java nio之 channel通道(二)
阿新 • • 發佈:2017-08-13
java nio
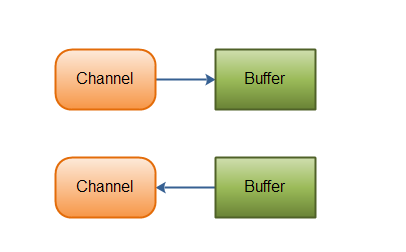
java nio 通道上一篇文章裏就講述過,channel總是寫數據的時候,要先把數據寫入到bytebuffer,讀數據的時候總是要先從channel中讀入到bytebuffer。如下圖,這個圖是好多知名博客常用的圖,很好理解這個channel。
channel分為一下幾種:
FileChannel
SocketChannel
ServerSocketChannel
DatagramChannel
FileChannel:
經常說的FileChannel都是拿下面的例子說事
代碼如下:
package com.nio.basic;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
/**
* Created by sdc on 2017/8/13.
*/
public class RandomAccessFileTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
readFile();
}
/**
* 讀取文件
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void readFile(){
String fileName = "C:\\Users\\sdc\\Desktop\\gc (2).log";
RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = null;
try{
randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile(fileName, "r");
long fileLength = randomAccessFile.length();
System.out.print("length" + fileLength);
int start = 100;
randomAccessFile.seek(start);
byte[] bytes = new byte[20];
int read = 0;
while ((read = randomAccessFile.read(bytes)) != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(bytes, "UTF-8"));
}
System.out.println(bytes.length);
System.out.println(new String(bytes, "UTF-8"));
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (randomAccessFile != null) {
try {
randomAccessFile.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}還有這樣的例子:
FileInputStream is = new FileInputStream(new File(src)); FileChannel channelFrom = is.getChannel();
其實這兩個是用到了nio的channel,不妨自己寫一個例子試試。
SocketChannel和ServerSocketChannel一般是兩個集合起來說的,一個用於客戶端連接,一個用於服務端連接。
package com.nio.basic;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* nio 服務端
* Created by sdc on 2017/8/13.
*/
public class NIoServer {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.println("server started...");
try {
new NIoServer().run();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void run () throws Exception {
//打開服務器端的套接字通道
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//服務器端設置為非阻塞
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//服務端進行綁定
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8000));
//註冊感興趣的事件
Selector selector = Selector.open();
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while (true) {
int selectCount = selector.select();
if( selectCount ==0 ) {
continue;
}
selector.select();
Set<SelectionKey> keys = selector.selectedKeys();
//獲取叠代器
Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = keys.iterator();
while (keyIterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next();
if (!key.isValid()) {
continue;
}
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
ServerSocketChannel sscTemp = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
//得到一個連接好的SocketChannel,並把它註冊到Selector上,興趣操作為READ
SocketChannel socketChannel = sscTemp.accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
System.out.println("REGISTER CHANNEL , CHANNEL NUMBER IS:" + selector.keys().size());
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
//讀取通道中的數據
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
read(channel);
}
keyIterator.remove(); //該事件已經處理,可以丟棄
}
}
}
private void read(SocketChannel channel) throws IOException {
int count ;
buffer.clear();
try {
while ((count = channel.read(buffer)) > 0) {
buffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[buffer.remaining()];
buffer.get(bytes);
System.out.println("READ FROM CLIENT:" + new String(bytes));
}
if (count < 0) {
channel.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}package com.nio.basic;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* nio 客戶端
* Created by sdc on 2017/8/13.
*/
public class NioClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
executorService.submit(new Client("nio-client-1"));
executorService.submit(new Client("nio-client-2"));
executorService.submit(new Client("nio-client-3"));
executorService.shutdown();
}
static class Client extends Thread {
private String clientThreadName;
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
Random random = new Random(20);
Client(String clientThreadName) {
this.clientThreadName = clientThreadName;
}
@Override
public void run() {
SocketChannel channel = null;
try {
channel = SocketChannel.open();
channel.configureBlocking(false);
channel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8000));
while (!channel.finishConnect()) {
TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(100);
}
for (int i=0; i<5; i++) {
TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(100 * random.nextInt());
String message = "send message " + i + " from" + clientThreadName;
buffer.put(message.getBytes());
buffer.flip();
//buffer先把數據讀入到buffer,然後channel先把buffer中的數據寫入到channel,
channel.write(buffer);
buffer.clear();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
channel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}本文出自 “不積跬步無以至千裏” 博客,請務必保留此出處http://shangdc.blog.51cto.com/10093778/1955874
java nio之 channel通道(二)
