tensorflowxun訓練自己的數據集之從tfrecords讀取數據
阿新 • • 發佈:2017-07-29
str 兩個 圖片文件 lines 註意 file ans span 數據集
當訓練數據量較小時,采用直接讀取文件的方式,當訓練數據量非常大時,直接讀取文件的方式太耗內存,這時應采用高效的讀取方法,讀取tfrecords文件,這其實是一種二進制文件。tensorflow為其內置了各種存儲和讀取的函數,方便調用。
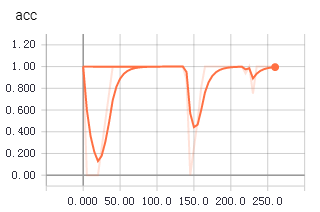
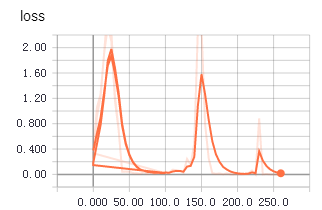
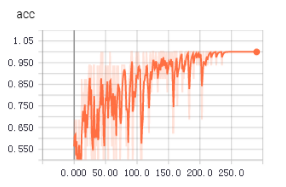
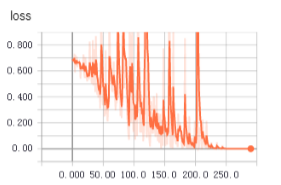
不知道為啥,從tfrecords中讀取數據用於訓練時,收斂得更快,更平穩。上面兩個圖是使用tfrecords的準確率和loss值變化,下面是直接讀取文件的準確率和loss值變化。
1 生成記錄樣本的記錄文件
1 root_dir = os.getcwd() 2 3 def getTrianList(): 4 with open("train.txt","w") as f: 5 for file in os.listdir(root_dir+‘\\dataSet‘): 6 for picFile in os.listdir(root_dir+"\\dataSet\\"+file): 7 f.write("dataSet/"+file+"/"+picFile+" "+file+"\n") 8 print(picFile) 9 if __name__=="__main__": 10 getTrianList()
將樣本文件路徑和標簽統一記錄到一個txt中,後面生成tfrecords文件就是通過讀取這些信息。
註意文件路徑和標簽之間采用空格,不要使用制表符。
2 讀取txt存於數組中
1 def load_file(example_list_file): 2 lines = np.genfromtxt(example_list_file,delimiter=" ",dtype=[(‘col1‘, ‘S120‘), (‘col2‘, ‘i8‘)]) 3 examples = [] 4 labels = [] 5 for example,label inlines: 6 examples.append(example) 7 labels.append(label) 8 #convert to numpy array 9 return np.asarray(examples),np.asarray(labels),len(lines)
這段代碼主要用來讀取第1步生成的txt,將文件路徑和標簽存於數組中
3 讀取圖片
1 def extract_image(filename,height,width): 2 print(filename) 3 image = cv2.imread(filename) 4 image = cv2.resize(image,(height,width)) 5 b,g,r = cv2.split(image) 6 rgb_image = cv2.merge([r,g,b]) 7 return rgb_image
使用cv2讀取圖片文件
4 轉化為tfrecords文件
1 def trans2tfRecord(trainFile,name,output_dir,height,width): 2 if not os.path.exists(output_dir) or os.path.isfile(output_dir): 3 os.makedirs(output_dir) 4 _examples,_labels,examples_num = load_file(train_file) 5 filename = name + ‘.tfrecords‘ 6 writer = tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(filename) 7 for i,[example,label] in enumerate(zip(_examples,_labels)): 8 print("NO{}".format(i)) 9 #need to convert the example(bytes) to utf-8 10 example = example.decode("UTF-8") 11 image = extract_image(example,height,width) 12 image_raw = image.tostring() 13 example = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={ 14 ‘image_raw‘:_bytes_feature(image_raw), 15 ‘height‘:_int64_feature(image.shape[0]), 16 ‘width‘: _int64_feature(32), 17 ‘depth‘: _int64_feature(32), 18 ‘label‘: _int64_feature(label) 19 })) 20 writer.write(example.SerializeToString()) 21 writer.close()
1 def _int64_feature(value): 2 return tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[value])) 3 4 def _bytes_feature(value): 5 return tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[value]))
5 從tfrecords中讀取訓練數據
1 def read_tfRecord(file_tfRecord): 2 queue = tf.train.string_input_producer([file_tfRecord]) 3 reader = tf.TFRecordReader() 4 _,serialized_example = reader.read(queue) 5 features = tf.parse_single_example( 6 serialized_example, 7 features={ 8 ‘image_raw‘: tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string), 9 ‘height‘: tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64), 10 ‘width‘:tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64), 11 ‘depth‘: tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64), 12 ‘label‘: tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64) 13 } 14 ) 15 image = tf.decode_raw(features[‘image_raw‘],tf.uint8) 16 #height = tf.cast(features[‘height‘], tf.int64) 17 #width = tf.cast(features[‘width‘], tf.int64) 18 image = tf.reshape(image,[32,32,3]) 19 image = tf.cast(image, tf.float32) 20 image = tf.image.per_image_standardization(image) 21 label = tf.cast(features[‘label‘], tf.int64) 22 print(image,label) 23 return image,label
從tfrecords文件中讀取image和label,訓練的時候,直接使用tf.train.batch函數生成用於訓練的batch即可。
1 image_batches,label_batches = tf.train.batch([image, label], batch_size=16, capacity=20)
其余的部分跟之前的訓練步驟一樣。
tensorflowxun訓練自己的數據集之從tfrecords讀取數據
