Android總結篇——Intent機制詳解及示例總結
一.Intent介紹:
Intent的中文意思是“意圖,意向”,在Android中提供了Intent機制來協助應用間的交互與通訊,Intent負責對應用中一次操作的動 作、動作涉及數據、附加數據進行描述,Android則根據此Intent的描述,負責找到對應的組件,將 Intent傳遞給調用的組件,並完成組件的調用。Intent不僅可用於應用程序之間,也可用於應用程序內部的Activity/Service之間的 交互。因此,可以將Intent理解為不同組件之間通信的“媒介”專門提供組件互相調用的相關信息。
二、Intent作用:
Intent 是一個將要執行的動作的抽象的描述,一般來說是作為參數來使用,由Intent來協助完成android各個組件之間的通訊。比如說調用 startActivity()來啟動一個activity,或者由broadcaseIntent()來傳遞給所有感興趣的 BroadcaseReceiver, 再或者由startService()/bindservice()來啟動一個後臺的service.所以可以看出來,intent主要是用來啟動其他的 activity 或者service,所以可以將intent理解成activity之間的粘合劑。
三.Inten啟動組件的方法:
Intent可以啟動一個Activity,也可以啟動一個Service,還可以發起一個廣播Broadcasts。具體方法如下:
|
組件名稱 |
方法名稱 |
|
Activity |
startActvity( ) startActivity( ) |
|
Service |
startService( ) bindService( ) |
|
Broadcasts |
sendBroadcasts( ) sendOrderedBroadcasts( ) sendStickyBroadcasts( ) |
四.Intent的幾個重要屬性,下面進行詳解:
動作(Action),數據(Data),分類(Category),類型(Type),組件(Compent)以及擴展信(Extra)。其中最常用的是Action屬性和Data屬性。
1.Action屬性:
對於有如下聲明的Activity:
<activity android:name=".TargetActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.scott.intent.action.TARGET"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/>
</intent-filter>
</activity>
TargetActivity在其<intent-filter>中聲明了<action>,即目標action,如果我們需要做一個跳轉的動作,就需要在Intent中指定目標的action,如下:
public void gotoTargetActivity(View view) {
Intent intent = new Intent("com.scott.intent.action.TARGET");
startActivity(intent);
}
當我們為Intent指定相應的action,然後調用startActivity方法後,系統會根據action跳轉到對應的Activity。
除了自定義的action之外,Intent也內含了很多默認的action,下面列舉幾個:
public static final String ACTION_MAIN = "android.intent.action.MAIN"; public static final String ACTION_VIEW = "android.intent.action.VIEW"; public static final String ACTION_WEB_SEARCH = "android.intent.action.WEB_SEARCH"; public static final String ACTION_CALL = "android.intent.action.CALL";
每一個action都有其特定的用途。
2.data和extras,即執行動作要操作的數據和傳遞到目標的附加信息:
下面舉一個與瀏覽器交互的例子:
/**
* 打開指定網頁
* @param view
*/
public void invokeWebBrowser(View view) {
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW);
intent.setData(Uri.parse("http://www.google.com.hk"));
startActivity(intent);
}
/**
* 進行關鍵字搜索
* @param view
*/
public void invokeWebSearch(View view) {
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_WEB_SEARCH);
intent.putExtra(SearchManager.QUERY, "android"); //關鍵字
startActivity(intent);
}
上面兩種方法分別是啟動瀏覽器並打開指定網頁、進行關鍵字搜索,分別對應的action是Intent.ACTION_VIEW和 Intent.ACTION_WEB_SEARCH,前者需指定相應的網頁地址,後者需指定關鍵字信息,對於關鍵字搜索來說,瀏覽器會按照自己設置的默認 的搜索引擎進行搜索。
我們註意到,在打開網頁時,為Intent指定一個data屬性,這其實是指定要操作的數據,是一個URI的形式,我們可以將一個指定前綴的字符串轉換成 特定的URI類型,如:“http:”或“https:”表示網絡地址類型,“tel:”表示電話號碼類型,“mailto:”表示郵件地址類型,等等。
例如,我們要呼叫給定的號碼,可以這樣做:
public void call(View view) {
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_CALL);
intent.setData(Uri.parse("tel:12345678"));
startActivity(intent);
}
那麽我們如何知道目標是否接受這種前綴呢?這就需要看一下目標中<data/>元素的匹配規則了。
在目標<data/>標簽中包含了以下幾種子元素,他們定義了url的匹配規則:
android:scheme 匹配url中的前綴,除了“http”、“https”、“tel”...之外,我們可以定義自己的前綴
android:host 匹配url中的主機名部分,如“google.com”,如果定義為“*”則表示任意主機名
android:port 匹配url中的端口
android:path 匹配url中的路徑
我們改動一下TargetActivity的聲明信息:
<activity android:name=".TargetActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.scott.intent.action.TARGET"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/>
<data android:scheme="scott" android:host="com.scott.intent.data" android:port="7788" android:path="/target"/>
</intent-filter>
</activity>
這個時候如果只指定action就不夠了,我們需要為其設置data值,如下:
public void gotoTargetActivity(View view) {
Intent intent = new Intent("com.scott.intent.action.TARGET");
intent.setData(Uri.parse("scott://com.scott.intent.data:7788/target"));
startActivity(intent);
}
此時,url中的每個部分和TargetActivity配置信息中全部一致才能跳轉成功,否則就被系統拒絕。
不過有時候對path限定死了也不太好,比如我們有這樣的url:(scott://com.scott.intent.data:7788/target/hello)(scott://com.scott.intent.data:7788/target/hi) 這個時候該怎麽辦呢? 我們需要使用另外一個元素:android:pathPrefix,表示路徑前綴。 我們把android:path="/target"修改為android:pathPrefix="/target",然後就可以滿足以上的要求了。 而在進行搜索時,我們使用了一個putExtra方法,將關鍵字做為參數放置在Intent中,我們成為extras(附加信息),這裏面涉及到了一個Bundle對象。
