160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists【easy】
阿新 • • 發佈:2017-10-14
win ogr 斷開 notes .com nod slow res original
160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists【easy】
Write a program to find the node at which the intersection of two singly linked lists begins.
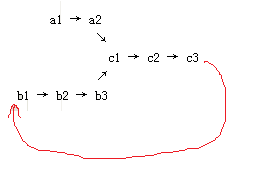
For example, the following two linked lists:
A: a1 → a2
↘
c1 → c2 → c3
↗
B: b1 → b2 → b3
begin to intersect at node c1.
Notes:
- If the two linked lists have no intersection at all, return
null. - The linked lists must retain their original structure after the function returns.
- You may assume there are no cycles anywhere in the entire linked structure.
- Your code should preferably run in O(n) time and use only O(1) memory.
解法一:
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 /** 4 * @param headA: the first list 5 * @param headB: the second list 6 * @return: a ListNode 7 */ 8 ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) { 9 // write your code here 10 if(headA == NULL || headB == NULL) 11 return NULL; 12 ListNode* iter1 = headA; 13 ListNode* iter2 = headB; 14 int len1 = 1; 15 while(iter1->next != NULL) 16 { 17 iter1 = iter1->next; 18 len1 ++; 19 } 20 int len2 = 1; 21 while(iter2->next != NULL) 22 { 23 iter2 = iter2->next; 24 len2 ++; 25 } 26 if(iter1 != iter2) 27 return NULL; 28 if(len1 > len2) 29 { 30 for(int i = 0; i < len1-len2; i ++) 31 headA = headA->next; 32 } 33 else if(len2 > len1) 34 { 35 for(int i = 0; i < len2-len1; i ++) 36 headB = headB->next; 37 } 38 while(headA != headB) 39 { 40 headA = headA->next; 41 headB = headB->next; 42 } 43 return headA; 44 } 45 };
先算長度,然後長的先走差值步,然後同時走
解法二:
1 public class Solution { 2 /** 3 * @param headA: the first list 4 * @param headB: the second list 5 * @return: a ListNode 6 */ 7 public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { 8 if (headA == null || headB == null) { 9 return null; 10 } 11 12 // get the tail of list A. 13 ListNode node = headA; 14 while (node.next != null) { 15 node = node.next; 16 } 17 node.next = headB; 18 ListNode result = listCycleII(headA); 19 node.next = null; 20 return result; 21 } 22 23 private ListNode listCycleII(ListNode head) { 24 ListNode slow = head, fast = head.next; 25 26 while (slow != fast) { 27 if (fast == null || fast.next == null) { 28 return null; 29 } 30 31 slow = slow.next; 32 fast = fast.next.next; 33 } 34 35 slow = head; 36 fast = fast.next; 37 while (slow != fast) { 38 slow = slow.next; 39 fast = fast.next; 40 } 41 42 return slow; 43 } 44 }
先弄成環,轉換為找環的入口問題,找到之後再斷開環
找環的問題解法可以參見(142. Linked List Cycle II【easy】)
160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists【easy】
