決策樹的圖形可視化
阿新 • • 發佈:2017-11-01
分類 turn utf-8 port logs ace ann ring return
在Python 中使用 Matplotlib 註釋繪制決策樹形圖
上次我們對數據生成決策樹有了一定了解,但樹是以字典的形式表達的,非常不易於理解;因此,通過決策樹的圖形可視化有助於我們對決策樹的理解和認識。利用強大的Matplotlib 庫就可以解決實際的需求。
1 生成決策樹的完整的代碼
新建一個test.py 文件,用於寫決策樹的建立代碼
1 # coding=utf-8 2 from math import log 3 import operator 4 def calcShannonEnt(dataSet): 5 numEntries = len(dataSet)6 labelCounts = {} 7 for featVec in dataSet: 8 currentLabel = featVec[-1] # 提取類標號的屬性值 9 # 把類標號不同的屬性值及其個數存入字典中 10 if currentLabel not in labelCounts .keys(): 11 labelCounts [currentLabel ]=0 12 labelCounts [currentLabel]+=1 13 shannonEnt = 0.0 14# 計算類標號的平均信息量,如公式中H(S) 15 for key in labelCounts : 16 prob = float(labelCounts [key])/numEntries 17 shannonEnt -= prob * log(prob,2) 18 return shannonEnt 19 20 def createDataSet(): 21 dataSet = [[1, 1, ‘yes‘], 22 [1, 1, ‘yes‘], 23 [1, 0, ‘no‘], 24 [0, 1, ‘no‘], 25 [0, 1, ‘no‘]] 26 labels = [‘no surfacing‘,‘flippers‘] 27 #change to discrete values 28 return dataSet, labels 29 def createDataSet1(): 30 dataSet = [[u‘小於等於5‘,u‘高‘,u‘否‘,u‘一般‘,u‘否‘], 31 [u‘小於等於5‘, u‘高‘, u‘否‘, u‘好‘, u‘否‘], 32 [u‘5到10‘, u‘高‘, u‘否‘, u‘一般‘, u‘否‘], 33 [u‘大於等於10‘, u‘中‘, u‘否‘, u‘一般‘, u‘是‘], 34 [u‘大於等於10‘, u‘低‘, u‘是‘, u‘一般‘, u‘是‘], 35 [u‘5到10‘, u‘中‘, u‘否‘, u‘好‘, u‘否‘], 36 [u‘5到10‘, u‘高‘, u‘是‘, u‘一般‘, u‘是‘], 37 [u‘小於等於5‘, u‘中‘, u‘否‘, u‘一般‘, u‘否‘], 38 [u‘5到10‘, u‘中‘, u‘否‘, u‘好‘, u‘否‘], 39 [u‘大於等於10‘, u‘高‘, u‘是‘, u‘好‘, u‘是‘], 40 [u‘5到10‘, u‘低‘, u‘是‘, u‘一般‘, u‘是‘], 41 [u‘小於等於5‘, u‘中‘, u‘是‘, u‘一般‘, u‘是‘], 42 [u‘小於等於5‘, u‘低‘, u‘是‘, u‘一般‘, u‘是‘], 43 [u‘大於等於10‘, u‘中‘, u‘是‘, u‘好‘, u‘是‘]] 44 labels = [u‘役齡‘,u‘價格‘,u‘是否關鍵部件‘,u‘磨損程度‘] 45 return dataSet ,labels 46 47 # 按照給定特征劃分數據集,把符合給定屬性值的對象組成新的列表 48 def splitDataSet(dataSet,axis,value): 49 retDataSet = [] 50 for featVec in dataSet: 51 # 選擇符合給定屬性值的對象 52 if featVec[axis] == value: 53 reduceFeatVec = featVec[:axis] # 對對象的屬性值去除給定的特征的屬性值 54 reduceFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis+1:]) 55 retDataSet.append(reduceFeatVec ) # 把符合且處理過的對象添加到新的列表中 56 return retDataSet 57 58 # 選取最佳特征的信息增益,並返回其列號 59 def chooseBestFeaturesplit(dataSet): 60 numFeatures = len(dataSet[0])-1 # 獲得樣本集S 除類標號之外的屬性個數,如公式中的k 61 baseEntropy = calcShannonEnt(dataSet) # 獲得類標號屬性的平均信息量,如公式中H(S) 62 63 bestInfoGain = 0.0 # 對最佳信息增益的初始化 64 bestFeature = -1 # 最佳信息增益的屬性在樣本集中列號的初始化 65 66 # 對除類標號之外的所有樣本屬性一一計算其平均信息量 67 for i in range(numFeatures ): 68 featList = [example[i] for example in dataSet] # 提取第i 個特征的所有屬性值 69 uniqueVals = set(featList ) # 第i 個特征所有不同屬性值的集合,如公式中 aq 70 newEntropy = 0.0 # 對第i 個特征的平均信息量的初始化 71 # 計算第i 個特征的不同屬性值的平均信息量,如公式中H(S| Ai) 72 for value in uniqueVals: 73 subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet,i,value ) # 提取第i 個特征,其屬性值為value的對象集合 74 prob = len (subDataSet )/float(len(dataSet)) # 計算公式中P(Cpq)的概率 75 newEntropy += prob * calcShannonEnt(subDataSet ) # 第i個特征的平均信息量,如 公式中H(S| Ai) 76 infoGain = baseEntropy - newEntropy # 第i 個的信息增益量 77 if (infoGain > bestInfoGain ): # 選取最佳特征的信息增益,並返回其列號 