Spark Shuffle(二)Executor、Driver之間Shuffle結果消息傳遞、追蹤(轉載)
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-06-21
red free 只需要 sub rem 直接 nod 包含著 des 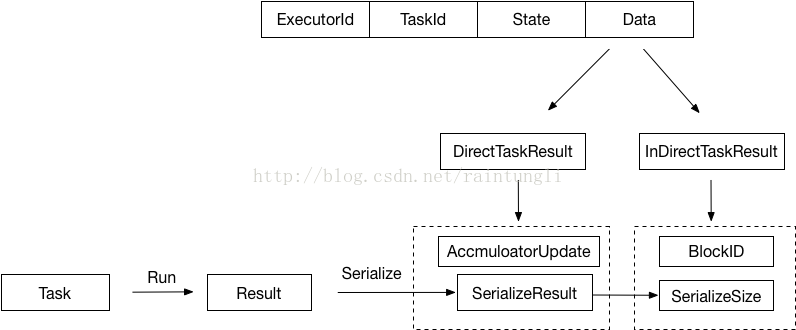 整個結構體中包含了
整個結構體中包含了

 也就是每個ResultTask會去獲取所有不同的MapId中相同的PartitionID部分Shuffle文件,而不是繼續按前面的Map進行分配,那意味著ResultTask將會去獲取所有Shuffle文件
Shuffle_shuffleId_mapId_0.data中的Partition那部分進行Action操作,這樣可以適當避免在ShuffledMapTask中分配的數據不均衡,導致單個Shuffle_shuffleId_mapId_0.data文件數據過大的問題。
具體的代碼實現如下:
也就是每個ResultTask會去獲取所有不同的MapId中相同的PartitionID部分Shuffle文件,而不是繼續按前面的Map進行分配,那意味著ResultTask將會去獲取所有Shuffle文件
Shuffle_shuffleId_mapId_0.data中的Partition那部分進行Action操作,這樣可以適當避免在ShuffledMapTask中分配的數據不均衡,導致單個Shuffle_shuffleId_mapId_0.data文件數據過大的問題。
具體的代碼實現如下:
1. 前言
在博客裏介紹了ShuffleWrite關於shuffleMapTask如何運行,輸出Shuffle結果到Shuffle_shuffleId_mapId_0.data數據文件中,每個executor需要向Driver匯報當前節點的Shuffle結果狀態,Driver保存結果信息進行下個Task的調度。2. StatusUpdate消息
當Executor運行完Task的時候需要向Driver匯報StatusUpdate的消息override def statusUpdate(taskId: Long, state: TaskState, data: ByteBuffer) { val msg= StatusUpdate(executorId, taskId, state, data) driver match { case Some(driverRef) => driverRef.send(msg) case None => logWarning(s"Drop $msg because has not yet connected to driver") } }
 整個結構體中包含了
整個結構體中包含了
- ExecutorId: Executor自己的ID
- TaskId: task分配的ID
- State: Task的運行狀態
LAUNCHING, RUNNING, FINISHED, FAILED, KILLED, LOST
- Data: 保存序列化的Result
2.1 Executor端發送
在Task運行後的結果,Executor會將結果首先序列化成ByteBuffer封裝成DirectTaskResult,再次序列化DirectTaskResult成ByteBuffer,很顯然序列化的結果的大小會決定不同的傳遞策略。在這裏會有兩個筏值來控制- 最大的返回結果大小,如果超過設定的最大返回結果時,返回的結果內容會被丟棄,只是返回序列化的InDirectTaskResult,裏面包含著BlockID和序列化後的結果大小
spark.driver.maxResultSize
- 最大的直接返回結果大小:如果返回的結果大於最大的直接返回結果大小,小於最大的返回結果大小,采用了保存的折中的策略,將序列化DirectTaskResult保存到BlockManager中,關於BlockManager可以參考前面寫的BlockManager系列,返回InDirectTaskResult,裏面包含著BlockID和序列化的結果大小
spark.task.maxDirectResultSize
- 直接返回:如果返回的結果小於等於最大的直接返回結果大小,將直接將序列化的DirectTaskResult返回給Driver端
val serializedResult: ByteBuffer = { if (maxResultSize > 0 && resultSize > maxResultSize) { logWarning(s"Finished $taskName (TID $taskId). Result is larger than maxResultSize " + s"(${Utils.bytesToString(resultSize)} > ${Utils.bytesToString(maxResultSize)}), " + s"dropping it.") ser.serialize(new IndirectTaskResult[Any](TaskResultBlockId(taskId), resultSize)) } else if (resultSize > maxDirectResultSize) { val blockId = TaskResultBlockId(taskId) env.blockManager.putBytes( blockId, new ChunkedByteBuffer(serializedDirectResult.duplicate()), StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK_SER) logInfo( s"Finished $taskName (TID $taskId). $resultSize bytes result sent via BlockManager)") ser.serialize(new IndirectTaskResult[Any](blockId, resultSize)) } else { logInfo(s"Finished $taskName (TID $taskId). $resultSize bytes result sent to driver") serializedDirectResult } }
2.2 Driver端接收
Driver端處理StatusUpdate的消息的代碼如下:
case StatusUpdate(executorId, taskId, state, data) => scheduler.statusUpdate(taskId, state, data.value) if (TaskState.isFinished(state)) { executorDataMap.get(executorId) match { case Some(executorInfo) => executorInfo.freeCores += scheduler.CPUS_PER_TASK makeOffers(executorId) case None => // Ignoring the update since we don‘t know about the executor. logWarning(s"Ignored task status update ($taskId state $state) " + s"from unknown executor with ID $executorId") } }
