鎖之ReentrantLock
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-06-26
獲取 ima images 操作 同步 zab ext 增加 private 源碼結構圖
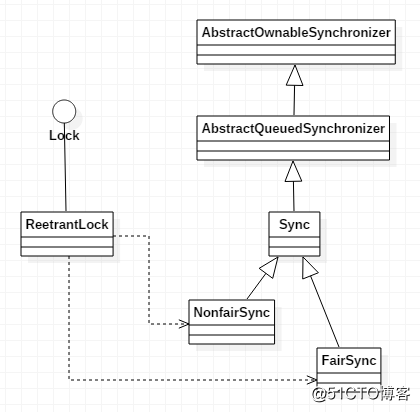
Lock源碼
public interface Lock { //獲取鎖 void lock(); /** *當前線程的鎖沒有中斷才能獲取鎖 * if (Thread.interrupted()) * throw new InterruptedException(); */ void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException; //獲取鎖是否成功。true表示獲取到鎖,false表示沒有獲取到鎖 boolean tryLock(); // 嘗試獲取鎖,並等待指定的時間 boolean tryLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException; // 釋放鎖 void unlock(); // LOCK條件 Condition newCondition(); }
ReentrantLock源碼
public class ReentrantLock implements Lock, java.io.Serializable { // 同步器,是整個鎖機制的實現者 private final Sync sync; // 定義的抽象靜態內部類。實現基本的功能 abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer { // 抽象方法。由公平鎖和非公平鎖自己實現 abstract void lock(); // 釋放鎖 protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) { // 鎖的計數器。釋放一次計數器減1,直到為0,則整個鎖完全釋放,才能被其他線程獲取該鎖。 int c = getState() - releases; // 此類型鎖是可重入鎖。因此是以thread為粒度的。必須判斷當前線程是否與持有鎖線程一致。 if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread()) throw new IllegalMonitorStateException(); boolean free = false; // 當鎖的計數器為0時,整個鎖釋放。 if (c == 0) { free = true; setExclusiveOwnerThread(null); } setState(c); return free; } // 默認實現的一個非公平鎖的獲取嘗試獲取方法 final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) { final Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); int c = getState(); // 如果鎖的計數器為0,則表示沒有鎖。 if (c == 0) { // compareAndSetState方法實際調用的是unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, expect, update); // 直接操作的JVM。並給當前線程持有鎖。 if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) { setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); return true; } } // 如果計數器不為0,但當前線程就是持有鎖的線程。則鎖的計數器增加。 else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) { int nextc = c + acquires; if (nextc < 0) // overflow throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded"); setState(nextc); return true; } // 如果計數器不為0,同時當前線程不是持有鎖的線程。則加鎖失敗。 return false; } } // 非公平所的實現器 static final class NonfairSync extends Sync { // 加鎖。 final void lock() { if (compareAndSetState(0, 1)) //非公平加鎖 setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread()); else acquire(1); // 如果加鎖不成功,則放入隊列 } // 試著加鎖 protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) { return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires); } } // 公平鎖 static final class FairSync extends Sync { // 加鎖,隊列 final void lock() { acquire(1); } // 試著加鎖 protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) { final Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); int c = getState(); if (c == 0) { if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() && compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) { setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); return true; } } else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) { int nextc = c + acquires; if (nextc < 0) throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded"); setState(nextc); return true; } return false; } } }
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer源碼
// 存儲隊列鎖的存儲node.是一個雙向的鏈表結構。 static final class Node { // 前一個node volatile Node prev; // 後一個node volatile Node next; // 該node所對應的線程 volatile Thread thread; } // 整個隊列鎖的第一個node. private transient volatile Node head; // 整個隊列鎖的第後個node. private transient volatile Node tail; // 鎖的狀態。計數器 private volatile int state; // 加鎖的關鍵點。通過navtive 方法unsafe直接操作CPU。 protected final boolean compareAndSetState(int expect, int update) { return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, expect, update); }
總結
Lock這種以類的方式來實現鎖的機制。
優點:
1.加鎖和釋放鎖獨立,可以分開來控制。
2.tryLock的方法可以嘗試加鎖,不會像sychnorized一致阻塞。
3.實現了公平鎖和非公平鎖。sychnorized只能是非公平鎖。
缺點:
1.增加了代碼的復雜度。
2.相比sychnorized的自動加鎖和釋放鎖,Lock需要手動,容易忘記,從而出現重大的隱患。
經過JDK的不斷更新,sychnorized與lock的性能相差不大,官方建議使用sychnorized方法加鎖。
鎖之ReentrantLock
