數學建模--matlab基礎知識
雖然python也能做數據分析,不過參加數學建模,咱還是用專業的
1. Matlab-入門篇:Hello world!
程序員入門第一式:
disp(‘hello world!’)
2. 基本運算
先了解基本的運算符,做一些簡單的嘗試:
+ Plus; addition operator.
- Minus; subtraction operator.
* Scalar and matrix multiplication operator.
^ Scalar and matrix exponentiation operator.
/ Right-division operator.
: Colon; generates regularly spaced elements and represents an entire row or column.
[ ] Brackets; enclosures array elements.
… Ellipsis; line-continuation operator
; Semicolon; separates columns and suppresses display.
% Percent sign; designates a comment and specifies formatting.
+-*/都知道,^是冪運算
: 形成一個一個有規律間隔的序列:
1:2:10
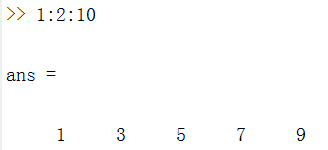
…連接長語句,一行寫不完,加…換到下一行寫

% 註釋
Command windows神器!!!:
doc 查找幫助文檔
dos
現在,command窗口搖身一變,變成啥了呢?

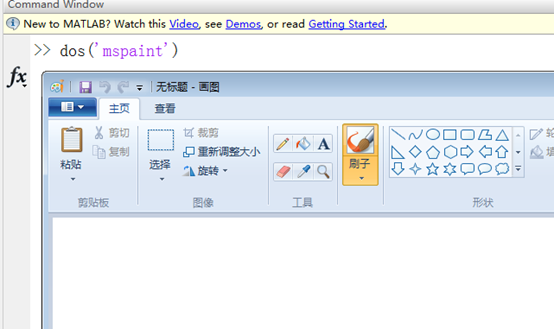
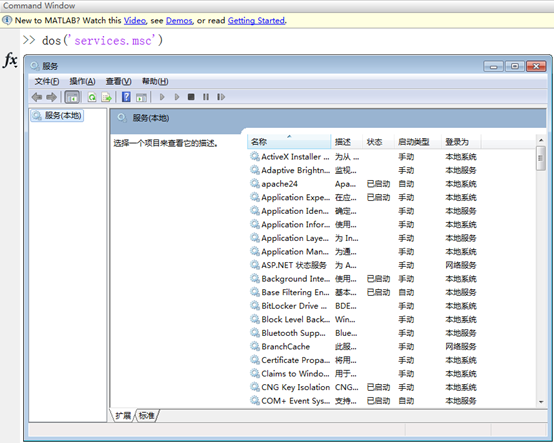
是的,dos()函數和win+r的運行窗口一樣一樣的!
命令:
|
命令 |
目的/作用 |
|
clc |
清除命令窗口。 |
|
clear |
從內存中刪除變量。 |
|
exist |
檢查存在的文件或變量。 |
|
global |
聲明變量為全局。 |
|
help |
搜索幫助主題。 |
|
lookfor |
搜索幫助關鍵字條目。 |
|
quit |
停止MATLAB。 |
|
who |
列出當前變量。(很好很強大,你值得擁有) |
|
whos |
列出當前變量(長顯示)。 |
clc,clear,who,whos,help,quit是不是很強大呢,誰用誰知道
who 命令顯示所有已經使用的變量名。
whos 命令顯示多一點有關變量:
當前內存中的變量
每個變量的類型
內存分配給每個變量
無論他們是復雜的變量與否
clear命令刪除所有(或指定)從內存中的變量(S)。
系統命令
MATLAB提供各種有用的命令與系統工作,在工作區中當前的工作,如保存為一個文件,並加載文件。
它還提供了其他系統相關的活動,如各種命令,顯示日期,列出目錄中的文件,顯示當前目錄等。
下表顯示了一些常用的系統相關的命令:
|
命令 |
目的/作用 |
|
cd |
改變當前目錄。 |
|
date |
顯示當前日期。 |
|
delete |
刪除一個文件。 |
|
diary |
日記文件記錄開/關切換。 |
|
dir |
列出當前目錄中的所有文件。 |
|
load |
負載工作區從一個文件中的變量。 |
|
path |
顯示搜索路徑。 |
|
pwd |
顯示當前目錄。 |
|
save |
保存在一個文件中的工作區變量。 |
|
type |
顯示一個文件的??內容。 |
|
what |
列出所有MATLAB文件在當前目錄中。 |
|
wklread |
讀取.wk1電子表格文件。 |
Command窗口可以直接使用cd,dir這些命令,是不是很爽呢(其實dos(‘dir’也是可以的)但是,dos(‘cd ..’)並不能更換matlab command的路徑)
Edit命令創建文件
3.常量及變量
常量:
ans Most recent answer.
eps Accuracy of floating-yiibai precision.
i,j The imaginary unit √-1.