scheduler實例是TaskSchedulerImpl.scala
if (TaskState.isFinished(state)) { cleanupTaskState(tid) taskSet.removeRunningTask(tid) if (state == TaskState.FINISHED) { taskResultGetter.enqueueSuccessfulTask(taskSet, tid, serializedData) } else if (Set(TaskState.FAILED, TaskState.KILLED, TaskState.LOST).contains(state)) { taskResultGetter.enqueueFailedTask(taskSet, tid, state, serializedData) } }
statusUpdate函數調用了enqueueSuccessfulTask方法
def enqueueSuccessfulTask( taskSetManager: TaskSetManager, tid: Long, serializedData: ByteBuffer): Unit = { getTaskResultExecutor.execute(new Runnable { override def run(): Unit = Utils.logUncaughtExceptions { try { val (result, size) = serializer.get().deserialize[TaskResult[_]](serializedData) match { case directResult: DirectTaskResult[_] => if (!taskSetManager.canFetchMoreResults(serializedData.limit())) { return } // deserialize "value" without holding any lock so that it won‘t block other threads. // We should call it here, so that when it‘s called again in // "TaskSetManager.handleSuccessfulTask", it does not need to deserialize the value. directResult.value(taskResultSerializer.get()) (directResult, serializedData.limit()) case IndirectTaskResult(blockId, size) => if (!taskSetManager.canFetchMoreResults(size)) { // dropped by executor if size is larger than maxResultSize sparkEnv.blockManager.master.removeBlock(blockId) return } logDebug("Fetching indirect task result for TID %s".format(tid)) scheduler.handleTaskGettingResult(taskSetManager, tid) val serializedTaskResult = sparkEnv.blockManager.getRemoteBytes(blockId) if (!serializedTaskResult.isDefined) { /* We won‘t be able to get the task result if the machine that ran the task failed * between when the task ended and when we tried to fetch the result, or if the * block manager had to flush the result. */ scheduler.handleFailedTask( taskSetManager, tid, TaskState.FINISHED, TaskResultLost) return } val deserializedResult = serializer.get().deserialize[DirectTaskResult[_]]( serializedTaskResult.get.toByteBuffer) // force deserialization of referenced value deserializedResult.value(taskResultSerializer.get()) sparkEnv.blockManager.master.removeBlock(blockId) (deserializedResult, size) } // Set the task result size in the accumulator updates received from the executors. // We need to do this here on the driver because if we did this on the executors then // we would have to serialize the result again after updating the size. result.accumUpdates = result.accumUpdates.map { a => if (a.name == Some(InternalAccumulator.RESULT_SIZE)) { val acc = a.asInstanceOf[LongAccumulator] assert(acc.sum == 0L, "task result size should not have been set on the executors") acc.setValue(size.toLong) acc } else { a } } scheduler.handleSuccessfulTask(taskSetManager, tid, result) } catch { case cnf: ClassNotFoundException => val loader = Thread.currentThread.getContextClassLoader taskSetManager.abort("ClassNotFound with classloader: " + loader) // Matching NonFatal so we don‘t catch the ControlThrowable from the "return" above. case NonFatal(ex) => logError("Exception while getting task result", ex) taskSetManager.abort("Exception while getting task result: %s".format(ex)) } } }) }在函數中,反序列化的過程是通過線程池裏的線程來運行的,Netty的接收數據線程是不能被堵塞(同時還接受著別的消息),反序列化是耗時的任務,不能在Netty的消息處理線程中運行。
