洛谷 P3576 [POI2014]MRO-Ant colony
P3576 [POI2014]MRO-Ant colony
題目描述
The ants are scavenging an abandoned ant hill in search of food.
The ant hill has nn chambers and n-1n−1 corridors connecting them.
We know that each chamber can be reached via a unique path from every other chamber.
In other words, the chambers and the corridors form a tree.
There is an entrance to the ant hill in every chamber with only one corridor leading into (or out of) it.
At each entry, there are gg groups of m_1,m_2,\cdots,m_gm?1??,m?2??,?,m?g?? ants respectively.
These groups will enter the ant hill one after another, each successive group entering once there are no ants inside.
Inside the hill, the ants explore it in the following way:
-
Upon entering a chamber with dd outgoing corridors yet unexplored by the group,the group divides into dd groups of equal size. Each newly created group follows one of the d corridors.If d=0d=0, then the group exits the ant hill.
- If the ants cannot divide into equal groups, then the stronger ants eat the weaker until a perfect division is possible.Note that such a division is always possible since eventually the number of ants drops down to zero.Nothing can stop the ants from allowing divisibility - in particular, an ant can eat itself, and the last one remaining will do so if the group is smaller than dd.
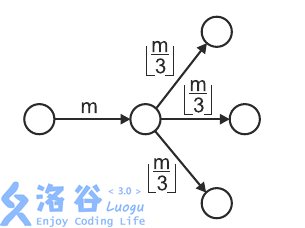
The following figure depicts mm ants upon entering a chamber with three outgoing unexplored corridors, dividing themselves into three (equal) groups of \left \lfloor m/3 \right \rfloor⌊m/3⌋ ants each.
A hungry anteater dug into one of the corridors and can now eat all the ants passing through it.
However, just like the ants, the anteater is very picky when it comes to numbers.
It will devour a passing group if and only if it consists of exactly kk ants.
We want to know how many ants the anteater will eat.
給一棵樹,對於每個葉子節點,都有g群螞蟻要從外面進來,每群螞蟻在行進過程中只要碰到岔路,就將平均地分成岔路口數-1那麽多份,然後平均地走向剩下的那些岔路口,余下的螞蟻自動消失,樹上有一個關鍵邊,假如有一群螞蟻通過了這條邊且數量恰好為k,這k只螞蟻就被吃掉,問一共有多少只螞蟻被吃掉
輸入輸出格式
輸入格式:
The first line of the standard input contains three integers nn, gg, kk(2\le n,g\le 1\ 000\ 0002≤n,g≤1 000 000, 1\le k\le 10^91≤k≤10?9??), separated by single spaces.
These specify the number of chambers, the number of ant groups and the number of ants the anteater devours at once. The chambers are numbered from 1 to nn.
The second line contains gg integers m_1,m_2,\cdots,m_gm?1??,m?2??,?,m?g?? (1\le m_i\le 10^91≤m?i??≤10?9??), separated by single spaces, where m_im?i?? gives the number of ants in the ii-th group at every entrance to the ant hill. The n-1n−1 lines that follow describe the corridors within the ant hill;the ii-th such line contains two integers a_ia?i??,b_ib?i?? (1\le a_i,b_i\le n1≤a?i??,b?i??≤n), separated by a single space, that indicate that the chambers no. a_ia?i?? and b_ib?i?? are linked by a corridor. The anteater has dug into the corridor that appears first on input.
輸出格式:
Your program should print to the standard output a single line containing a single integer: the number of ants eaten by the anteater.
