Python操作文件模擬SQL語句功能
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-01-03
enc arc env con 支持 span 字典 adding 功能 一、要求
當然此表你在文件存儲時可以這樣表示
1,li,22,18230393840,IT,2013-06-01 現需要對這個員工信息文件,實現增刪改查操作
1. 可進行模糊查詢,語法至少支持下面3種:
1. select name,age from staff_table where age > 22
2. select * from staff_table where dept = "IT"
3. select * from staff_table where enroll_date like "2013“
2. 可修改員工信息,語法如下:
1. UPDATE staff_table SET dept="Market" WHERE where dept = "IT"註意:以上需求,要充分使用函數,請盡你的最大限度來減少重復代碼!
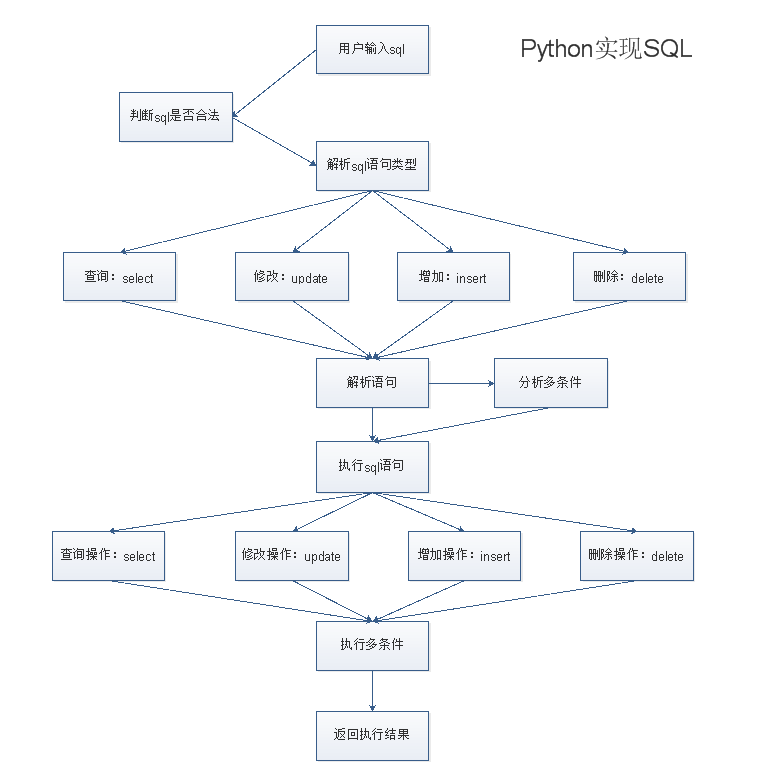
二、實現流程
第一部分:SQL解析
1.接收用戶SQL
判斷用戶輸入是否為SQL
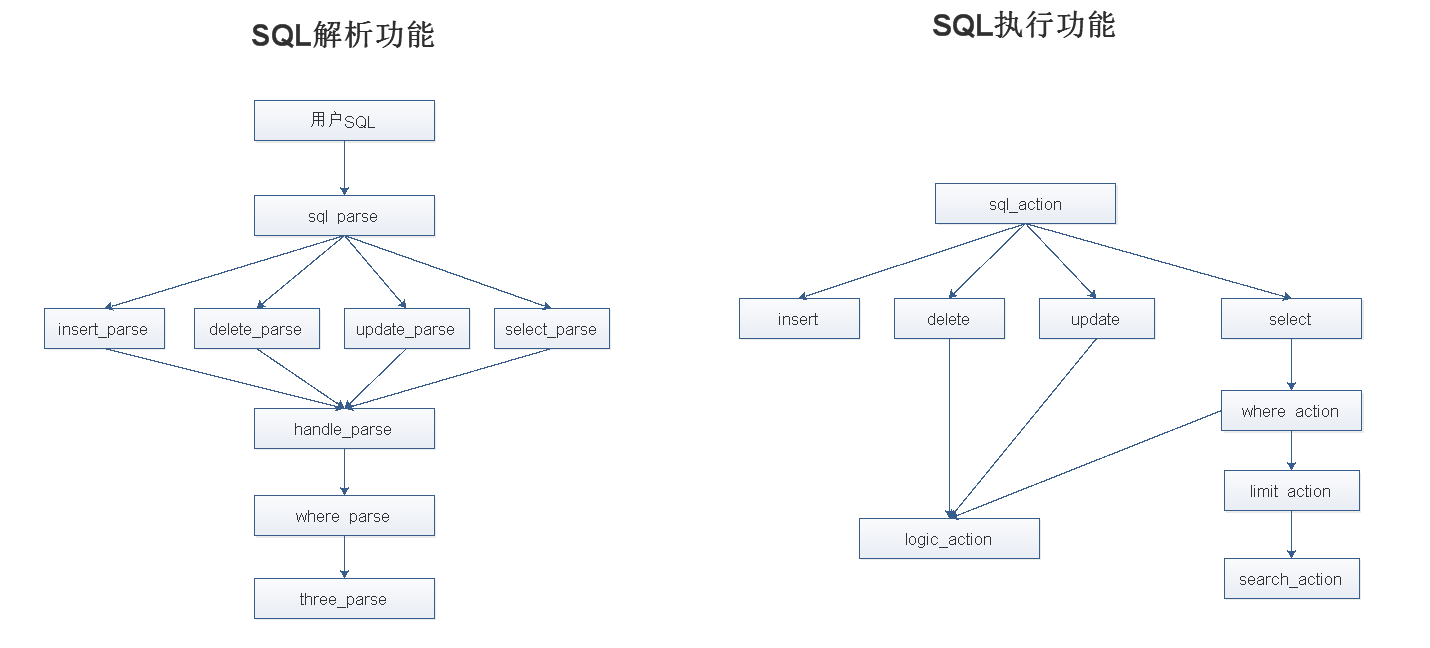
2.SQL解析主函數sql_parse
where_parse
three_parse
insert_parse
delete_parse
update_parse
select_parse
分發SQL給對應語句的函數來做解析
解析後交給handle_parse,來控制返回
解析SQL語句中的多條件
返回解析後的SQL
第二部分:SQL執行
1.接收解析後的SQL
2.SQL執行主函數sql_action
where_action
logic_action
limit_action
search_action
insert
delete
update
select
分發SQL給對應函數來執行
執行SQL語句時的多條件
返回執行SQL的結果
三、圖解
代碼:
#/usr/local/env python
#_*_coding:utf-8_*_
#第一部分:sql解析
import os
def sql_parse(sql): #用戶輸入sql 轉成結構化的字典
'''
第一步:sql解析 流程
1.收到 sql查詢條件
2.sql_parse 來分發要求給 select_parse
3.select_parse 調用 handle_parse 解析sql
4.handle_parse 返回解析sql後的結果 sql_dic 給 select_parse
5.select_parse 把 sql_dic 返回給sql_parse
sql_dic=sql_parse(sql) #用戶輸入sql 轉成結構化的字典sql_dic
sql語句四種操作格式:insert delete update select
提取用戶輸入sql 的操作關鍵詞 再進行分析和分發操作
把sql字符串切分,提取命令信息,分發給具體解析函數去解析
:param sql:用戶輸入的字符串
:return:返回字典格式sql解析結果
'''
#sql命令操作 解析函數的字典 根據用戶的命令來找相對應的函數
parse_func={
'insert':insert_parse,
'delete':delete_parse,
'update':update_parse,
'select':select_parse,
}
#print('用戶輸入 sql str is : %s' %sql) #打印用戶輸入的sql
sql_l=sql.split(' ') #按空格切割用戶sql 成列表 方便提取命令信息
func=sql_l[0] #取出用戶的sql命令
