孔維瀅 20171010110《面向物件程式設計(java)》第十週學習總結
理論知識:
1.泛型類的定義,一個泛型類就是具有一個或多 個型別變數的類,即建立用型別作為引數的類。 如: class Generics<K,V>;
2.泛型方法,除了泛型類外,還可以只單獨定義一個方法作為泛型方法,用於指定方法引數或者返回值為 泛型型別,留待方法呼叫時確定。泛型方法可以宣告在泛型類中,也可以宣告在普通類中。
3.泛型介面的定義,public interface IPool <T> { T get(); int add(T t); }
4.泛型變數的限定,上界:public class NumberGeneric< T extends Number>
下界:List<? superCashCard> cards = new ArrayList<T>();
5.萬用字元的型別限定,Pair<? extends Employee>
1、實驗目的與要求
(1) 理解泛型概念;
(2) 掌握泛型類的定義與使用;
(3) 掌握泛型方法的宣告與使用;
(4) 掌握泛型介面的定義與實現;
(5)瞭解泛型程式設計,理解其用途。
2、實驗內容和步驟
實驗1:
測試程式1:
Pair.java
package pair1;
/**
* @version 1.00 2004-05-10
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class Pair<T> //Pair類引入一個型別變數T
{
private T first;//類定義中的型別變數指定方法的返回型別以及域和區域性變數的型別
private T second;
public Pair() { first = null; second = null; }
public Pair(T first, T second) { this.first = first; this.second = second; }
public T getFirst() { return first; }
public T getSecond() { return second; }
public void setFirst(T newValue) { first = newValue; }
public void setSecond(T newValue) { second = newValue; }
}
PairTest.java
package pair1;
/**
* @version 1.01 2012-01-26
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class PairTest1
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String[] words = { "Mary", "had", "a", "little", "lamb" };//初始化String物件陣列
Pair<String> mm = ArrayAlg.minmax(words);//通過類名呼叫minmax方法