78 bestInfoGain = infoGain 79 80 bestFeature = i 81 return bestFeature 82 83 # 選擇列表中重復次數最多的一項 84 def majorityCnt(classList): 85 classCount= {} 86 for vote in classList : 87 if vote not in classCount .keys(): 88 classCount [vote] =0 89 classCount[vote] += 1 90 sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.iteritems() , 91 key=operator.itemgetter(1), 92 reverse= True ) # 按逆序進行排列,並返回由元組組成元素的列表 93 return sortedClassCount[0][0] 94 95 # 創建決策樹 96 def createTree(dataSet,labels): 97 Labels = labels [:] # 防止改變最初的特征列表 98 classList = [example[-1] for example in dataSet ] # 獲得樣本集中的類標號所有屬性值 99 if classList.count(classList [0]) == len(classList): # 類標號的屬性值完全相同則停止繼續劃分 100 return classList[0] 101 if len(dataSet[0]) == 1: # 遍歷完所有的特征時,仍然類標號不同的屬性值,則返回出現次數最多的屬性值 102 return majorityCnt(classList) 103 bestFeat = chooseBestFeaturesplit(dataSet) # 選擇劃分最佳的特征,返回的是特征在樣本集中的列號 104 bestFeatLabel = Labels[bestFeat] # 提取最佳特征的名稱 105 myTree = {bestFeatLabel :{}} # 創建一個字典,用於存放決策樹 106 del(Labels[bestFeat]) # 從特征列表中刪除已經選擇的最佳特征 107 featValues = [example[bestFeat] for example in dataSet ] # 提取最佳特征的所有屬性值 108 uniqueVals = set(featValues ) # 獲得最佳特征的不同的屬性值 109 for value in uniqueVals : 110 subLabels = Labels[:] # 把去除最佳特征的特征列表賦值於subLabels 111 myTree [bestFeatLabel][value] = createTree(splitDataSet(dataSet ,bestFeat ,value ), 112 subLabels ) # 遞歸調用createTree() 113 return myTree 114 115 # 決策樹的存儲 116 def storeTree(inputTree,filename): 117 import pickle 118 fw = open(filename,‘w‘) 119 pickle.dump(inputTree ,fw) 120 fw.close() 121 122 def grabTree(filename): 123 import pickle 124 fr = open(filename) 125 return pickle.load(fr) 126 127 128 # 使用決策樹的分類函數 129 def classify(inputTree,featLabels,testVec): 130 firstStr = inputTree.keys()[0] # 獲得距離根節點最近的最佳特征 131 secondDict = inputTree[firstStr ] # 最佳特征的分支 132 featIndex = featLabels .index(firstStr) # 獲取最佳特征在特征列表中索引號 133 for key in secondDict .keys(): # 遍歷分支 134 if testVec [featIndex ] == key: # 確定待查數據和最佳特征的屬性值相同的分支 135 if type(secondDict [key]).__name__ == ‘dict‘: # 判斷找出的分支是否是“根節點” 136 classLabel = classify(secondDict[key],featLabels ,testVec) # 利用遞歸調用查找葉子節點 137 else: 138 classLabel = secondDict [key] # 找出的分支是葉子節點 139 return classLabel
2 決策樹的圖形可視化
另外新建一個文件 treeplotter.py , 編寫決策樹圖形可視化的代碼。
1 # coding=utf-8 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 import sys 4 import test 5 reload(sys) 6 sys.setdefaultencoding(‘utf-8‘) 7 decisionNode = dict(boxstyle="sawtooth", fc="0.8") 8 leafNode = dict(boxstyle="round4", fc="0.8") 9 arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle="<-") 10 11 # 獲得葉子節點的數目 12 def getNumLeafs(myTree): 13 numLeafs = 0 14 firstStr = myTree.keys()[0] 15 secondDict = myTree[firstStr] 16 for key in secondDict.keys(): 17 if type(secondDict[key]).__name__==‘dict‘:#test to see if the nodes are dictonaires, if not they are leaf nodes 18 numLeafs += getNumLeafs(secondDict[key]) 19 else: numLeafs +=1 20 return numLeafs 21 22 # 獲得決策樹的層數 23 def getTreeDepth(myTree): 24 maxDepth = 0 25 firstStr = myTree.keys()[0] 26 secondDict = myTree[firstStr] 27 for key in secondDict.keys(): 28 if type(secondDict[key]).