2.2.1 DirectTaskResult處理過程
- 直接反序列化成DirectTaskResult,反序列化後進行了整體返回內容的大小的判斷,在前面的2.1中介紹參數:spark.driver.maxResultSize,這個參數是Driver端的參數控制的,在Spark中會啟動多個Task,參數的控制是一個整體的控制所有的Tasks的返回結果的數量大小,當然單個task使用該筏值的控制也是沒有問題,因為只要有一個任務返回的結果超過maxResultSize,整體返回的數據也會超過maxResultSize。
- 對DirectTaskResult裏的result進行了反序列化。
2.2.2 InDirectTaskResult處理過程
- 通過size判斷大小是否超過spark.driver.maxResultSize筏值控制
- 通過BlockManager來獲取BlockID的內容反序列化成DirectTaskResult
- 對DirectTaskResult裏的result進行了反序列化
最後調用handleSuccessfulTask方法
sched.dagScheduler.taskEnded(tasks(index), Success, result.value(), result.accumUpdates, info)
回到了Dag的調度,向eventProcessLoop的隊列裏提交了CompletionEvent的事件
def taskEnded( task: Task[_], reason: TaskEndReason, result: Any, accumUpdates: Seq[AccumulatorV2[_, _]], taskInfo: TaskInfo): Unit = { eventProcessLoop.post( CompletionEvent(task, reason, result, accumUpdates, taskInfo)) }處理eventProcessLoop隊列的event是在DAG的線程處理的,在這裏我們不討論DAG的任務調度。
2.3 MapOutputTracker
MapOutputTracker是當運行完ShuffleMapTask的時候,ShuffleWrite會生成Shuffle_shuffleId_mapId_0.data、index文件,Executor需要將具體的信息返回給Driver,當Driver進行下一步的Task運算的時候,Executor也需要獲取具體Shuffle數據文件的信息進行下一步的action算子的運算,結構的保存、管理就是通過MapOutputTracker跟蹤器進行追蹤的。
2.3.1 RegisterMapOutput
Execute端 在ShuffleMapTask中運行後會生成一個MapStatus,也就是上圖的Map0結構,ComressedMapStatus、HighlyCompressedMapStatus這裏的兩個區別主要是增對Partition1...的size long的壓縮,但這裏的壓縮算法並不準確比,如CompressedMapStatus的算法:def compressSize(size: Long): Byte = { if (size == 0) { 0 } else if (size <= 1L) { 1 } else { math.min(255, math.ceil(math.log(size) / math.log(LOG_BASE)).toInt).toByte } }求Log1.1(size)的整數轉為byte,也就是支持最大1.1^255=35G左右 為何不需要計算精準的尺寸? 還記得前面博客裏提到的Shuffle_shuffleId_mapId_reduceId.index文件麽,這裏才是精準的位置,當讀取本地文件的時候,並不使用MapStatus裏的Size Size有何用? 有存在別的Execute獲取別的Execute的Shuffle結果文件,此時的size是獲取文件的大概位置。 MapStatus是ShuffleMapTask運行的結果,被序列化成DirectTaskResult中的value,通過StatusUpdate消息傳遞 Driver端 DAG線程調度處理CompletionEvent的事件
private[scheduler] def handleTaskCompletion(event: CompletionEvent) { ............ case smt: ShuffleMapTask => val shuffleStage = stage.asInstanceOf[ShuffleMapStage] updateAccumulators(event) val status = event.result.asInstanceOf[MapStatus] val execId = status.location.executorId logDebug("ShuffleMapTask finished on " + execId) if (failedEpoch.contains(execId) && smt.epoch <= failedEpoch(execId)) { logInfo(s"Ignoring possibly bogus $smt completion from executor $execId") } else { shuffleStage.addOutputLoc(smt.partitionId, status) } if (runningStages.contains(shuffleStage) && shuffleStage.pendingPartitions.isEmpty) { markStageAsFinished(shuffleStage) logInfo("looking for newly runnable stages") logInfo("running: " + runningStages) logInfo("waiting: " + waitingStages) logInfo("failed: " + failedStages) // We supply true to increment the epoch number here in case this is a // recomputation of the map outputs. In that case, some