關於HashMap的一些研究
關於擴容,在resize()方法中,一般是擴容一倍 newCap = oldCap << 1. 擴容的同時,若原table中存在元素,則需要將原table中的元素進行重新計算哈希桶位置.
在設置初始值的時候,需要將容器大小設置為最接近2次冪的值,例如new HashMap<>(5);則初始容器大小為8.源碼為:
1 //Returns a power of two size for the given target capacity. 2 static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) { 3 int n = cap - 1;4 n |= n >>> 1; 5 n |= n >>> 2; 6 n |= n >>> 4; 7 n |= n >>> 8; 8 n |= n >>> 16; 9 return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1; 10 }
為什麽HashMap的容量一定要設置為2次冪呢? 方便put和get. 一般獲取位置使用取余運算%,h % length即可得到哈希值所在的位置,而HashMap中由於容量為2次冪,它使用的是
h & (length - 1),取余運算m % n可以等效於m - m / n * n,位運算比取余運算快了不少.在jdk1.7中,存在方法indexFor用於計算哈希值的位置
1 /** 2 * Returns index for hash code h. 3 */ 4 static int indexFor(int h, int length) { 5 // assert Integer.bitCount(length) == 1 : "length must be a non-zero power of 2"; 6 return h & (length-1);7 }
而在jdk1.8中,該方法已經不存在了,直接使用在各個方法中,例如 putVal中 p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]
關於哈希沖突,由於 h & (n - 1) 會得到同一個位置的值,就會造成沖突.當沖突小時,HashMap會將該桶轉換成一個鏈表,每個桶的元素為:
1 static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { 2 final int hash; 3 final K key; 4 V value; 5 Node<K,V> next; 6 //省略其他代碼 7 }
可以看出當next沒值時,就沒有哈希沖突,當next有值時,該桶即為一個鏈表結構.當沖突高於某個界限(這個界限為TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8)時,該桶將轉變為一顆紅黑樹. 為什麽要轉換成紅黑樹呢? 當存在哈希沖突時,對鏈表的查找復雜度為 O(N),是線性的,當沖突較大時,查找會較慢,此時轉換成紅黑樹,紅黑樹的查找復雜度為O(logN),比鏈表快.源代碼如下:
1 //是否沖突,不沖突直接插入到該桶 2 if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) 3 tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); 4 else { 5 //存在沖突 6 Node<K,V> e; K k; 7 if (p.hash == hash && 8 ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 9 e = p; //key的hash相等以及值也相等,則覆蓋 10 else if (p instanceof TreeNode) 11 e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); //已經是顆紅黑樹,則往樹裏插入元素 12 else { //鏈表 13 for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { 14 if ((e = p.next) == null) { 15 //將桶轉變成鏈表 16 p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); 17 if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st 18 //大於界限,轉換成紅黑樹 19 treeifyBin(tab, hash); 20 break; 21 } 22 if (e.hash == hash && 23 ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 24 break; 25 p = e; 26 } 27 } 28 if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key 29 V oldValue = e.value; 30 if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) 31 e.value = value; 32 afterNodeAccess(e); 33 return oldValue; 34 } 35 }
哈希沖突時很常見的
當存在不規範的代碼,即對象hashcode相等當時equals不相等時,該對象當key必存在沖突.
1 Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>(); 2 map.put("a","a"); 3 map.put("b","a"); 4 map.put("c","a"); 5 map.put("d","a"); 6 map.put("e","a"); 7 map.put("f","a"); 8 map.put("g","a"); 9 map.put("r","a"); 10 map.put("s","a"); 11 map.put("t","a"); 12 map.put("w","a"); 13 map.put("x","a"); 14 map.put("y","a"); 15 map.put("z","a");
在上面這段代碼中,跟蹤程序,當執行到14行時,由於存在了13個元素,大於16*0.75,此時擴容,跟蹤HashMap中的table
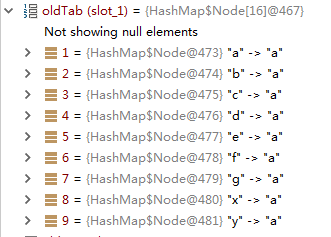
擴容後重新計算元素的哈希桶位置後
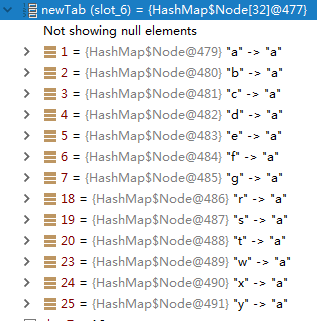
原先為9個桶13個元素,重新計算後得到13個桶13個元素,可以判斷出此時已經存在哈希沖突. 進一步跟蹤,可以得到沖突的桶:
b -> a.next = r -> a c -> a.next = s -> a d -> a.next = t -> a g -> a.next = w -> a
關於HashMap的一些研究