#判斷用戶輸入的sql命令 是否在定義好的sql命令函數的字典裏面,如果不在字典裏面,則返回空
res=''
if func in parse_func:
res=parse_func[func](sql_l) #把切割後的 用戶sql的列表 傳入對應的sql命令函數裏
return res
def insert_parse(sql_l):
'''
定義insert語句的語法結構,執行sql解析操作,返回sql_dic
:param sql:sql按照空格分割的列表
:return:返回字典格式的sql解析結果
'''
sql_dic={
'func':insert, #函數名
'insert':[], #insert選項,留出擴展
'into':[], #表名
'values':[], #值
}
return handle_parse(sql_l,sql_dic)
def delete_parse(sql_l):
'''
定義delete語句的語法結構,執行sql解析操作,返回sql_dic
:param sql:sql按照空格分割的列表
:return:返回字典格式的sql解析結果
'''
sql_dic = {
'func': delete,
'delete': [], # delete選項,留出擴展
'from': [], # 表名
'where': [], # filter條件
}
return handle_parse(sql_l, sql_dic)
def update_parse(sql_l):
'''
定義update語句的語法結構,執行sql解析操作,返回sql_dic
:param sql:sql按照空格分割的列表
:return:返回字典格式的sql解析結果
'''
sql_dic = {
'func': update,
'update': [], # update選項,留出擴展
'set': [], # 修改的值
'where': [], # filter條件
}
return handle_parse(sql_l, sql_dic)
def select_parse(sql_l):
'''
定義select語句的語法結構,執行sql解析操作,返回sql_dic
:param sql:sql按照空格分割的列表
:return:返回字典格式的sql解析結果
'''
# print('from in the select_parse :\033[42;1m%s\033[0m' %sql_l)
# select語句多種條件查詢,列成字典,不同條件不同列表
sql_dic={
'func':select, #執行select語句
'select':[], #查詢字段
'from':[], #數據庫.表
'where':[], #filter條件,怎麽找
'limit':[], #limit條件,限制
}
return handle_parse(sql_l,sql_dic)
def handle_parse(sql_l,sql_dic): #專門做sql解析操作
'''
執行sql解析操作,返回sql_dic
:param sql_l: sql按照空格分割的列表
:param sql_dic: 待填充的字典
:return: 返回字典格式的sql解析結果
'''
# print('sql_l is \033[41;1m%s\033[0m \nsql_dic is \033[41;1m%s\033[0m' %(sql_l,sql_dic))
tag=False #設置警報 默認是關閉False
for item in sql_l: #循環 按空格切割用戶sql的列表
if tag and item in sql_dic: #判斷警報拉響是True 並且用戶sql的條件 在條件select語句字典裏面,則關閉警報
tag=False #關閉警報