System.out.println("min = " + mm.getFirst());
System.out.println("max = " + mm.getSecond());
}
}
class ArrayAlg
{
/**
* Gets the minimum and maximum of an array of strings.
* @param a an array of strings
* @return a pair with the min and max value, or null if a is null or empty
*/
public static Pair<String> minmax(String[] a)//在非泛型類中宣告一個泛型方法
{
if (a == null || a.length == 0) return null;
String min = a[0];
String max = a[0];
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++)
{
if (min.compareTo(a[i]) > 0) min = a[i];//字串物件比較,ASCII碼比較
if (max.compareTo(a[i]) < 0) max = a[i];
}
return new Pair<>(min, max);//泛型類作為返回值
}
}
輸出結果:
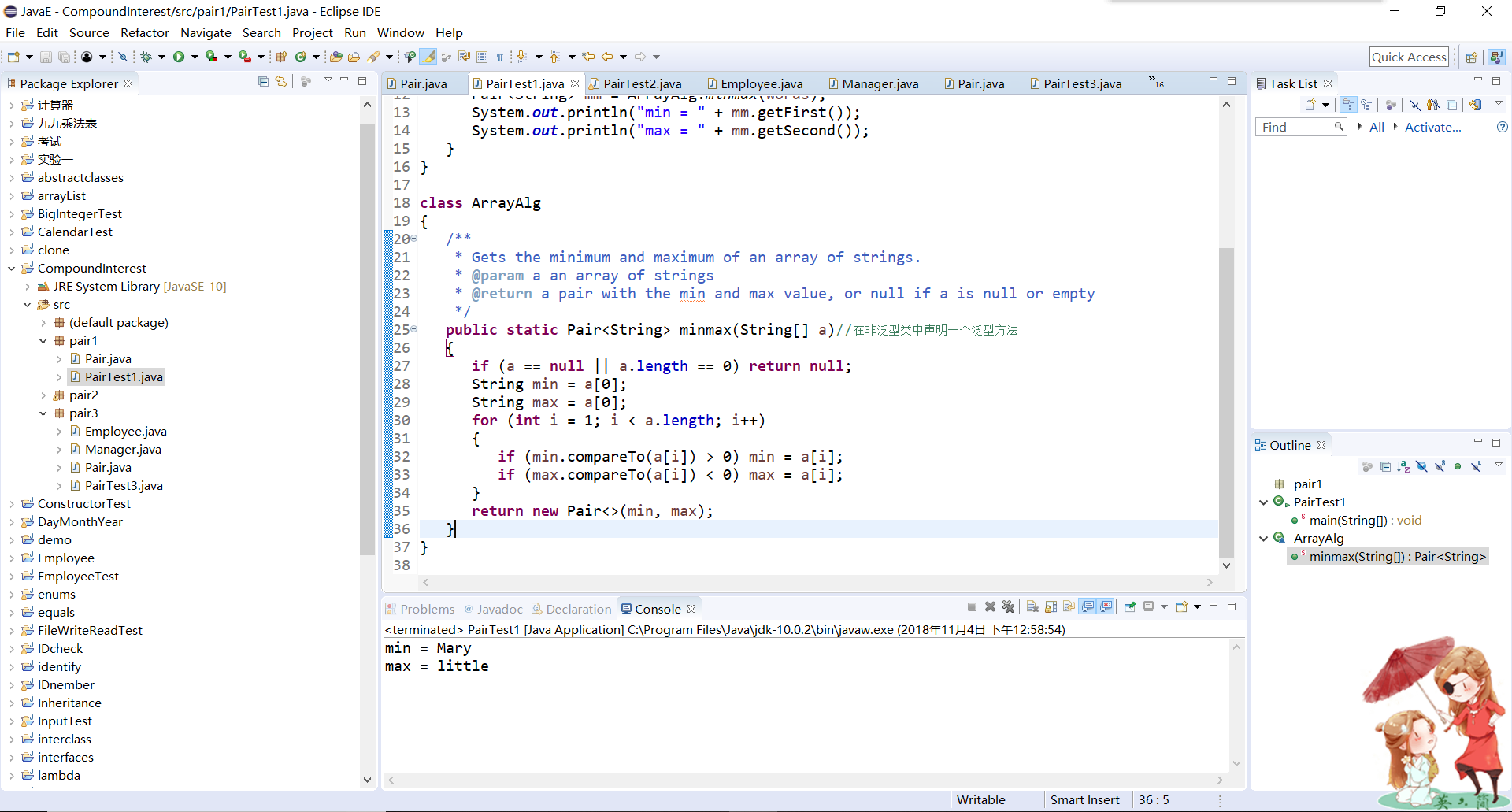
測試程式2:
PairTest2.java
package pair2;
import java.time.*;
/**
* @version 1.02 2015-06-21
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class PairTest2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LocalDate[] birthdays =
{
LocalDate.of(1906, 12, 9), // G. Hopper
LocalDate.of(1815, 12, 10), // A. Lovelace
LocalDate.of(1903, 12, 3), // J. von Neumann
LocalDate.of(1910, 6, 22), // K. Zuse
};//初始化LocalDate物件陣列
Pair<LocalDate> mm = ArrayAlg.minmax(birthdays);//通過類名呼叫minmax方法
System.out.println("min = " + mm.getFirst());
System.out.println("max = " + mm.getSecond());
}
}
class ArrayAlg
{
/**
Gets the minimum and maximum of an array of objects of type T.