nodes may have cached // locations with holes (from when we detected the error) and will need the // epoch incremented to refetch them. // TODO: Only increment the epoch number if this is not the first time // we registered these map outputs. mapOutputTracker.registerMapOutputs( shuffleStage.shuffleDep.shuffleId, shuffleStage.outputLocInMapOutputTrackerFormat(), changeEpoch = true) clearCacheLocs() if (!shuffleStage.isAvailable) { // Some tasks had failed; let‘s resubmit this shuffleStage // TODO: Lower-level scheduler should also deal with this logInfo("Resubmitting " + shuffleStage + " (" + shuffleStage.name + ") because some of its tasks had failed: " + shuffleStage.findMissingPartitions().mkString(", ")) submitStage(shuffleStage) } else { // Mark any map-stage jobs waiting on this stage as finished if (shuffleStage.mapStageJobs.nonEmpty) { val stats = mapOutputTracker.getStatistics(shuffleStage.shuffleDep) for (job <- shuffleStage.mapStageJobs) { markMapStageJobAsFinished(job, stats) } } submitWaitingChildStages(shuffleStage) } }
當處理shuffleMapTask的結果的時候,mapOutputTracker.registerMapOutputs進行了MapOutputs的註冊
protected val mapStatuses = new ConcurrentHashMap[Int, Array[MapStatus]]().asScala def registerMapOutputs(shuffleId: Int, statuses: Array[MapStatus], changeEpoch: Boolean = false) { mapStatuses.put(shuffleId, statuses.clone()) if (changeEpoch) { incrementEpoch() } }在Driver端保存了一個Map是以ShuffldId為Key的MapStatus的數組
2.3.2 獲取MapStatus
在ResultTask中,通過獲取反序列化的ShuffledRDD,在Fetch Shuffle數據文件的時候val blockFetcherItr = new ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator( context, blockManager.shuffleClient, blockManager, mapOutputTracker.getMapSizesByExecutorId(handle.shuffleId, startPartition, endPartition), // Note: we use getSizeAsMb when no suffix is provided for backwards compatibility SparkEnv.get.conf.getSizeAsMb("spark.reducer.maxSizeInFlight", "48m") * 1024 * 1024, SparkEnv.get.conf.getInt("spark.reducer.maxReqsInFlight", Int.MaxValue))
通過getMapSizesByExecutorId獲取ShuffledId所對應的MapStatus
def getMapSizesByExecutorId(shuffleId: Int, startPartition: Int, endPartition: Int) : Seq[(BlockManagerId, Seq[(BlockId, Long)])] = { logDebug(s"Fetching outputs for shuffle $shuffleId, partitions $startPartition-$endPartition") val statuses = getStatuses(shuffleId) // Synchronize on the returned array because, on the driver, it gets mutated in place statuses.synchronized { return MapOutputTracker.convertMapStatuses(shuffleId, startPartition, endPartition, statuses) } }
在getStatuses方法中
private def getStatuses(shuffleId: Int): Array[MapStatus] = { val statuses = mapStatuses.get(shuffleId).orNull if (statuses == null) { logInfo("Don‘t have map outputs for shuffle " + shuffleId + ", fetching them") val startTime = System.currentTimeMillis var fetchedStatuses: Array[MapStatus] = null fetching.synchronized { // Someone else is fetching it; wait for them to be done while (fetching.contains(shuffleId)) { try { fetching.wait() } catch { case e: InterruptedException => } } // Either while we waited the fetch happened successfully, or // someone fetched it in between the get and the