if not tag and item in sql_dic: #判斷警報沒有拉響 並且用戶sql的條件 在條件select語句字典裏面
tag=True #拉響警報
key=item #取出用戶sql的條件
continue #跳出本次判斷
if tag: #判斷報警拉響
sql_dic[key].append(item) #把取出的用戶sql 添加到 select語句多種條件對應的字典裏
if sql_dic.get('where'): #判斷 用戶sql where語句
sql_dic['where']=where_parse(sql_dic.get('where')) #['id>4','and','id<10'] #調用where_parse函數 把整理好的用戶sql的where語句 覆蓋之前沒整理好的
# print('from in the handle_parse sql_dic is \033[43;1m%s\033[0m' %sql_dic)
return sql_dic #返回 解析好的 用戶sql 字典
def where_parse(where_l): #['id>','4','and','id','<10'] ---> #['id>4','and','id<10']
'''
分析用戶sql where的各種條件,再拼成合理的條件字符串
:param where_l:用戶輸入where後對應的過濾條件列表
:return:
'''
res=[] #存放最後整理好條件的列表
key=['and','or','not'] #邏輯運算符
char='' #存放拼接時的字符串
for i in where_l: #循環用戶sql
if len(i) == 0 :continue #判斷 長度是0 就繼續循環
if i in key:
#i為key當中存放的邏輯運算符
if len(char) != 0: #必須 char的長度大於0
char=three_parse(char) #把char字符串 轉成列表的形式
res.append(char) #把之前char的字符串,加入res #char='id>4'--->char=['id','>','4']
res.append(i) #把用戶sql 的邏輯運算符 加入res
char='' #清空 char ,為了下次加入char到res時 數據不重復
else:
char+=i #'id>4' #除了邏輯運算符,都加入char #char='id<10'--->char=['id','>','4']
else:
char = three_parse(char) # 把char字符串 轉成列表的形式
res.append(char) #循環完成後 char裏面有數據 ,再加入到res裏面
# ['id>4','and','id<10'] ---> #['id','>','4','and','id','<','10']
# print('from in the where_parse res is \033[43;1m%s\033[0m' % res)
return res #返回整理好的 where語句列表
def three_parse(exp_str): # 把where_parse函數裏面 char的字符串 轉成字典
'''
將每一個小的過濾條件如,name>=1轉換成['name','>=','1']
:param exp_str:條件表達式的字符串形式,例如'name>=1'
:return:
'''
key=['>','<','='] #區分運算符
res=[] #定義空列表 存放最終值
char='' #拼接 值的字符串
opt='' #拼接 運算符
tag=False #定義警報
for i in exp_str: #循環 字符串和運算符
if i in key: #判斷 當是運算符時
tag=True #拉響警報
if len(char) != 0: #判斷char的長度不等於0時(方便添加連續運算符)才做列表添加