@param a an array of objects of type T
@return a pair with the min and max value, or null if a is
null or empty
*/
public static <T extends Comparable> Pair<T> minmax(T[] a) //將T限制為實現了Comparable介面的類,Comparable介面本身就是一個泛型類
{
if (a == null || a.length == 0) return null;
T min = a[0];
T max = a[0];
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++)
{
if (min.compareTo(a[i]) > 0) min = a[i];
if (max.compareTo(a[i]) < 0) max = a[i];
}
return new Pair<>(min, max);
}
}
輸出結果:

測試程式3:
Employee.java
package pair3;
/**
* @version 1.01 2012-01-26
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class PairTest3
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Manager ceo = new Manager("Gus Greedy", 800000, 2003, 12, 15);
Manager cfo = new Manager("Sid Sneaky", 600000, 2003, 12, 15);
Pair<Manager> buddies = new Pair<>(ceo, cfo);//buddies裡Manager物件
printBuddies(buddies);
ceo.setBonus(1000000);
cfo.setBonus(500000);
Manager[] managers = { ceo, cfo };
Pair<Employee> result = new Pair<>();//result裡Employee物件
minmaxBonus(managers, result);
System.out.println("first: " + result.getFirst().getName()
+ ", second: " + result.getSecond().getName());
maxminBonus(managers, result);
System.out.println("first: " + result.getFirst().getName()
+ ", second: " + result.getSecond().getName());
}
public static void printBuddies(Pair<? extends Employee> p)
{
Employee first = p.getFirst();
Employee second = p.getSecond();
System.out.println(first.getName() + " and " + second.getName() + " are buddies.");
}
public static void minmaxBonus(Manager[] a, Pair<? super Manager> result)
{
if (a.length == 0) return;
Manager min = a[0];
Manager max = a[0];
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++)
{
if (min.getBonus() > a[i].getBonus()) min = a[i];
if (max.getBonus() < a[i].getBonus()) max = a[i];
}
result.setFirst(min);
result.setSecond(max);
}
public static void maxminBonus(Manager[] a, Pair<? super Manager> result)//該方法的引數result的Manager的父類的物件
{
minmaxBonus(a, result);
PairAlg.swapHelper(result); // OK--swapHelper captures wildcard type
}
// Can't write public static <T super manager> ...
}
class PairAlg
{
public static boolean hasNulls(Pair<?> p)
{
return p.getFirst() == null || p.getSecond() == null;
}
public static void swap(Pair<?> p) //引數p任意一種型別的物件
{ swapHelper(p); }
public static <T> void swapHelper(Pair<T> p)//p呼叫方法時指定的一種型別T的物件
