【python3】leetcode 160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists(easy)
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-09
160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists(easy)
Write a program to find the node at which the intersection of two singly linked lists begins.
For example, the following two linked lists:
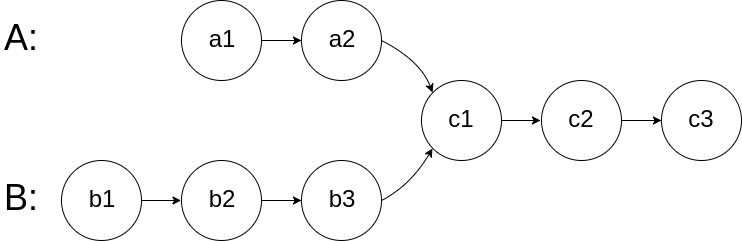
begin to intersect at node c1.
Example 1:
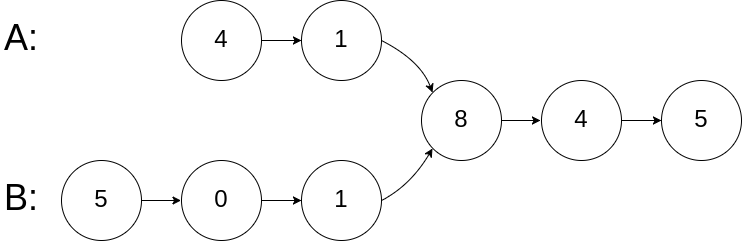 Input: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3 Output:Reference of the node with value = 8 Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 8 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [4,1,8,4,5]. From the head of B, it reads as [5,0,1,8,4,5]. There are 2 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in B.
Input: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3 Output:Reference of the node with value = 8 Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 8 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [4,1,8,4,5]. From the head of B, it reads as [5,0,1,8,4,5]. There are 2 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in B.
Example 2:
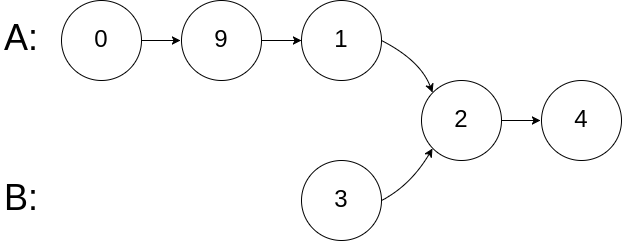 Input: intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1 Output: Reference of the node with value = 2 Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 2 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [0,9,1,2,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [3,2,4]. There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 1 node before the intersected node in B.
Input: intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1 Output: Reference of the node with value = 2 Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 2 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [0,9,1,2,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [3,2,4]. There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 1 node before the intersected node in B.
Example 3:
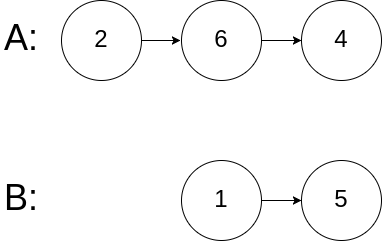 Input: intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2 Output: null Input Explanation: From the head of A, it reads as [2,6,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [1,5]. Since the two lists do not intersect, intersectVal must be 0, while skipA and skipB can be arbitrary values. Explanation: The two lists do not intersect, so return null.
Input: intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2 Output: null Input Explanation: From the head of A, it reads as [2,6,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [1,5]. Since the two lists do not intersect, intersectVal must be 0, while skipA and skipB can be arbitrary values. Explanation: The two lists do not intersect, so return null.
Notes:
- If the two linked lists have no intersection at all, return
null.- The linked lists must retain their original structure after the function returns.
- You may assume there are no cycles anywhere in the entire linked structure.
- Your code should preferably run in O(n) time and use only O(1) memory.
1 O(n) memory ,O(n) time
使用list儲存並遍歷,非常慢
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution(object):
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA, headB):
"""
:type head1, head1: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
n1 ,n2 = 0,0
h1,h2 = headA,headB
list1 = [];list2 = []
while(h1):
n1 += 1
list1.append(h1)
h1 = h1.next
while(h2):
n2 += 1
list2.append(h2)
h2 = h2.next
for node in list1:
if node in list2:return node2 O(1)memory O(n)time,從後面長度相同的地方開始遍歷判斷
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution(object):
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA, headB):
"""
:type head1, head1: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
h1,h2 = headA,headB
n1 ,n2 = 0,0
while(h1):
n1 += 1
h1 = h1.next
while(h2):
n2 += 1
h2 = h2.next
n = min(n1,n2)
h1,h2 = headA,headB
if n1 > n2:
for i in range((n1 - n2)):
h1 = h1.next
elif n2 > n1:
for i in range((n2 - n1)):
h2 = h2.next
while(h1 != None and h2 != None):
if h1 == h2 :return h1
h1 = h1.next
h2 = h2.next