res.append(char) #把拼接的字符串加入 res列表
char='' #清空char 使下次循環不重復添加數據到res列表
opt+=i #把循環的運算符加入opt
if not tag: #判斷 警報沒有拉響
char+=i #把循環的字符串加入 char
if tag and i not in key: #判斷 警報拉響(表示上次循環到運算符),並且本次循環的不是運算符
tag=False #關閉警報
res.append(opt) #把opt裏面的運算符 加入res列表
opt='' #清空opt 使下次循環不重復添加數據到res列表
char+=i #把循環到的 字符串加入char
else:
res.append(char) #循環結束,把最後char的字符串加入res列表
#新增解析 like的功能
if len(res) == 1: #判斷 ['namelike李'] 是個整體
res=res[0].split('like') #以like切分字符串
res.insert(1,'like') #加入like字符串,因為上面切分的時候剔除了like
# print('three_parse res is \033[43;1m%s\033[0m' % res)
return res #返回res列表結果
#第二部分:sql執行
def sql_action(sql_dic): #接收用戶輸入的sql 的結構化的字典 然後執行sql
'''
從字典sql_dic提取命令,分發給具體的命令執行函數去執行
執行sql的統一接口,內部執行細節對用戶完全透明
:param sql_dic:
:return:
'''
return sql_dic.get('func')(sql_dic) #接收用戶sql,分發sql,執行命令
def insert(sql_dic):
print('insert %s' %sql_dic)
db,table=sql_dic.get('into')[0].split('.') #切分文件路徑,相對應數據庫,表
with open('%s/%s' %(db,table),'ab+') as fh: #安裝上面的路徑 打開文件 ab+模式
# 讀出文件最後一行,賦值給last 配合+
offs = -100 #
while True:
fh.seek(offs,2)
lines = fh.readlines()
if len(lines)>1:
last = lines[-1]
break
offs *= 2
last=last.decode(encoding='utf-8')
last_id=int(last.split(',')[0]) #取出最後一行id號
new_id=last_id+1 #id號加1 實現id自增效果
#insert into db1.emp values alex,30,18500841678,運維,2007-8-1
record=sql_dic.get('values')[0].split(',') #提取用戶想要 添加的sql
record.insert(0,str(new_id)) #加入自增後的id 到用戶sql的頭部
#['26','alex','35','13910015353','運維','2005 - 06 - 27\n']
record_str=','.join(record)+'\n' #把用戶sql列表切成字符串
fh.write(bytes(record_str,encoding='utf-8')) #把添加 id後的用戶想添加的sql 用bytes寫入文件
fh.flush()
return [['insert successful']]
def delete(sql_dic):
db,table=sql_dic.get('from')[0].split('.')