{
T t = p.getFirst();
p.setFirst(p.getSecond());
p.setSecond(t);
}
}
Employee.java
package pair3;
import java.time.*;
public class Employee
{
private String name;
private double salary;
private LocalDate hireDay;
public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day)
{
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day);
}
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
public double getSalary()
{
return salary;
}
public LocalDate getHireDay()
{
return hireDay;
}
public void raiseSalary(double byPercent)
{
double raise = salary * byPercent / 100;
salary += raise;
}
}
Manager.java
package pair3;
public class Manager extends Employee
{
private double bonus;
/**
@param name the employee's name
@param salary the salary
@param year the hire year
@param month the hire month
@param day the hire day
*/
public Manager(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day)
{
super(name, salary, year, month, day);
bonus = 0;
}
public double getSalary()
{
double baseSalary = super.getSalary();
return baseSalary + bonus;
}
public void setBonus(double b)
{
bonus = b;
}
public double getBonus()
{
return bonus;
}
}
輸出結果:
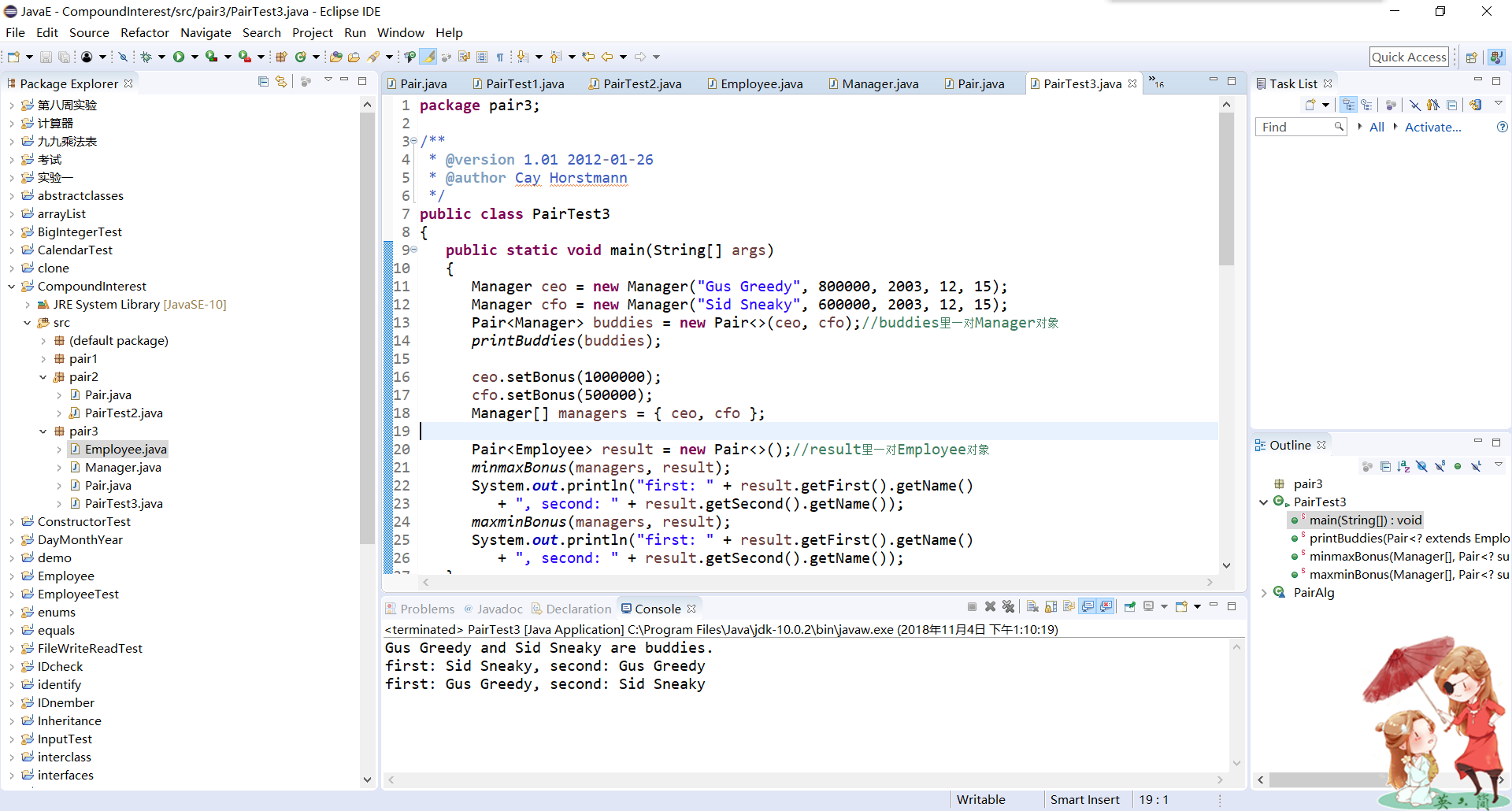
實驗2:程式設計練習:
程式設計練習1:實驗九程式設計題總結
總結1:
程式總體結構說明:Identify類和Person類
模組說明:Identify類和Person類
Identify.java
package 第八週實驗;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Identify {
private static ArrayList<Person> personlist;
public static void main(String[] args) {
personlist = new ArrayList<>();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
File file = new File("E:\\身份證號.txt");
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis));
String temp = null;
while ((temp = in.readLine()) != null) {
Scanner linescanner = new Scanner(temp);
linescanner.useDelimiter(" ");
String name = linescanner.next();
String number = linescanner.next();
String sex = linescanner.next();
String age = linescanner.next();
String hometown = linescanner.nextLine();
Person person = new Person();
person.setName(name);
person.setnumber(number);
person.setsex(sex);
int A = Integer.parseInt(age);
person.setage(A);
person.sethometown(hometown);
personlist.add(person);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("身份資訊檔案找不到");
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("身份資訊檔案讀取錯誤");
e.printStackTrace();
}
boolean isTrue = true;
while (isTrue) {
