間,比如client執行一條命令整體耗時20s,但是slowlog記錄的耗時只有10s; ###4.slowlog中時間戳的含義 切記這個時間戳是redis產生slowlog的時間,不是執行redis命令的時間。 ##自己的一些思考 如果開發人員反饋redis響應變慢了,我們應該從哪些方面去排查呢? 1.檢視slowlog分析是否有慢查情況,比如使用使用了keys *等命令; 2.slowlog中沒有慢日誌,可以結合應用程式中一些埋點來分析,可能是網路問題,找運維協助檢視網路是否丟包、頻寬是否被打滿等問題; 3.如果排除網路問題,那可能是redis機器本身負載過高,排查記憶體、swap、負載等情況; 4.任何以高效能著稱的元件都不是銀彈,使用時一定要了解其api,比如keys命令,作者已經明確的說了其時間複雜度為O(N)資料量大時會有效能問題。  推薦閱讀 [Redis常見延遲問題排查手冊]( https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/MK-4Vf3P10OCwMH6ZLq0jw ) [redis原始碼學習之工作流程初探](https://www.cnblogs.com/chopper-poet/p/13207546.html) 來我的公眾號與我交流 <