bak_file=table+'_bak'
with open("%s/%s" %(db,table),'r',encoding='utf-8') as r_file, open('%s/%s' %(db,bak_file),'w',encoding='utf-8') as w_file:
del_count=0
for line in r_file:
title="id,name,age,phone,dept,enroll_date"
dic=dict(zip(title.split(','),line.split(',')))
filter_res=logic_action(dic,sql_dic.get('where'))
if not filter_res:
w_file.write(line)
else:
del_count+=1
w_file.flush()
os.remove("%s/%s" % (db, table))
os.rename("%s/%s" %(db,bak_file),"%s/%s" %(db,table))
return [[del_count],['delete successful']]
def update(sql_dic):
#update db1.emp set id='sb' where name like alex
db,table=sql_dic.get('update')[0].split('.')
set=sql_dic.get('set')[0].split(',')
set_l=[]
for i in set:
set_l.append(i.split('='))
bak_file=table+'_bak'
with open("%s/%s" %(db,table),'r',encoding='utf-8') as r_file, open('%s/%s' %(db,bak_file),'w',encoding='utf-8') as w_file:
update_count=0
for line in r_file:
title="id,name,age,phone,dept,enroll_date"
dic=dict(zip(title.split(','),line.split(',')))
filter_res=logic_action(dic,sql_dic.get('where'))
if filter_res:
for i in set_l:
k=i[0]
v=i[-1].strip("'")
print('k v %s %s' %(k,v))
dic[k]=v
print('change dic is %s ' %dic)
line=[]
for i in title.split(','):
line.append(dic[i])
update_count+=1
line=','.join(line)
w_file.write(line)
w_file.flush()
os.remove("%s/%s" % (db, table))
os.rename("%s/%s" %(db,bak_file),"%s/%s" %(db,table))
return [[update_count],['update successful']]
def select(sql_dic):
'''
執行select語句,接收解析好的sql字典
:param sql_dic:
:return:
'''
# print('from select sql_dic is %s' %sql_dic) #打印 解析好的sql字典
# first:form
db,table=sql_dic.get('from')[0].split('.') #切分出庫名和表名,就是文件路徑
fh=open("%s/%s" %(db,table),'r',encoding='utf-8') #打開文件 根據取到的路徑
#second:where
filter_res=where_action(fh,sql_dic.get('where')) #定義where執行函數,查詢條件
fh.close()
# for record in filter_res: # 循環打印 用戶sql where的執行結果
# print('file res is %s' %record)
#third:limit
limit_res=limit_action(filter_res,sql_dic.get('limit')) #定義limit執行函數,限制行數
# for record in limit_res: # 循環打印 顯示用戶sql limit的執行結果
# print('limit res is %s' %record)
#lase:select
search_res=search_action(limit_res,sql_dic.get('select')) #定義select執行函數
# for record in search_res: # 循環打印 顯示用戶sql select的執行結果
# print('select res is %s' %record)
return search_res
def where_action(fh,where_l): #執行where條件語句 where_l=where的多條件解析後的列表
#id,name,age,phone,dept,enroll_data
#10,吳東杭,21,17710890829,運維,1995-08-29
#['id>7', 'and', 'id<10', 'or', 'namelike']
# print('in where_action \033[41;1m%s\033[0m' %where_l)
res=[] #定義最後返回值的列表
logic_l=['and','or','not'] #定義邏輯運算符
title="id,name,age,phone,dept,enroll_data" #定義好表文件內容的標題
if len(where_l) != 0: #判斷用戶sql 是否有where語句
for line in fh: #循環 表文件
dic=dict(zip(title.split(','),line.split(','))) #一條記錄 讓標題和文件內容一一對應
#邏輯判斷
logic_res=logic_action(dic,where_l) #讓 logic_action函數來操作對比
if logic_res: #如果邏輯判斷為True