System.out.println("0.按姓名字典序輸出人員資訊;");
System.out.println("1.查詢最大年齡人員資訊;;");
System.out.println("2.查詢最小年齡人員資訊;");
System.out.println("3.尋找同鄉;");
System.out.println("4.尋找年齡相近的人;");
System.out.println("5.退出。");
String W = scanner.next();
switch(W) {
case "0":
Collections.sort(personlist);
System.out.println(personlist.toString());
break;
case "1":
int a = 0;
int j, c1 = 0, d1 = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < personlist.size(); i++) {
j = personlist.get(i).getage();
if (j > a) {
a = j;
c1 = i;
}
}
System.out.println("年齡最大:" + personlist.get(c1));
break;
case "2":
int b = 100;
int j1,c2 = 0,d2 = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < personlist.size(); i++) {
j1 = personlist.get(i).getage();
if (j1 < b) {
b = j1;
d2 = i;
}
}
System.out.println("年齡最小:" + personlist.get(d2));
break;
case "3":
System.out.println("籍貫:");
String search = scanner.next();
String place = search.substring(0, 3);
int i = 0;
for (; i < personlist.size(); i++) {
if (personlist.get(i).gethometown().substring(1, 4).equals(place))
System.out.println("你的同鄉是:" + personlist.get(i));
}
break;
case "4":
System.out.println("年齡:");
int yourage = scanner.nextInt();
int nearaga = agenear(yourage);
int value = yourage - personlist.get(nearaga).getage();
System.out.println("" + personlist.get(nearaga));
break;
case "5":
isTrue = false;
System.out.println("退出程式!");
break;
default:
System.out.println("檢查輸入!");
}
}
}
public static int agenear(int age) {
int j = 0, b = 53, value = 0, c = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < personlist.size(); i++) {
value = personlist.get(i).getage() - age;
if (value < 0)
value = -value;
if (value < b) {
b = value;
c = i;
}
}
return c;
}
}
Person.java
public class Person implements Comparable<Person> {
private String name;
private String number;
private String sex;
private int age;
private String hometown;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getnumber() {
return number;
}
public void setnumber(String number) {
this.number = number;
}
public String getsex() {
return sex;
}
public void setsex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public int getage() {
return age;
}
public void setage(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String gethometown() {
return hometown;
}
public void sethometown(String hometown) {
this.hometown = hometown;
}
public int compareTo(Person o) {
