【Python+Tensorflow】Deep Q Network (DQN) 迷宮示例程式碼整理
Overview
本文程式碼整理自Morvan Zhou(莫煩Python [1])的機器學習相關教程 - 強化學習 - DQN部分 [2]
Deep Q Network簡稱DQN,結合了Q learning和Neural networks的優勢。如果我們使用tabular Q learning,對於每一個state,action我們都需要存放在一張q_table的表中。而在現實生活中,情況可就比迷宮的狀況複雜多了,我們有千千萬萬個state,如果將這千萬個state的值都放在表中,受限於我們計算機硬體,這樣從表中獲取資料,更新資料是沒有效率的,這就是 DQN 產生的原因了。我們可以使用神經網路來估算這個state的值,這樣就不需要一張表了。
演算法流程:
網路結構:
為了使用Tensorflow來實現DQN,比較推薦的方式是搭建兩個神經網路:target_net用於預測q_target值,不會及時更新引數;eval_net用於預測q_eval,這個神經網路擁有最新的神經網路引數。不過這兩個神經網路結構是完全一樣的,只是裡面的引數不一樣。

程式碼中還提供了一種修改版DQN:
將q_target的計算也加在了Tensorflow的graph裡面。不過實測的時候效率會比之前的方法慢10%左右,原因我想應該是使用了one hot,而且貌似丟失了一點精度,因為在q_target轉換的時候,之前是用numpy在做,而且是以float64的進度計算的,但是如果將q_target的計算全部挪進tf中,精度都是float32。不過這種結構還是有好處的,作為學習樣本的話,計算結構全部在tensorboard上,程式碼結構也更好理解。

詳細程式碼另可參考:GitHub [3]
Code
本教程程式碼主要基於一個簡單的迷宮環境,重點在實現 DQN 演算法
迷宮如下圖所示,紅色表示explorer,黃色表示paradise,黑色表示hell,白色表示ground(可自定義)
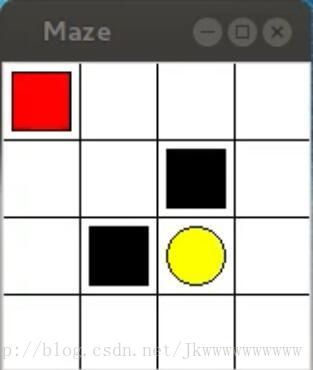
本演算法主要模擬的是learn to move explorer to paradise的過程
之後我們可以再拿著做好的DQN演算法去嘗試其他更有意思的環境
#!/usr/bin/env python
#-*- coding: utf-8 -*-
########################################################### References
[1] 教程一覽 - 莫煩Python
[2] DQN演算法更新 (Tensorflow) - 莫煩Python
[3] GitHub - MorvanZhou/tutorials
希望能夠對大家有所幫助~