Inf Infinity.(無窮大)
NaN Undefined numerical result (not a number).
pi The number π(在處理sin(pi / 2)的時候,就是sin90度)
變量
在MATLAB環境下,每一個變量是一個數組或矩陣。
在一個簡單的方法,您可以指定變量。例如,
x = 3 % defining x and initializing it with a value
MATLAB將執行上面的語句,並返回以下結果:
x =
3
它創建了一個1-1的矩陣名為x和的值存儲在其元素。讓我們查看另一個例子,
x = sqrt(16) % defining x and initializing it with an expression
MATLAB將執行上面的語句,並返回以下結果:
x =
4
請註意:
一旦一個變量被輸入到系統中,你可以引用它。
變量在使用它們之前,必須有值。
當表達式返回一個結果,不分配給任何變量,系統分配給一個變量命名ans,以後可以使用。
sqrt(78)
MATLAB將執行上面的語句,並返回以下結果:
ans =
8.8318
可以使用這個變量 ans:
9876/ans
MATLAB將執行上面的語句,並返回以下結果:
ans =
1.1182e+03
4.分支語句:
|
語句 |
描述 |
|
if ... end statement |
An if ... end statement consists of a boolean expression followed by one or more statements. |
|
if...else...end statement |
An if statement can be followed by an optional else statement, which executes when the boolean expression is false. |
|
If... elseif...elseif...else...end statements |
An if statement can be followed by an (or more) optional elseif...and an else statement, which is very useful to test various condition. |
|
nested if statements |
You can use one if or elseif statement inside another if or elseif statement(s). |
|
switch statement |
A switch statement allows a variable to be tested for equality against a list of values. |
|
nested switch statements |
You can use one swicth statement inside another switch statement(s). |
在MATLAB 中 switch 語句的語法是:
switch <switch_expression>
case <case_expression>
<statements>
case <case_expression>
<statements>
...
...
otherwise
<statements>
end
5.循環語句:
|
while 循環 |
一個給定的條件為真時重復語句或語句組。測試條件才執行循環體。 |
|
for 循環 |
執行的語句序列多次縮寫管理循環變量的代碼。 |
|
nested 循環 |
可以使用一個或多個環路內任何另一個循環。 |
|
控制語句 |
描述 |
|
break 語句 |
終止循環語句,將執行的語句緊隨循環。 |
|
continue 語句 |
導致循環,跳過它的身體的其余部分,並立即重新再次測試前的狀況。 |
在MATLAB 中 while循環的語法是:
while <expression>
<statements>
end
在MATLAB中的 for循環的語法是:
for index = values
<program statements>
...