return this.name.compareTo(o.getName());
}
public String toString() {
return name + " " + sex + " " + age + " " + number + " " + hometown + "\n";
}
}
目前程式設計存在的困難與問題:
1.對於程式碼功能的使用不熟練;
2.對於編寫程式碼時,關於程式碼整體構造沒有一個清晰的想法;
3.總是無法寫出完全符合題目要求的程式碼,總出現報錯;
總結2:
程式總體結構說明 : Exam類 main函式
模組說明:Exam類
Exam.java
package 計算器;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Random;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class Exam{
int sum;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Exam exam = new Exam();
exam.sum = 0;
Random r = new Random ();
PrintWriter output = null;
try {
output = new PrintWriter("E://text.txt");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
for(int i = 0;i<10;i++) {
exam.score();
}
System.out.println("你的總分為:"+exam.sum);
output.println("你的總分為:"+exam.sum);
output.close();
}
private void score() {
Random r = new Random ();
int m;
m = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 4);
switch(m) {
case 0:
int a,b,c;
a = r.nextInt() % 100;
b = r.nextInt() % 100;
System.out.println(a + "+" + "(" + b + ")=");
Scanner x = new Scanner(System.in);
c = x.nextInt();
if(c != a+b)
System.out.println("答案錯誤!");
else {
System.out.println("答案正確!");
sum += 10;
}
break;
case 1:
int o,p,q;
o = r.nextInt() % 100;
p = r.nextInt() % 100;
System.out.println(o + "-" + "(" + p + ")=");
Scanner y = new Scanner(System.in);
q = y.nextInt();
if(q != o-p)
System.out.println("答案錯誤!");
else {
System.out.println("答案正確!");
sum += 10;
}
break;
case 2:
int d,e,f;
d = r.nextInt() % 100;
e = r.nextInt() % 100;
System.out.println(d + "*" +"("+ e + ")" + "=");
Scanner z = new Scanner(System.in);
f = z.nextInt();
if(f != d * e)
System.out.println("答案錯誤!");
else {
System.out.println("答案正確!");
sum += 10;
}
break;
case 3:
int h,i,j;
h = r.nextInt() % 100;
i = r.nextInt() % 100;
if(i == 0)
i++;
System.out.println(h + "/" +"("+ i + ")" + "=");
Scanner u = new Scanner(System.in);
j = u.nextInt();
if(j != h/i)
System.out.println("答案錯誤!");
else {
System.out.println("答案正確!");
sum += 10;
}
break;
}
}
}
目前程式設計存在的困難與問題:
1.程式碼不完美,並不完全符合題目要求;
2.計算題的除法運算存在問題,在上面的程式碼中,如果除數 i 為0,則 i 累加1,而不是隨機在給出一個不為0的數。
3.執行多次,會出現只給出8道題或9道題的情況。
程式設計練習2:
Student.java
package 計算器;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Studentexam {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
Studentexam s = new Studentexam();
PrintWriter out = null;
