廣度優先搜尋雙佇列通用程式設計模板
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-10-31
廣度優先搜尋主要用於解決求最短問題,如最短路徑,最少變化步數問題等等,思想是從起點出發,按層遍歷,直到搜尋到目標或者已經搜尋完全部區域。通常利用佇列實現廣度優先搜尋,我這裡使用的雙佇列法,用一個佇列cur表示當前層,next表示由當前層擴充套件的下一層,用雙佇列有個好處是我們只需要定義一個全域性變數level就能記錄擴充套件的層數(即路徑長度),如果要求輸出具體最短路徑的話,我們還需要利用一個unordered_map物件來儲存路徑樹,為了避免搜尋重複節點,我們需要標記已經搜尋過的狀態,這裡利用unordered_set物件來儲存已經搜尋過的狀態(注意如果unordered_map或unordered_set儲存的是自定義的結構體時,我們需要自己定義==操作符合hash函式);我們還需要一個變數isfinsh來標記是否已經搜尋到目標。
下面用一個具體的例子來說明廣度優先搜尋雙佇列程式設計模板的使用:
具體實現的程式如下:
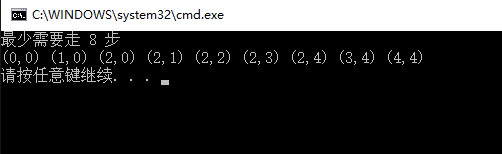
程式執行結果如下:#include "stdafx.h" #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <unordered_map> #include <unordered_set> using namespace std; typedef struct node { int x; int y; node(int x=0,int y=0):x(x),y(y){}; bool operator==(const node &rhs) const { return x==rhs.x && y==rhs.y; }; }state; struct hash_func //自定義的hash 函式 { size_t operator()(const node &myNode) const { return 999*myNode.x+myNode.y; } }; //根據father儲存的路徑樹得到具體路徑 void findPath(vector<vector<int>> &result,unordered_map<state,state,hash_func> &father,state start,state child) { state tmpState=child; while(tmpState.x!=start.x || tmpState.y!=start.y) { int tmpPoint[2]={tmpState.x,tmpState.y}; vector<int> tmpResult(tmpPoint,tmpPoint+2); result.push_back(tmpResult); tmpState=father[tmpState]; } int tmpPoint[2]={tmpState.x,tmpState.y}; vector<int> tmpResult(tmpPoint,tmpPoint+2); result.push_back(tmpResult); reverse(result.begin(),result.end()); } vector<vector<int>> bfs(vector<vector<int>> &map,int &step,state &start,state &end) { vector<vector<int>> result; if (map.size()<=0) { return result; } if (start.x==end.x && start.y==end.y) { return result; } int row=map.size(); int col=map[0].size(); int extend[4][2]={{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}}; //按右-下-左-上順時針方向擴充套件狀態 //用於標記已經擴充套件過的狀態,此處也可以利用一個二維bool陣列,但是為了更具一般性,此處採用unordered_set //注意:要使用unordered_set,unordered_map,node需要有定義的==運算子和hash函式。 unordered_set<state,hash_func> selected; unordered_map<state,state,hash_func> father;//用於記錄路徑樹 queue<state> cur; //用於儲存當前層的狀態 queue<state> next; //儲存由cur擴展出的下一層狀態 int level=0; //用於標記擴充套件的層數,可用於求最短路徑長度 bool isFinish=false; //標記搜尋是否結束 cur.push(start); selected.insert(start); while(!cur.empty()&&!isFinish) { ++step; while(!cur.empty()&&!isFinish) { state curState=cur.front(); cur.pop(); for(int i=0;i<4;++i) { int tmpr=curState.x+extend[i][0]; int tmpc=curState.y+extend[i][1]; if (tmpc<0 ||tmpc>=row ||tmpr<0 || tmpr>=col) continue; if (map[tmpr][tmpc]==1) continue; state tmpState(tmpr,tmpc); if (tmpc==end.x && tmpr==end.y) { isFinish=true; father[tmpState]=curState; break; } if (selected.count(tmpState)==0) { next.push(tmpState); father[tmpState]=curState; selected.insert(tmpState); } } } swap(cur,next); } if (isFinish) { findPath(result,father,start,end); } return result; } int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { int inputArray[5][5]={{0,1,0,0,0},{0,1,0,1,0},{0,0,0,0,0},{0,1,1,1,0},{0,0,0,1,0}}; vector<vector<int>> result; vector<vector<int>> map; for (int i=0;i<5;++i) { vector<int> tmpMap(inputArray[i],inputArray[i]+5); map.push_back(tmpMap); } int step=0; state start(0,0); state end(4,4); result=bfs(map,step,start,end); cout<<"最少需要走 "<<step<<" 步"<<endl; for (int i=0;i<result.size();++i) { cout<<"("<<result[i][0]<<","<<result[i][1]<<")"<<" "; } cout<<endl; return 0; }