end
6.數據類型
Matlab是弱數據類型,可直接復制,先找一個值,再給他賦一個變量名
MATLAB 提供15個基本數據類型。每種數據類型的數據存儲在矩陣或陣列的形式。這個矩陣的大小或陣列是一個最低 0-0,這可以長大為任何規模大小的矩陣或數組。
下表顯示了在 MATLAB 中最常用的數據類型:
數據類型 描述
int8 8-bit signed integer
uint8 8-bit unsigned integer
int16 16-bit signed integer
uint16 16-bit unsigned integer
int32 32-bit signed integer
uint32 32-bit unsigned integer
int64 64-bit signed integer
uint64 64-bit unsigned integer
single single precision numerical data
double double precision numerical data
logical logical values of 1 or 0, represent true and false respectively
char character data (strings are stored as vector of characters)
cell array array of indexed cells, each capable of storing an array of a different dimension and data type
structure C-like structures, each structure having named fields capable of storing an array of a different dimension and data type
function handle yiibaier to a function
下面這兩個說明我們可以調用自己定義的類和java文件
user classes objects constructed from a user-defined class
java classes objects constructed from a Java class
7.運算符
運算符是一個符號,它告訴編譯器執行特定的數學或邏輯操作。 MATLAB 設計工作主要是對整個矩陣和陣列。因此,運算符在 MATLAB 工作標和非標量數據。 MATLAB 允許以下類型的基本運算:
l 算術運算符
l 關系運算符
l 邏輯運算符
l 位運算
l 集合運算
算術運算符
MATLAB允許兩種不同類型的算術運算:
- 矩陣算術運算
- 陣列算術運算
|
運算符 |
描述 |
|
+ |
加法或一元加號。A + B將A和B。 A和B必須具有相同的尺寸,除非一個人是一個標量。一個標量,可以被添加到任何大小的矩陣。 |
|
- |
Subtraction or unary minus. A-B subtracts B from A. A and B must have the same size, unless one is a scalar. A scalar can be subtracted from a matrix of any size. |
|
* |
Matrix multiplication. C = A*B is the linear algebraic product of the matrices A and B. More precisely,
For nonscalar A and B, the number of columns of A must equal the number of rows of B. A scalar can multiply a matrix of any size. |
|
.* |
Array multiplication. A.*B is the element-by-element product of the arrays A and B. A and B must have the same size, unless one of them is a scalar. |
|
/ |
Slash or matrix right division. B/A is roughly the same as B*inv(A). More precisely, B/A = (A‘B‘)‘. |
|
./ |
Array right division. A./B is the matrix with elements A(i,j)/B(i,j). A and B must have the same size, unless one of them is a scalar. |
|
Backslash or matrix left division. If A is a square matrix, AB is roughly the same as inv(A)*B, except it is computed in a different way. If A is an n-by-n matrix and B is a column vector with n components, or a matrix with several such columns, then X = AB is the solution to the equation AX = B. A warning message is displayed if A is badly scaled or nearly singular. |
|
|
. |
Array left division. A.B is the matrix with elements B(i,j)/A(i,j). A and B must have the same size, unless one of them is a scalar. |
|
^ |
Matrix power. X^p is X to the power p, if p is a scalar. If p is an integer, the power is computed by repeated squaring. If the integer is negative, X is inverted first. For other values of p, the calculation involves eigenvalues and eigenvectors, such that if [V,D] = eig(X), then X^p = V*D.^p/V. |
|
.^ |
Array power. A.^B is the matrix with elements A(i,j) to the B(i,j) power. A and B must have the same size, unless one of them is a scalar. |
|
‘ |
Matrix transpose. A‘ is the linear algebraic transpose of A. For complex matrices, this is the complex conjugate transpose. |
|
.‘ |
Array transpose. A.‘ is the array transpose of A. For complex matrices, this does not involve conjugation. |
算術運算功能
除了在上述的算術運算符,MATLAB 用於類似的目的提供了以下的命令/功能:
|
函數 |
描述 |
|
uplus(a) |
Unary plus; increments by the amount a |
|
plus (a,b) |
Plus; returns a + b |
|
uminus(a) |
Unary minus; decrements by the amount a |
|
minus(a, b) |
Minus; returns a - b |
|
times(a, b) |
Array multiply; returns a.*b |
|
mtimes(a, b) |
Matrix multiplication; returns a* b |
|
rdivide(a, b) |
Right array division; returns a ./ b |
|
ldivide(a, b) |
Left array division; returns a. b |
|
mrdivide(A, B) |
Solve systems of linear equations xA = B for x |
|
mldivide(A, B) |
Solve systems of linear equations Ax = B for x |
|
power(a, b) |
Array power; returns a.^b |
|
mpower(a, b) |
Matrix power; returns a ^ b |
|
cumprod(A) |
Cumulative product; returns an array the same size as the array A containing the cumulative product.
|
|
cumprod(A, dim) |
Returns the cumulative product along dimension dim. |
|
cumsum(A) |
Cumulative sum; returns an array A containing the cumulative sum.
|
|
cumsum(A, dim) |
returns the cumulative sum of the elements along dimension dim. |
|
diff(X) |
Differences and approximate derivatives; calculates differences between adjacent elements of X.
|
|
diff(X,n) |
Applies diff recursively n times, resulting in the nth difference. |
|
diff(X,n,dim) |
It is the nth difference function calculated along the dimension specified by scalar dim. If order n equals or exceeds the length of dimension dim, diff returns an empty array. |
|
prod(A) |
Product of array elements; returns the product of the array elements of A.