Bundle和Intent有著密不可分的關系,主要負責為Intent保存附加參數信息,它實現了android.os.Paracelable接口, 內部維護一個Map類型的屬性,用於以鍵值對的形式存放附加參數信息。在我們使用Intent的putExtra方法放置附加信息時,該方法會檢查默認的 Bundle實例為不為空,如果為空,則新創建一個Bundle實例,然後將具體的參數信息放置到Bundle實例中。我們也可以自己創建Bundle對 象,然後為Intent指定這個Bundle即可,如下:
public void gotoTargetActivity(View view) {
Intent intent = new Intent("com.scott.intent.action.TARGET");
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putInt("id", 0);
bundle.putString("name", "scott");
intent.putExtras(bundle);
startActivity(intent);
}
需要註意的是,在使用putExtras方法設置Bundle對象之後,系統進行的不是引用操作,而是復制操作,所以如果設置完之後再更改bundle實 例中的數據,將不會影響Intent內部的附加信息。那我們如何獲取設置在Intent中的附加信息呢?與之對應的是,我們要從Intent中獲取到 Bundle實例,然後再從中取出對應的鍵值信息:
Bundle bundle = intent.getExtras();
int id = bundle.getInt("id");
String name = bundle.getString("name");
當然我們也可以使用Intent的getIntExtra和getStringExtra方法獲取,其數據源都是Intent中的Bundle類型的實例對象。
3.category,要執行動作的目標所具有的特質或行為歸類
例如:在我們的應用主界面Activity通常有如下配置:
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
代表該目標Activity是該應用所在task中的初始Activity並且出現在系統launcher的應用列表中。
幾個常見的category如下:
|
常量 |
解釋 |
|
CATEGORY_DEFAULT |
默認的category |
|
CATEGORY_BROWSABLE |
指定了此category後,在網頁上點擊圖片或鏈接時,系統會考慮將此目標Activity列入可選列表,供用戶選擇以打開圖片或鏈接。 |
|
CATEGORY_GADGET |
The activity can be embedded inside of another activity that hosts gadgets. |
|
CATEGORY_HOME |
The activity displays the home screen, the first screen the user sees when the device is turned on or when the HOME key is pressed. |
|
CATEGORY_LAUNCHER |
The activity can be the initial activity of a task and is listed in the top-level application launcher. |
|
CATEGORY_PREFERENCE |
表示該目標Activity是一個首選項界面; |
在為Intent設置category時,應使用addCategory(String category)方法向Intent中添加指定的類別信息,來匹配聲明了此類別的目標Activity。
下面舉一個回到Home界面的例子:
main.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="測試Intent Category"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/Button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="轉到Home界面"
/>
</LinearLayout>
strings.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<string name="hello">Hello World, MainActivity!</string>
<string name="app_name">IntentCategoryDemo</string>
</resources>
MainActivity.java:
package com.android.category.activity;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private Button btn;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
btn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.Button1);
btn.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setAction(Intent.ACTION_MAIN);// 添加Action屬性
intent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_HOME);// 添加Category屬性
startActivity(intent);// 啟動Activity
}
});
}
}
效果圖如下:
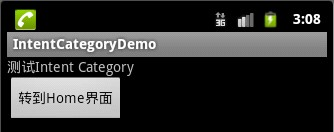
Home:
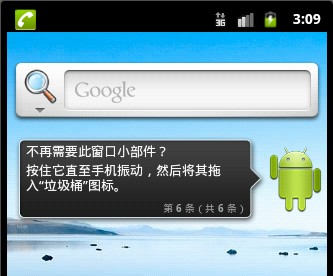
4.type:要執行動作的目標Activity所能處理的MIME數據類型
例如:一個可以處理圖片的目標Activity在其聲明中包含這樣的mimeType:
<data android:mimeType="image/*" />
在使用Intent進行匹配時,我們可以使用setType(String type)或者setDataAndType(Uri data, String type)來設置mimeType。
5.component,目標組件的包或類名稱
在使用component進行匹配時,一般采用以下幾種形式:
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName(getApplicationContext(), TargetActivity.class));
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName(getApplicationContext(), "com.scott.intent.TargetActivity"));
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName("com.scott.other", "com.scott.other.TargetActivity"));
其中,前兩種是用於匹配同一包內的目標,第三種是用於匹配其他包內的目標。
【註意】:如果我們在Intent中指定了component屬性,系統將不會再對action、data/type、category進行匹配。
五、Intent用法示例全面總結:
1. 調用撥號程序
// 給移動客服10086撥打電話
Uri uri = Uri.parse("tel:10086");
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_DIAL, uri);
startActivity(intent);
2.發送短信或彩信
// 給10086發送內容為“Hello”的短信
Uri uri = Uri.parse("smsto:10086");
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_SENDTO, uri);
intent.putExtra("sms_body", "Hello");
startActivity(intent);
// 發送彩信(相當於發送帶附件的短信)
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_SEND);
intent.putExtra("sms_body", "Hello");
Uri uri = Uri.parse("content://media/external/images/media/23");