fetching.synchronized. fetchedStatuses = mapStatuses.get(shuffleId).orNull if (fetchedStatuses == null) { // We have to do the fetch, get others to wait for us. fetching += shuffleId } } if (fetchedStatuses == null) { // We won the race to fetch the statuses; do so logInfo("Doing the fetch; tracker endpoint = " + trackerEndpoint) // This try-finally prevents hangs due to timeouts: try { val fetchedBytes = askTracker[Array[Byte]](GetMapOutputStatuses(shuffleId)) fetchedStatuses = MapOutputTracker.deserializeMapStatuses(fetchedBytes) logInfo("Got the output locations") mapStatuses.put(shuffleId, fetchedStatuses) } finally { fetching.synchronized { fetching -= shuffleId fetching.notifyAll() } } } logDebug(s"Fetching map output statuses for shuffle $shuffleId took " + s"${System.currentTimeMillis - startTime} ms") if (fetchedStatuses != null) { return fetchedStatuses } else { logError("Missing all output locations for shuffle " + shuffleId) throw new MetadataFetchFailedException( shuffleId, -1, "Missing all output locations for shuffle " + shuffleId) } } else { return statuses } }
- 封裝了一層緩存mapStatus,對同一個Executor來說,裏面的線程都是運行同一個Driver的提交的任務,對相同的shuffeID,MapStatus是一樣的
- 對同一個Executor、ShuffeID來說,通過Driver獲取信息只需要一次,Driver裏保存的Shuffle的結果是單點的,對同一個Executor來說獲取同一個ShuffleID只需要請求一次,在Traker裏面保存了一個隊列fetching,裏面保存的ShuffeID代表的是有線程正在從Driver端獲取ShuffleID的MapStatus,如果發現有值,當前線程會等待,直到其他的線程獲取ShuffleID狀態並保存到緩存結束,當前線程直接從緩存中獲取當前狀態
- Executor 向Driver發送GetMapOutputStatuses(shuffleId)消息
- Driver收到GetMapOutputStatuses消息後保存到消息隊列mapOutputRequests,Map-Output-Dispatcher-x多線程處理消息隊列,返回序列化的MapStatus
- Executor反序列化成MapStatus
2.2.3 以BlockManagerId為key的Shuffle的序列
在前面的博客裏提到過Driver分配Task的數量的策略是依賴於Partition,在單個任務ShuffledMapTask對Data進行分片也是依賴於Partition 前面一個的Partition 是MapId,後面一個Partition 指的是ReduceId 在ResultTask裏所取的Shuffle數據文件中的Partition是ReduceId,而不是MapId 也就是每個ResultTask會去獲取所有不同的MapId中相同的PartitionID部分Shuffle文件,而不是繼續按前面的Map進行分配,那意味著ResultTask將會去獲取所有Shuffle文件
Shuffle_shuffleId_mapId_0.data中的Partition那部分進行Action操作,這樣可以適當避免在ShuffledMapTask中分配的數據不均衡,導致單個Shuffle_shuffleId_mapId_0.data文件數據過大的問題。
具體的代碼實現如下:
也就是每個ResultTask會去獲取所有不同的MapId中相同的PartitionID部分Shuffle文件,而不是繼續按前面的Map進行分配,那意味著ResultTask將會去獲取所有Shuffle文件
Shuffle_shuffleId_mapId_0.data中的Partition那部分進行Action操作,這樣可以適當避免在ShuffledMapTask中分配的數據不均衡,導致單個Shuffle_shuffleId_mapId_0.data文件數據過大的問題。
具體的代碼實現如下:
private def convertMapStatuses( shuffleId: Int, startPartition: Int, endPartition: Int, statuses: Array[MapStatus]): Seq[(BlockManagerId, Seq[(BlockId, Long)])] = { assert (statuses != null) val splitsByAddress = new HashMap[BlockManagerId, ArrayBuffer[(BlockId, Long)]] for ((status, mapId) <- statuses.zipWithIndex) { if (status == null) { val errorMessage = s"Missing an output location for shuffle $shuffleId" logError(errorMessage) throw new MetadataFetchFailedException(shuffleId, startPartition, errorMessage) } else { for (part <- startPartition until endPartition) { splitsByAddress.getOrElseUpdate(status.location, ArrayBuffer()) += ((ShuffleBlockId(shuffleId, mapId, part), status.getSizeForBlock(part))) } } } splitsByAddress.toSeq }
Spark Shuffle(二)Executor、Driver之間Shuffle結果消息傳遞、追蹤(轉載)