The prod function computes and returns B as single if the input, A, is single. For all other numeric and logical data types, prod computes and returns B as double |
|
prod(A,dim) |
Returns the products along dimension dim. For example, if A is a matrix, prod(A,2) is a column vector containing the products of each row. |
|
prod(___,datatype) |
multiplies in and returns an array in the class specified by datatype. |
|
sum(A) |
|
|
sum(A,dim) |
Sums along the dimension of A specified by scalar dim. |
|
sum(..., ‘double‘) sum(..., dim,‘double‘) |
Perform additions in double-precision and return an answer of type double, even if A has data type single or an integer data type. This is the default for integer data types. |
|
sum(..., ‘native‘) sum(..., dim,‘native‘) |
Perform additions in the native data type of A and return an answer of the same data type. This is the default for single and double. |
|
ceil(A) |
Round toward positive infinity; rounds the elements of A to the nearest integers greater than or equal to A. |
|
fix(A) |
Round toward zero |
|
floor(A) |
Round toward negative infinity; rounds the elements of A to the nearest integers less than or equal to A. |
|
idivide(a, b) idivide(a, b,‘fix‘) |
Integer division with rounding option; is the same as a./b except that fractional quotients are rounded toward zero to the nearest integers. |
|
idivide(a, b, ‘round‘) |
Fractional quotients are rounded to the nearest integers. |
|
idivide(A, B, ‘floor‘) |
Fractional quotients are rounded toward negative infinity to the nearest integers. |
|
idivide(A, B, ‘ceil‘) |
Fractional quotients are rounded toward infinity to the nearest integers. |
|
mod (X,Y) |
Modulus after division; returns X - n.*Y where n = floor(X./Y). If Y is not an integer and the quotient X./Y is within roundoff error of an integer, then n is that integer. The inputs X and Y must be real arrays of the same size, or real scalars (provided Y ~=0). Please note:
|
|
rem (X,Y) |
Remainder after division; returns X - n.*Y where n = fix(X./Y). If Y is not an integer and the quotient X./Y is within roundoff error of an integer, then n is that integer. The inputs X and Y must be real arrays of the same size, or real scalars(provided Y ~=0). Please note that:
|
|
round(X) |
Round to nearest integer; rounds the elements of X to the nearest integers. Positive elements with a fractional part of 0.5 round up to the nearest positive integer. Negative elements with a fractional part of -0.5 round down to the nearest negative integer. |
關系運算符
關系運算符標和非標量數據上也能正常工作。關系運算符對數組進行元素元素元素設置為邏輯1(真)的關系是真實的和元素設置為邏輯0(假),它是兩個陣列,並返回一個同樣大小的邏輯陣列之間的比較。
|
函數 |
描述 |
|
eq(a, b) |
Tests whether a is equal to b |
|
ge(a, b) |
Tests whether a is greater than or equal to b |
|
gt(a, b) |
Tests whether a is greater than b |
|
le(a, b) |
Tests whether a is less than or equal to b |
|
lt(a, b) |
Tests whether a is less than b |
|
ne(a, b) |
Tests whether a is not equal to b |
|
isequal |
Tests arrays for equality |
|
isequaln |
Tests arrays for equality, treating NaN values as equal |
下表顯示了 MATLAB 中的關系運算符:
|
運算符 |
描述 |
|
< |
Less than |
|
<= |
Less than or equal to |
|
> |
Greater than |
|
>= |
Greater than or equal to |
|
== |
Equal to |
|
~= |
Not equal to |
邏輯運算符
MATLAB提供了兩種類型的邏輯運算符和函數:
- Element-wise -這些運算符的邏輯陣列上運行相應的元素。
- Short-circuit -這些運算上的標量,邏輯表達式。
Element-wise 的邏輯運算符操作元素元素邏輯陣列。符號&,|和?邏輯數組運算符AND,OR,NOT。
允許短路短路邏輯運算符,邏輯運算。符號 && 和 | | 是短路邏輯符 AND 和 OR。
除了在上述的邏輯運算符,MATLAB 提供下面的命令或函數用於同樣的目的:
|
函數 |
描述 |
|
and(A, B) |
Finds logical AND of array or scalar inputs; performs a logical AND of all input arrays A, B, etc. and returns an array containing elements set to either logical 1 (true) or logical 0 (false). An element of the output array is set to 1 if all input arrays contain a nonzero element at that same array location. Otherwise, that element is set to 0. |
|
not(A) |
Finds logical NOT of array or scalar input; performs a logical NOT of input array A and returns an array containing elements set to either logical 1 (true) or logical 0 (false). An element of the output array is set to 1 if the input array contains a zero value element at that same array location. Otherwise, that element is set to 0. |
|
or(A, B) |
Finds logical OR of array or scalar inputs; performs a logical OR of all input arrays A, B, etc. and returns an array containing elements set to either logical 1 (true) or logical 0 (false). An element of the output array is set to 1 if any input arrays contain a nonzero element at that same array location. Otherwise, that element is set to 0. |
|
xor(A, B) |
Logical exclusive-OR; performs an exclusive OR operation on the corresponding elements of arrays A and B. The resulting element C(i,j,...) is logical true (1) if A(i,j,...) or B(i,j,...), but not both, is nonzero. |
|
all(A) |
Determine if all array elements of array A are nonzero or true.
