後綴表達式
我經常不厭其煩地向開發人員強調數據結構的重要性,也經常和團隊分享一些常見算法。也許是大家寫慣了業務代碼,往往對數據結構的知識並不太在意。可不是嘛,只需要玩轉QUID就能解決90%以上的問題,還費腦細胞學習基礎知識幹什麽?當然,所有人都會回答“基礎知識很重要,數據結構很重要”。然而,當你發現工作幾年的開發人員甚至不知道Array和List的區別時,也許會覺得他們當初是在說謊。這是真的,我發現大部分人不知道還有個鏈表叫“循環鏈表”。
下面講述的是多年前的故事。
表格曾是我們在JSP頁面常用的布局方式,碰到合並單元格時會不停的使用collspan和rowspan。為了簡化操作,我規劃了一個布局管理器,用一個字符串代替表格布局。大概長這個樣子:
當時我把這個任務分配給一個工作了4年左右開發人員,並告訴他去看看後綴表達式,並順便看看解析器模式。
兩天後我得到了任務完成的答復,然後開始review。
這下好玩了,布局管理器變成了這樣:layout="3;C2:bop1,bop2;C3:bop3;bop4"。似乎沒那麽壞,至少還能工作,但看起來沒那麽直觀了,似乎也不能更加隨意。私自更改設計的原因很簡單——這樣可以更容易使用split,哈,貌似沒有理解如何使用數據結構。
後來使用後綴表達式重寫了實現。這實際上是棧結構的典型應用,遍歷字符串,根據各種符號為節點,不斷入棧出棧。具體過程如下:
1. 刨除前面的默認列數
2. cellMap存儲最終解析結果,key對應bop名稱,value對應布局,即合並幾行幾列;
3. 遍歷布局管理器字符串
3.1. 遇到數字或字母直接並入atom
3.2 遇到左括號,將atom壓入stack,清空atom
3.3 遇到逗號, 如果stack不為空, 將stack中的所有xspan表達式代表的含義賦予bop, 將bop壓入cellMap,清空atom; 如果stack為空, 清空atom
3.4 遇到右括號, 將stack中的所有xspan表達式代表的含義賦予bop, 將bop壓入cellMap, 從stack彈出一項.
4.布局管理器字符串遍歷結束,cellMap是最終結果
以R2(C2(bop1, bop2)),C3(bop3, bop4)為例:
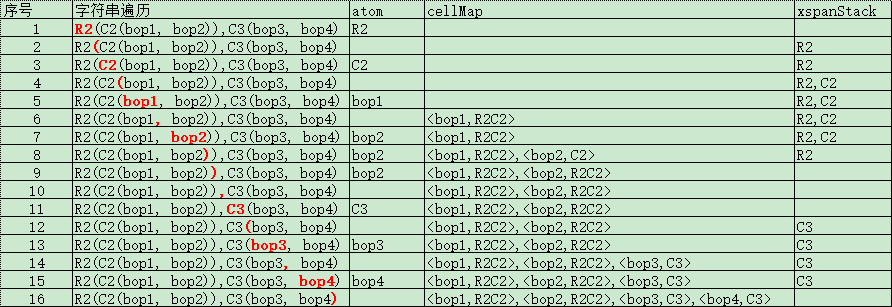
1.遍歷字符串,atom="R2"
2.遇到"(",stack.push(atom),atom="", stack棧頂元素為"R2"
3.繼續遍歷字符串,atom="C2"
4.遇到"(",stack.push(atom),atom="", stack棧頂元素為"C2",第二個元素為"R2"
5.繼續遍歷字符串,atom="bop1"
6.遇到",",cellMap.put("bop1", "C2,R2"),atom=""
7.繼續遍歷字符串,atom="bop2"
8.遇到")",cellMap.put("bop2", Cell.C2),stack.pop(), stack中C2出棧,R2升到棧頂
9.遇到")",cellMap.put("bop2", Cell.R2),stack.pop(), stack中R2出棧,stack為空
10.遇到",",此時stack為空,所以atom=""
11.繼續遍歷字符串,atom="C3"
12.遇到"(",stack.push(atom),atom="", stack棧頂元素為"C3"
13.繼續遍歷字符串,atom="bop3"
14.遇到",",cellMap.put("bop3", "C3"),atom=""
15.繼續遍歷字符串,atom="bop4"
16.遇到")",cellMap.put("bop4", "C3"),stack.pop(), stack中C3出棧,stack為空
17.遍歷結束,最終得到cellMap
代碼示例:
1 /** 2 * 3 * 布局管理器表達式解釋器 4 */ 5 public class Interpreter { 6 7 /* 8 * 布局管理器表達式 9 * 布局管理器表達式示例: 10 * 1. 3;C2(bop1, bop2),C3(bop3, bop4); 11 * 默認3列,bop1,bop2合並2列,bop3,bop4合並3列; 12 * 2. 4;R2(C2(bop1, bop2)),C3(bop3, bop4) 13 * 默認4列,bop1,bop2合並2列2行,bop3,bop4合並3列; 14 * 3. 粗粒度組件布局管理器表達式類似: C2(boid1, boid2). 15 */ 16 private String layoutStr; 17 private int columns; //布局的列數 18 /* 19 * key : vcSign, value : formCell 20 * vcSign:如果是細粒度組件,vcSign表示細粒度組件標簽的bind屬性; 21 * 如果是粗粒度組件,vcSign表示粗粒度組件標簽的id屬性。 22 */ 23 private Map<String, Cell> cellMap = new HashMap<String, Cell>(); 24 25 private final String EXPRESSION_SPLIT = ";"; 26 private final char FC_SPLIT = ‘,‘; 27 private final char LEFT_BRACKET = ‘(‘; 28 private final char RIGHT_BRACKET = ‘)‘; 29 30 /** 31 * @param layoutStr 布局管理器表達式 32 * @param defColumns 默認列數 33 */ 34 public Interpreter(String layoutStr, int defColumns) { 35 this.layoutStr = StringUtils.removeAllSpace(layoutStr); 36 this.columns = defColumns; 37 } 38 39 /** 40 * 解析布局管理器表達式. 41 */ 42 public void interpret() { 43 if(StringUtils.isEmpty(getLayoutStr())) 44 return; 45 46 String[] layoutSplit = StringUtils.split(getLayoutStr(), EXPRESSION_SPLIT); 47 if(StringUtils.isEmpty(layoutSplit)) 48 return; 49 50 interpertColumns(layoutSplit[0]); 51 for(String str : layoutSplit) { 52 if(StringUtils.isEmpty(str) || MatcherUtil.isNumber(str)) 53 continue; 54 55 interpertFormCell(str); 56 } 57 } 58 59 /** 60 * 解析默認列數 61 * @param str 布局管理器劃分的總列數 62 */ 63 private void interpertColumns(String str) { 64 Integer columns = StringUtils.convertToInteger(str); 65 if(columns != null && columns > 0) 66 setColumns(columns); 67 } 68 69 /** 70 * 構造每個bop的布局樣式 71 * R2(C2(bop1, bop2)) 或 R2(bop3, C2(bop1, bop2)) 72 * <li>1. 