intent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_STREAM, uri);
intent.setType("image/png");
startActivity(intent);
3.通過瀏覽器打開網頁
// 打開Google主頁
Uri uri = Uri.parse("http://www.google.com");
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, uri);
startActivity(intent);
4.發送電子郵件
// 給[email protected]發郵件 Uri uri = Uri.parse("mailto:[email protected]"); Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_SENDTO, uri); startActivity(intent);
// 給[email protected]發郵件發送內容為“Hello”的郵件 Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_SEND); intent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_EMAIL, "[email protected]"); intent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_SUBJECT, "Subject"); intent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_TEXT, "Hello"); intent.setType("text/plain"); startActivity(intent);
// 給多人發郵件
Intent intent=new Intent(Intent.ACTION_SEND);
String[] tos = {"[email protected]", "[email protected]"}; // 收件人
String[] ccs = {"[email protected]", "[email protected]"}; // 抄送
String[] bccs = {"[email protected]", "[email protected]"}; // 密送
intent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_EMAIL, tos);
intent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_CC, ccs);
intent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_BCC, bccs);
intent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_SUBJECT, "Subject");
intent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_TEXT, "Hello");
intent.setType("message/rfc822");
startActivity(intent);
5.顯示地圖與路徑規劃
// 打開Google地圖中國北京位置(北緯39.9,東經116.3)
Uri uri = Uri.parse("geo:39.9,116.3");
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, uri);
startActivity(intent);
// 路徑規劃:從北京某地(北緯39.9,東經116.3)到上海某地(北緯31.2,東經121.4)
Uri uri = Uri.parse("http://maps.google.com/maps?f=d&saddr=39.9 116.3&daddr=31.2 121.4");
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, uri);
startActivity(intent);
6. 播放多媒體
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW);
Uri uri = Uri.parse("file:///sdcard/foo.mp3");
intent.setDataAndType(uri, "audio/mp3");
startActivity(intent);
Uri uri = Uri.withAppendedPath(MediaStore.Audio.Media.INTERNAL_CONTENT_URI, "1");
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, uri);
startActivity(intent);
7. 拍照
// 打開拍照程序 Intent intent = new Intent(MediaStore.ACTION_IMAGE_CAPTURE); startActivityForResult(intent, 0);
// 取出照片數據
Bundle extras = intent.getExtras();
Bitmap bitmap = (Bitmap) extras.get("data");
8.獲取並剪切圖片
// 獲取並剪切圖片
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_GET_CONTENT);
intent.setType("image/*");
intent.putExtra("crop", "true"); // 開啟剪切
intent.putExtra("aspectX", 1); // 剪切的寬高比為1:2
intent.putExtra("aspectY", 2);
intent.putExtra("outputX", 20); // 保存圖片的寬和高
intent.putExtra("outputY", 40);
intent.putExtra("output", Uri.fromFile(new File("/mnt/sdcard/temp"))); // 保存路徑
intent.putExtra("outputFormat", "JPEG");// 返回格式
startActivityForResult(intent, 0);
// 剪切特定圖片
1 Intent intent = new Intent("com.android.camera.action.CROP");
2 intent.setClassName("com.android.camera", "com.android.camera.CropImage");
3 intent.setData(Uri.fromFile(new File("/mnt/sdcard/temp")));
4 intent.putExtra("outputX", 1); // 剪切的寬高比為1:2
5 intent.putExtra("outputY", 2);
6 intent.putExtra("aspectX", 20); // 保存圖片的寬和高
7 intent.putExtra("aspectY", 40);
8 intent.putExtra("scale", true);
9 intent.putExtra("noFaceDetection", true);
10 intent.putExtra("output", Uri.parse("file:///mnt/sdcard/temp"));
11 startActivityForResult(intent, 0);
9. 打開Google Market
// 打開Google Market直接進入該程序的詳細頁面
Uri uri = Uri.parse("market://details?id=" + "com.demo.app");
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, uri);
startActivity(intent);
10.安裝和卸載程序
Uri uri = Uri.fromParts("package", "com.demo.app", null);
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_DELETE, uri);
startActivity(intent);
11. 進入設置界面
// 進入無線網絡設置界面(其它可以舉一反三) Intent intent = new Intent(android.provider.Settings.ACTION_WIRELESS_SETTINGS); startActivityForResult(intent, 0);
Android總結篇——Intent機制詳解及示例總結