|
|
all(A, dim) |
Tests along the dimension of A specified by scalar dim. |
|
any(A) |
Determine if any array elements are nonzero; tests whether any of the elements along various dimensions of an array is a nonzero number or is logical 1 (true). The any function ignores entries that are NaN (Not a Number).
|
|
any(A,dim) |
Tests along the dimension of A specified by scalar dim. |
|
false |
Logical 0 (false) |
|
false(n) |
is an n-by-n matrix of logical zeros |
|
false(m, n) |
is an m-by-n matrix of logical zeros. |
|
false(m, n, p, ...) |
is an m-by-n-by-p-by-... array of logical zeros. |
|
false(size(A)) |
is an array of logical zeros that is the same size as array A. |
|
false(...,‘like‘,p) |
is an array of logical zeros of the same data type and sparsity as the logical array p. |
|
ind = find(X) |
Find indices and values of nonzero elements; locates all nonzero elements of array X, and returns the linear indices of those elements in a vector. If X is a row vector, then the returned vector is a row vector; otherwise, it returns a column vector. If X contains no nonzero elements or is an empty array, then an empty array is returned. |
|
ind = find(X, k) ind = find(X, k, ‘first‘) |
Returns at most the first k indices corresponding to the nonzero entries of X. k must be a positive integer, but it can be of any numeric data type. |
|
ind = find(X, k, ‘last‘) |
returns at most the last k indices corresponding to the nonzero entries of X. |
|
[row,col] = find(X, ...) |
Returns the row and column indices of the nonzero entries in the matrix X. This syntax is especially useful when working with sparse matrices. If X is an N-dimensional array with N > 2, col contains linear indices for the columns. |
|
[row,col,v] = find(X, ...) |
Returns a column or row vector v of the nonzero entries in X, as well as row and column indices. If X is a logical expression, then v is a logical array. Output v contains the non-zero elements of the logical array obtained by evaluating the expression X. |
|
islogical(A) |
Determine if input is logical array; returns true if A is a logical array and false otherwise. It also returns true if A is an instance of a class that is derived from the logical class. |
|
logical(A) |
Convert numeric values to logical; returns an array that can be used for logical indexing or logical tests. |
|
true |
Logical 1 (true) |
|
true(n) |
is an n-by-n matrix of logical ones. |
|
true(m, n) |
is an m-by-n matrix of logical ones. |
|
true(m, n, p, ...) |
is an m-by-n-by-p-by-... array of logical ones. |
|
true(size(A)) |
is an array of logical ones that is the same size as array A. |
|
true(...,‘like‘, p) |
is an array of logical ones of the same data type and sparsity as the logical array p. |
位運算
位運算符位和執行位位操作。 &,|和^的真值表如下:
|
p |
q |
p & q |
p | q |
p ^ q |
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
|
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
|
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
假設如果A= 60,B =13,他們現在以二進制格式將如下:
A = 0011 1100
B = 0000 1101
-----------------
A&B = 0000 1100
A|B = 0011 1101
A^B = 0011 0001
~A = 1100 0011
MATLAB提供位運算,如‘位‘,‘位‘和‘位不操作,移位操作等各種函數
以下的表格顯示了常用的按位運算:
|
函數 |
目的/作用 |
|
bitand(a, b) |
Bit-wise AND of integers a and b |
|
bitcmp(a) |
Bit-wise complement of a |
|
bitget(a,pos) |
Get bit at specified position pos, in the integer array a |
|
bitor(a, b) |
Bit-wise OR of integers a and b |
|
bitset(a, pos) |
Set bit at specific location pos of a |
|
bitshift(a, k) |
Returns a shifted to the left by k bits, equivalent to multiplying by 2k. Negative values of k correspond to shifting bits right or dividing by 2|k| and rounding to the nearest integer towards negative infinite. Any overflow bits are truncated. |