輸入輸出樣例
輸入樣例#1:7 5 3
3 4 1 9 11
1 2
1 4
4 3
4 5
4 6
6 7
輸出樣例#1:21
說明
給一棵樹,對於每個葉子節點,都有g群螞蟻要從外面進來,每群螞蟻在行進過程中只要碰到岔路,就將平均地分成岔路口數-1那麽多份,然後平均地走向剩下的那些岔路口,余下的螞蟻自動消失,樹上有一個關鍵邊,假如有一群螞蟻通過了這條邊且數量恰好為k,這k只螞蟻就被吃掉,問一共有多少只螞蟻被吃掉
題意:
題目描述:
給定一棵有n個節點的樹。在每個葉子節點,有g群螞蟻要從外面進來,其中第i群有m[i]只螞蟻。這些螞蟻會相繼進入樹中,而且要保證每一時刻每個節點最多只有一群螞蟻。這些螞蟻會按以下方式前進: ·在即將離開某個度數為d+1的點時,該群螞蟻有d個方向還沒有走過,這群螞蟻就會分裂成d群,每群數量都相等。如果d=0,那麽螞蟻會離開這棵樹。 ·如果螞蟻不能等分,那麽螞蟻之間會互相吞噬,直到可以等分為止,即一群螞蟻有m只,要分成d組,每組將會有floor(m/d)只,如下圖。 一只饑餓的食蟻獸埋伏在一條邊上,如果有一群螞蟻通過這條邊,並且數量恰為k只,它就會吞掉這群螞蟻。請計算一共有多少只螞蟻會被吞掉。
輸入描述:
第一行包含三個整數n,g,k,表示點數、螞蟻群數以及k。
第二行包含g個整數m[1],m[2],...,m[g],表示每群螞蟻中螞蟻的數量。
接下來n-1行每行兩個整數,表示一條邊,食蟻獸埋伏在輸入的第一條邊上。
思路:
這個題從葉子節點去算的話顯然很困難,所以我們可以從食蟻獸所在的兩個點開始倒著搞。
minn和maxn記錄每個節點最多和最少有多少個螞蟻才能讓食蟻獸恰好吃到k只。然後,分別以這兩個點為根節點,dfs一下求出所有的minn和maxn。
接著,二分答案,求一下對於每個節點,g群螞蟻中符合條件的螞蟻的群數。
最後,群數*k即為所求。
一只饑餓的食蟻獸埋伏在一條邊上,如果有一群螞蟻通過這條邊,並且數量恰為k只,它就會吞掉這群螞蟻。請計算一共有多少只螞蟻會被吞掉。
輸入描述:
第一行包含三個整數n,g,k,表示點數、螞蟻群數以及k。
第二行包含g個整數m[1],m[2],...,m[g],表示每群螞蟻中螞蟻的數量。
接下來n-1行每行兩個整數,表示一條邊,食蟻獸埋伏在輸入的第一條邊上。
思路:
這個題從葉子節點去算的話顯然很困難,所以我們可以從食蟻獸所在的兩個點開始倒著搞。
minn和maxn記錄每個節點最多和最少有多少個螞蟻才能讓食蟻獸恰好吃到k只。然後,分別以這兩個點為根節點,dfs一下求出所有的minn和maxn。
接著,二分答案,求一下對於每個節點,g群螞蟻中符合條件的螞蟻的群數。
最後,群數*k即為所求。
#include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #define MAXN 1000001 using namespace std; int n,g,K; int s,t,tot; long long ans; int outo[MAXN],dad[MAXN]; int to[MAXN],net[MAXN],head[MAXN]; long long m[MAXN],minn[MAXN],maxn[MAXN]; void add(int u,int v){ to[++tot]=v;net[tot]=head[u];head[u]=tot; to[++tot]=u;net[tot]=head[v];head[v]=tot; } void dfs(int now){ for(int i=head[now];i;i=net[i]) if(dad[now]!=to[i]){ dad[to[i]]=now; outo[now]++; } for(int i=head[now];i;i=net[i]) if(dad[now]!=to[i]){ minn[to[i]]=minn[now]*outo[now]; maxn[to[i]]=(maxn[now]+1)*outo[now]-1; maxn[to[i]]=min(maxn[to[i]],m[g]); if(minn[to[i]]<=m[g]) dfs(to[i]); } } long long cal(long long x){ int l=1,r=g,bns=0; while(l<=r){ int mid=(l+r)/2; if(m[mid]<x){ bns=max(bns,mid); l=mid+1; } else r=mid-1; } return bns; } int main(){ scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&g,&K); for(int i=1;i<=g;i++) scanf("%d",&m[i]); sort(m+1,m+1+g); scanf("%d%d",&s,&t); for(int i=2;i<n;i++){ int x,y; scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); add(x,y); } minn[s]=maxn[s]=minn[t]=maxn[t]=K; dfs(s); dfs(t); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) if(!outo[i]) ans+=cal(maxn[i]+1)-cal(minn[i]); cout<<ans*K; }
洛谷 P3576 [POI2014]MRO-Ant colony