__name__==‘dict‘:#test to see if the nodes are dictonaires, if not they are leaf nodes 29 thisDepth = 1 + getTreeDepth(secondDict[key]) 30 else: thisDepth = 1 31 if thisDepth > maxDepth: maxDepth = thisDepth 32 return maxDepth 33 34 def plotNode(nodeTxt, centerPt, parentPt, nodeType): 35 createPlot.ax1.annotate(nodeTxt, xy=parentPt, xycoords=‘axes fraction‘, 36 xytext=centerPt, textcoords=‘axes fraction‘, 37 va="center", ha="center", bbox=nodeType, arrowprops=arrow_args ) 38 39 def plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, txtString): 40 xMid = (parentPt[0]-cntrPt[0])/2.0 + cntrPt[0] 41 yMid = (parentPt[1]-cntrPt[1])/2.0 + cntrPt[1] 42 createPlot.ax1.text(xMid, yMid, txtString, va="center", ha="center", rotation=30) 43 44 def plotTree(myTree, parentPt, nodeTxt):#if the first key tells you what feat was split on 45 numLeafs = getNumLeafs(myTree) #this determines the x width of this tree 46 depth = getTreeDepth(myTree) 47 firstStr = myTree.keys()[0] #the text label for this node should be this 48 cntrPt = (plotTree.xOff + (1.0 + float(numLeafs))/2.0/plotTree.totalW, plotTree.yOff) 49 plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, nodeTxt) 50 plotNode(firstStr, cntrPt, parentPt, decisionNode) 51 secondDict = myTree[firstStr] 52 plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff - 1.0/plotTree.totalD 53 for key in secondDict.keys(): 54 if type(secondDict[key]).__name__==‘dict‘:#test to see if the nodes are dictonaires, if not they are leaf nodes 55 plotTree(secondDict[key],cntrPt,str(key)) #recursion 56 else: #it‘s a leaf node print the leaf node 57 plotTree.xOff = plotTree.xOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalW 58 plotNode(secondDict[key], (plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, leafNode) 59 plotMidText((plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, str(key)) 60 plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalD 61 #if you do get a dictonary you know it‘s a tree, and the first element will be another dict 62 63 def createPlot(inTree): 64 fig = plt.figure(1, facecolor=‘white‘) 65 fig.clf() 66 axprops = dict(xticks=[], yticks=[]) 67 createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False, **axprops) #no ticks 68 #createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False) #ticks for demo puropses 69 plotTree.totalW = float(getNumLeafs(inTree)) 70 plotTree.totalD = float(getTreeDepth(inTree)) 71 plotTree.xOff = -0.5/plotTree.totalW; plotTree.yOff = 1.0; 72 plotTree(inTree, (0.5,1.0), ‘‘) 73 plt.show() 74 75 76 if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: 77 dataSet, labels = test.createDataSet1() 78 myTree = test.createTree(dataSet, labels) 79 createPlot(myTree)
3 運行結果顯示
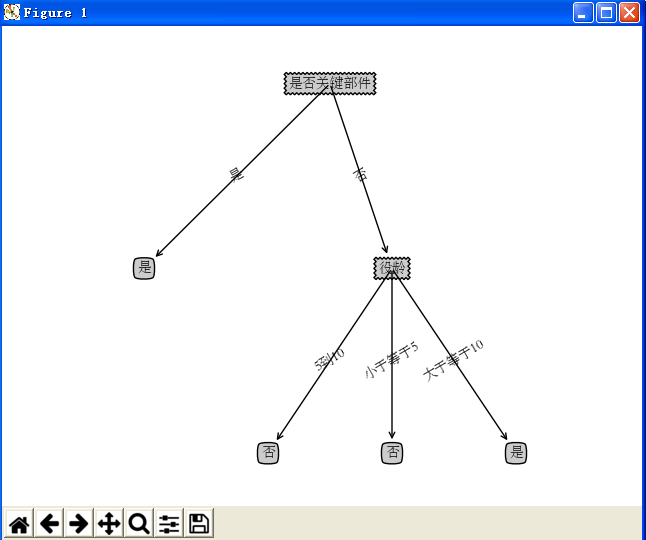
決策樹的圖形可視化