|
bitxor(a, b) |
Bit-wise XOR of integers a and b |
|
swapbytes |
Swap byte ordering |
MATLAB提供各種功能集合運算,如集,交集和測試組成員等。
下表顯示了一些常用的設置操作:
|
函數 |
描述 |
|
intersect(A,B) |
Set intersection of two arrays; returns the values common to both A and B. The values returned are in sorted order. |
|
intersect(A,B,‘rows‘) |
Treats each row of A and each row of B as single entities and returns the rows common to both A and B. The rows of the returned matrix are in sorted order. |
|
ismember(A,B) |
Returns an array the same size as A, containing 1 (true) where the elements of A are found in B. Elsewhere, it returns 0 (false). |
|
ismember(A,B,‘rows‘) |
Treats each row of A and each row of B as single entities and returns a vector containing 1 (true) where the rows of matrix A are also rows of B. Elsewhere, it returns 0 (false). |
|
issorted(A) |
Returns logical 1 (true) if the elements of A are in sorted order and logical 0 (false) otherwise. Input A can be a vector or an N-by-1 or 1-by-N cell array of strings. A is considered to be sorted if A and the output of sort(A) are equal. |
|
issorted(A, ‘rows‘) |
Returns logical 1 (true) if the rows of two-dimensional matrix A are in sorted order, and logical 0 (false) otherwise. Matrix A is considered to be sorted if A and the output of sortrows(A) are equal. |
|
setdiff(A,B) |
Set difference of two arrays; returns the values in A that are not in B. The values in the returned array are in sorted order. |
|
setdiff(A,B,‘rows‘) |
Treats each row of A and each row of B as single entities and returns the rows from A that are not in B. The rows of the returned matrix are in sorted order. The ‘rows‘ option does not support cell arrays. |
|
setxor |
Set exclusive OR of two arrays |
|
union |
Set union of two arrays |
|
unique |
Unique values in array |
集合運算:
|
函數 |
描述 |
|
intersect(A,B) |
Set intersection of two arrays; returns the values common to both A and B. The values returned are in sorted order. |
|
intersect(A,B,‘rows‘) |
Treats each row of A and each row of B as single entities and returns the rows common to both A and B. The rows of the returned matrix are in sorted order. |
|
ismember(A,B) |
Returns an array the same size as A, containing 1 (true) where the elements of A are found in B. Elsewhere, it returns 0 (false). |
|
ismember(A,B,‘rows‘) |
Treats each row of A and each row of B as single entities and returns a vector containing 1 (true) where the rows of matrix A are also rows of B. Elsewhere, it returns 0 (false). |
|
issorted(A) |
Returns logical 1 (true) if the elements of A are in sorted order, and logical 0 (false) otherwise. Input A can be a vector or an N-by-1 or 1-by-N cell array of strings. A is considered to be sorted if A and the output of sort(A) are equal. |
|
issorted(A, ‘rows‘) |
Returns logical 1 (true) if the rows of two-dimensional matrix A are in sorted order, and logical 0 (false) otherwise. Matrix A is considered to be sorted if A and the output of sortrows(A) are equal. |
|
setdiff(A,B) |
Set difference of two arrays; returns the values in A that are not in B. The values in the returned array are in sorted order. |
|
setdiff(A,B,‘rows‘) |
Treats each row of A and each row of B as single entities and returns the rows from A that are not in B. The rows of the returned matrix are in sorted order. The ‘rows‘ option does not support cell arrays. |
|
setxor |
Set exclusive OR of two arrays |
|
union |
Set union of two arrays |
|
unique |
Unique values in array |
格式命令
默認情況下,MATLAB 四個小數位值顯示數字。這就是所謂的 short format.