遍歷表達式, 解析子元素; 73 * <li>2. 遇到左括號,將R2, C2 表達式壓入表達式棧頂; 74 * <li>3. 遇到逗號, 如果棧不為空, 將棧中的所有表達式代表的含義賦予bop, 將bop壓入cellMap; 如果棧為空, 直接略過; 75 * <li>4. 遇到右括號, 將棧中的所有表達式代表的含義賦予bop, 將bop壓入cellMap, 從表達式棧頂彈出一項. 76 * @param str 77 */ 78 private void interpertFormCell(String str) { 79 //表達式棧, 存儲 R1, C1, R2, C2等合並單元格的表達式 80 Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>(); 81 82 //表達式的元素 83 String atom = ""; 84 //遍歷表達式, 解析子元素 85 for(int i = 0, length = str.length(); i < length; i++) { 86 char ch = str.charAt(i); 87 //遇到左括號,將R2, C2 表達式壓入表達式棧頂 88 if(LEFT_BRACKET == ch) { 89 stack.push(atom); 90 atom = ""; 91 } 92 //遇到逗號, 如果棧不為空, 將棧中的所有表達式代表的含義賦予bop, 將bop壓入cellMap; 93 //如果棧為空, 直接略過; 94 else if(FC_SPLIT == ch) { 95 if(ContainerUtil.isNotNull(stack)) 96 formatCell(atom, stack); 97 atom = ""; 98 } 99 //遇到右括號, 將棧中的所有表達式代表的含義賦予bop, 將bop壓入cellMap, 從表達式棧頂彈出一項 100 else if(RIGHT_BRACKET == ch) { 101 if(StringUtils.isNotEmpty(atom)) 102 formatCell(atom, stack); 103 stack.pop();105 } 106 else { 107 atom += ch; 108 } 109 } 110 } 111 112 /** 113 * 將bop壓入cellMap 114 * @param vcSign 115 * @param stack 表達式棧 116 */ 117 private void formatCell(String vcSign, Stack<String> stack) { 118 Cell cell = getCell(vcSign); 119 120 Iterator<String> itr = stack.iterator(); 121 while(itr.hasNext()) { 122 String expression = itr.next(); 123 if(isCELLSPAN(expression)) 124 cell.setCollSpan(getCallSpan(expression)); 125 else if(isROWSPAN(expression)) 126 cell.setRowSpan(getRowSpan(expression)); 127 } 128 129 cellMap.put(vcSign, cell); 130 } 131 132 private int getCallSpan(String expression) { 133 int collSpan = Integer.parseInt(expression.toUpperCase().replace("C", "")); 134 return collSpan > getColumns() ? getColumns() : collSpan; 135 } 136 137 private int getRowSpan(String expression) { 138 return Integer.parseInt(expression.toUpperCase().replace("R", "")); 139 } 140 141 private Cell getCell(String atom) { 142 Cell cell = cellMap.get(atom); 143 return cell == null ? new Cell() : cell; 144 } 145 146 private boolean isCELLSPAN(String str) { 147 return MatcherUtil.isAllMatch(str, "^[C|c]-?\\d+$"); 148 } 149 150 private boolean isROWSPAN(String str) { 151 return MatcherUtil.isAllMatch(str, "^[R|r]-?\\d+$"); 152 } 153 154 public int getColumns() { 155 return this.columns; 156 } 157 158 public void setColumns(int columns) { 159 this.columns = columns; 160 } 161 162 public String getLayoutStr() { 163 return layoutStr; 164 } 165 166 public void setLayoutStr(String layoutStr) { 167 this.layoutStr = layoutStr; 168 } 169 170 public Map<String, Cell> getCellMap() { 171 return cellMap; 172 } 173 174 public void setCellMap(Map<String, Cell> cellMap) { 175 this.cellMap = cellMap; 176 }
作者:我是8位的
出處:http://www.cnblogs.com/bigmonkey
本文以學習、研究和分享為主,如需轉載,請聯系本人,標明作者和出處,非商業用途!
後綴表達式