try {
out = new PrintWriter("test.txt");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("檔案輸出失敗");
e.printStackTrace();
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
int a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
int b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
int m;
Random rand = new Random();
m = (int) rand.nextInt(4) + 1;
switch (m) {
case 1:
a = b + (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
while(b == 0){
b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
}
while(a % b != 0){
a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
}
System.out.println(a + "/" + b + "=");
int c0 = in.nextInt();
out.println(a + "/" + b + "=" + c0);
if (c0 == s.chufa(a, b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("回答正確!");
}
else {
System.out.println("回答錯誤!");
}
break;
case 2:
System.out.println(a + "*" + b + "=");
int c = in.nextInt();
System.out.println(a + "*" + b + "=" + c);
if (c == s.chengfa(a, b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("回答正確!");
} else {
System.out.println("回答錯誤!");
}
break;
case 3:
System.out.println(a + "+" + b + "=");
int c1 = in.nextInt();
out.println(a + "+" + b + "=" + c1);
if (c1 == s.jiafa(a, b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("回答正確!");
} else {
System.out.println("回答錯誤!");
}
break;
case 4:
while (a < b) {
b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
}
System.out.println(a + "-" + b + "=");
int c2 = in.nextInt();
out.println(a + "-" + b + "=" + c2);
if (c2 == s.jianfa(a, b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("回答正確!");
} else {
System.out.println("回答錯誤!");
}
break;
}
}
System.out.println("你的總成績為" + sum);
out.println("你的總成績為" + sum);
out.close();
}
public int jiafa(int a,int b) {
return a + b;
}
public int jianfa(int a, int b) {
return a - b;
}
public int chengfa(int a, int b) {
return a * b;
}
public int chufa(int a, int b) {
if (b != 0 && a%b==0)
return a / b;
else
return 0;
}
}
Student.java
package 計算器;
public class Student<T> {
private T a;
private T b;
public Student() {
a = null;
b = null;
}
public Student(T a, T b) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
}
}
輸出結果:
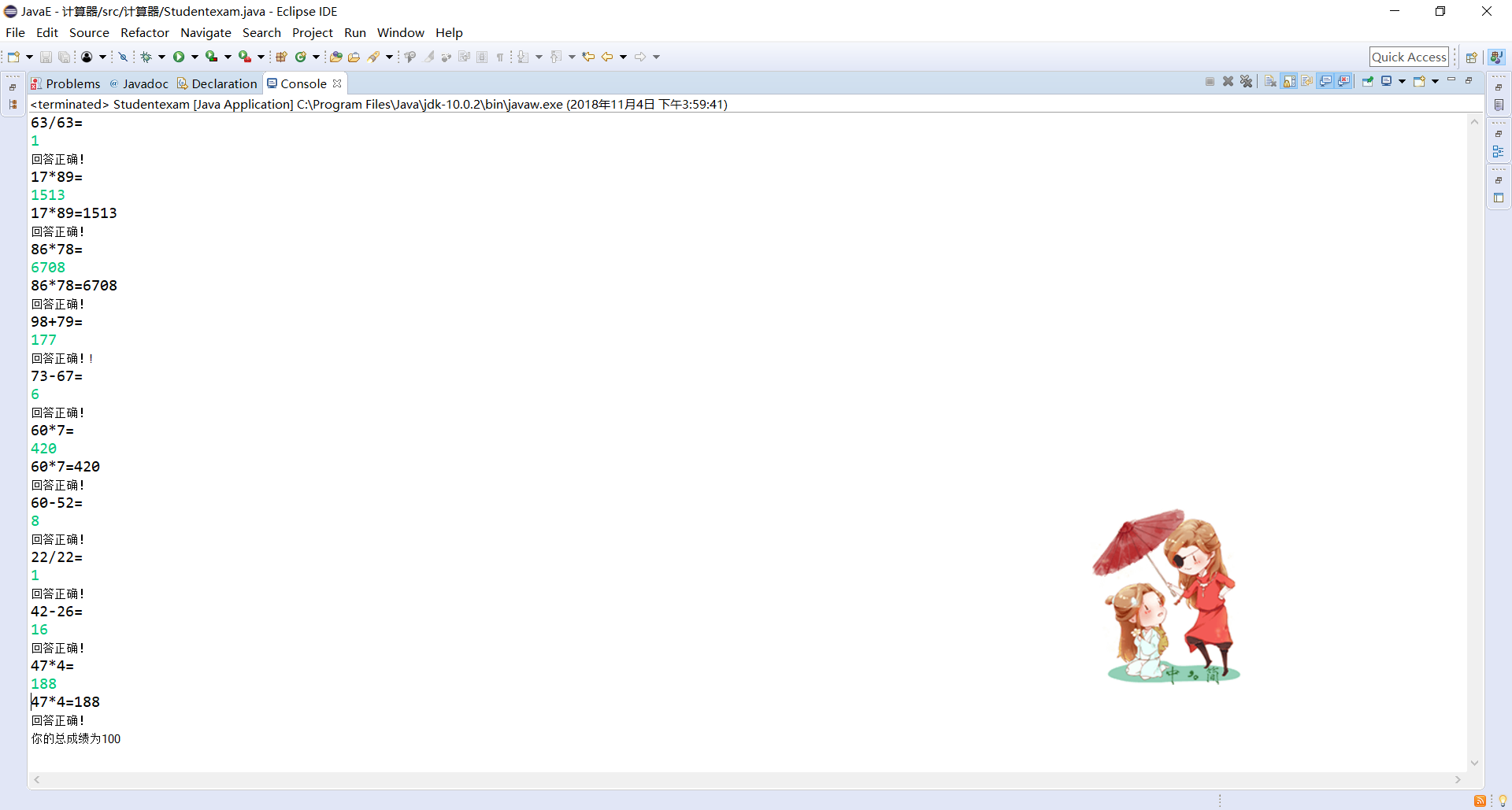
總結:
本週,我們學習了泛型程式設計,雖然對於泛型的定義不難理解但是我覺得自己的程式設計能力要比讀程式碼的能力弱,在寫程式時腦子對於程式構造裡沒有一個清晰完整的結構,總是想一點寫一點,平時對於Java的訓練太少,做PTA中的程式設計題時總是習慣用C語言去解決,如果想要更加熟練地運用Java,我還需要更加努力的學習。