format long e(科學計數法顯示結果)
但是,如果想更精確,需要使用 format 命令。
長(long ) 命令格式顯示小數點後16位。
format long 16
short 4
bank 2
format rat 格式大鼠命令給出最接近的有理表達式,從計算所得。例如,
format rat
4.678 * 4.9
MATLAB將執行上面的語句,並返回以下結果:
ans =
2063/90
輸入和輸出命令
MATLAB提供了以下輸入和輸出相關的命令:
|
命令 |
作用/目的 |
|
disp |
顯示一個數組或字符串的內容。 |
|
fscanf |
閱讀從文件格式的數據。 |
|
format |
控制屏幕顯示的格式。 |
|
fprintf |
執行格式化寫入到屏幕或文件。 |
|
input |
顯示提示並等待輸入。 |
|
; |
禁止顯示網版印刷 |
fscanf和fprintf命令的行為像C scanf和printf函數。他們支持格式如下代碼:
|
格式代碼 |
目的/作用 |
|
%s |
Format as a string. |
|
%d |
Format as an integer. |
|
%f |
Format as a floating yiibai value. |
|
%e |
Format as a floating yiibai value in scientific notation. |
|
%g |
Format in the most compact form: %f or %e. |
|
Insert a new line in the output string. |
|
|
Insert a tab in the output string. |
用於數字顯示格式的函數有以下幾種形式:
|
Format函數 |
最多可顯示 |
|
format short |
Four decimal digits (default). |
|
format long |
16 decimal digits. |
|
format short e |
Five digits plus exponent. |
|
format long e |
16 digits plus exponents. |
|
format bank |
Two decimal digits. |
|
format + |
Positive, negative, or zero. |
|
format rat |
Rational approximation. |
|
format compact |
Suppresses some line feeds. |
|
format loose |
Resets to less compact display mode. |
向量,矩陣和陣列命令
下表列出了各種命令用於工作數組,矩陣和向量:
|
命令 |
作用/目的 |
|
cat |
Concatenates arrays.連接數組 |
|
find |
Finds indices of nonzero elements. |
|
length |
Computes number of elements. |
|
linspace |
Creates regularly spaced vector. |
|
logspace |
Creates logarithmically spaced vector. |
|
max |
Returns largest element. |
|
min |
Returns smallest element. |
|
prod |
Product of each column. |
|
reshape |
Changes size. |
|
size |
Computes array size. |
|
sort |
Sorts each column. |
|
sum |
Sums each column. |
|
eye |
Creates an identity matrix. 創建單位矩陣 |
|
ones |
Creates an array of ones. 創建一個1的數組 |
|
zeros |
Creates an array of zeros. 創建一個0數組 |
|
cross |
Computes matrix cross products.計算矩陣交叉積 |
|
dot |
Computes matrix dot products. 點積 |
|
det |
Computes determinant of an array.計算行列式 |
|
inv |
Computes inverse of a matrix.計算行列式的逆 |
|
pinv |
Computes pseudoinverse of a matrix.計算行列式的違逆 |
|
rank |
Computes rank of a matrix.計算行列式的秩 |
|
rref |
Computes reduced row echelon form. |
|
cell |
Creates cell array. |
|
celldisp |
Displays cell array. |
|
cellplot |
Displays graphical representation of cell array. |
|
num2cell |
Converts numeric array to cell array. |
|
deal |
Matches input and output lists. |
|
iscell |
Identifies cell array. |
MATLAB提供了大量的命令,繪制圖表。下表列出了一些常用的命令繪制:
|
命令 |
作用/目的 |
|
axis |
Sets axis limits. |
|
fplot |
Intelligent plotting of functions. |
|
grid |
Displays gridlines. |
|
plot |
Generates xy plot. |
|
|
Prints plot or saves plot to a file. |
|
title |
Puts text at top of plot. |
|
xlabel |
Adds text label to x-axis. |
|
ylabel |
Adds text label to y-axis. |
|
axes |
Creates axes objects. |
|
close |
Closes the current plot. |
|
close all |
Closes all plots. |
|
figure |
Opens a new figure window. |
|
gtext |
Enables label placement by mouse. |
|
hold |
Freezes current plot. |
|
legend |
Legend placement by mouse. |
|
refresh |
Redraws current figure window. |
|
set |
Specifies properties of objects such as axes. |
|
subplot |
Creates plots in subwindows. |
|
text |
Places string in figure. |
|
bar |
Creates bar chart. |
|
loglog |
Creates log-log plot. |
|
polar |
Creates polar plot. |
|
semilogx |
Creates semilog plot. (logarithmic abscissa). |
|
semilogy |
Creates semilog plot. (logarithmic ordinate). |
|
stairs |
Creates stairs plot. |
|
stem |
Creates stem plot. |
數學建模--matlab基礎知識