res.append(line.split(',')) #加入res
else:
res=fh.readlines() #用戶sql 沒有where語句,則返回表文件所有內容
# print('>>>>>>>> %s' %res)
return res #返回執行 where 後的結果
def logic_action(dic,where_l):
'''
用戶sql select的where多條件 執行對比文件內容
文件內容 跟所有的 where_l 的條件比較
:param dic:
:param where_l:
:return:
'''
# print('from logic_action %s' %dic) #from logic_action {'id': '23', 'name': '翟超群', 'age': '24', 'phone': '13120378203', 'dept': '運維', 'enroll_data': '2013-3-1\n'}
# print('---- %s' %where_l) #[['name', 'like', '李'], 'or', ['id', '<=', '4']]
res=[] #存放 bool值 結果的空列表
# where_l=[['name', 'like', '李'], 'or', ['id', '<=', '4']]
for exp in where_l: #循環where條件列表,跟dic做比較
#dic與exp做bool運算
if type(exp) is list: #只留下 where_l列表裏 相關的條件
#如果是列表 做bool運算 #[['name', 'like', '李']
exp_k,opt,exp_v=exp #匹配 一個where條件列表的格式
if exp[1] == '=': #如果 列表的運算符是 =號
opt="%s=" %exp[1] #用字符串拼接出 兩個 ==號
if dic[exp_k].isdigit(): #判斷是否數字 用戶的條件是否對應文件內容(字典)
dic_v=int(dic[exp_k]) #文件內容的數字 轉成整形 做比較
exp_v=int(exp_v) #where_l列表的數字 轉成整形 做比較
else:
dic_v="'%s'" %dic[exp_k] #不是數字的時候 存取出來
if opt != 'like': #如果運算符 不是 like
exp=str(eval("%s%s%s" %(dic_v,opt,exp_v))) #轉成字符串(邏輯判斷後是bool值):做邏輯判斷:文件數字,運算符,用戶數字
else: #如果 運算符位置是 like
if exp_v in dic_v: #判斷 sql裏like的值 是否在 文件內容裏
exp='True'
else:
exp='False'
res.append(exp) #['True','or','False','or','true']
# print('---------- %s' %res)
res=eval(" ".join(res)) # 把bool值列表轉成字符串 然後再做邏輯判斷 結果是bool值
return res #返回 res結果
def limit_action(filter_res,limit_l): #執行limit條件 限制行數
res=[] #最後的返回值列表
if len(limit_l) != 0: #判斷 用戶sql 是否有 limit條件
index=int(limit_l[0]) #取出 用戶sql limit條件的數字
res=filter_res[0:index]
else: #如果 用戶sql 沒有 limit條件 就整個返回
res=filter_res
return res #返回最後的sql結果
def search_action(limit_res,select_l): #執行select執行函數
res=[] #最後的返回值列表
fileds_l = []
title = "id,name,age,phone,dept,enroll_data" #title = select的條件
if select_l[0] == '*' : #判斷 如果 用戶sql 的select 條件是 *
fields_l=title.split(',') #用戶sql 的select 條件是 * ,則匹配所有條件
res=limit_res #如果 用戶sql 的select 條件是 * 則返回全部
else: #判斷 如果用戶sql的select條件不是 * ,提取用戶的select語句條件
for record in limit_res: #循環 匹配好的where語句和limit語句的結果
dic=dict(zip(title.split(','),record)) #每條記錄都對應 select條件,生成字典
r_l=[] #存放用戶sql的select條件
fields_l=select_l[0].split(',') #取出用戶sql 的select條件
for i in fields_l: #循環用戶sql的select條件,區分多條件,id,name
r_l.append(dic[i].strip()) #把用戶sql的select多條件 加入 r_l列表
res.append(r_l) #把r_l列表 加入res
return (fields_l,res) #返回用戶sql的select條件,selcet執行結果
if __name__ == '__main__': #程序主函數
while True:
sql=input("sql> ").strip() #用戶輸入sql
if sql == 'exit':break #exit 隨時退出
if len(sql) == 0 :continue #用戶如果輸入空,繼續輸入
sql_dic=sql_parse(sql) #用戶輸入sql 轉成結構化的字典sql_dic
#print('main res is %s' %sql_dic) #打印用戶非法輸入
if len(sql_dic) == 0:continue #如果用戶輸入等於0 不執行sql_action 讓用戶繼續輸入sql
res=sql_action(sql_dic) #用戶執行sql之後的結果res
print('\033[43;1m%s\033[0m' %res[0]) #打印 select的條件
for i in res[-1]: # 循環打印 顯示用戶sql select的執行結果
print(i)
'''Python操作文件模擬SQL語句功能
