字串和String類
java字串是Unicode字元的有序集合,而且,在java中,字串是作為物件的。
java語言中使用java.lang包中的String、StringBuilder、StringBuffer來構造自定義字串,執行許多基本字串操作,
String物件
String類是不可變得,只要一旦建立了該物件,就不能修改該物件的值。有些字串操作看來似乎修改了String物件,實際上是返回一個包含修改內容的新String物件。
- 字串的定義和賦值
字串宣告:String stringName;
字串建立:stringName = new String(字串常量);或stringName = 字串常量;
String str1 = “hello”;
String str2 = new String(“hello”);
String str3 = “he”+“llo”;//“hello”
String str4 = new String(“he”)+new String(“llo”);
- 字串的常用方法
設的常量宣告和初始化
String s1 = " ABcdABcd123 ";
String s2 = “ABcdEFg”;
String s3,s4,s5,s6;
int i1, i2, i3, i4;
boolean b1, b2, b3, b4;
char char1, char2, char3, char4; - 字串長度和空判斷
int length(); //返回此字串的長度
boolean isEmpty(); // 判斷字串是否為空,如果字串的length()為0,則返回true。 - 獲取字串/擷取子字串
char chatAt(int index); //返回指定索引處的char值
String substring(int beginIndex); //擷取子字串:從索引beginIndex到結束。
String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex ); //擷取子字串:從索引beginIndex到endIndex.
索引編號從0開始,0<=索引<length() - 1; - 大小寫轉換
String toLowerCase(); //字串轉換為小寫
String toUpperCase(); //字串轉換為大寫 - 連線字元轉
String concat(String str); // 將指定字串連線到此字串的結尾
也可使用運算子“+”實現字串連線
s4 = s1 + “XYZ”
*取出字串前後的空白
String concat(String str); ///刪除字串前後的所有空格 - 比較字串的大小
boolean equals(Object anObject); //正常方式的比較
Boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString); //比較大小,不考慮大小寫
int compareTo(String anotherString); //按字典順序比較大小
int compareToIgnoreCase(String str); // 按字典順序比較大小,不考慮大小寫 - 查詢字元/字串
int indexOf(int ch); //查詢指定字元在字串中的第一個匹配項的索引位置
int indexOf(String str); //查詢指定字串在字串中的第一個匹配項的索引位置
int indexOf(int ch, int formIndex ); //從指定索引開始查詢指定字元
int indexOf(String str, int formIndex ); //從指定索引開始查詢指定字串 - 替換字元/字串
String replace(char oldChar, char newchar); //將字串中的指定字元oldChar替換為 newchar; - 拷貝整個陣列給dst陣列
void getChars(char dst[], int dstBegin) {
System.arraycopy(value, 0, dst, dstBegin, value.length);} - 格式化字串
static String format(String format , Object…args); //使用指定的格式字串和引數格式化字串 - 字串和字元陣列之間的轉換
char[] toCharArray(); //將字串轉化為一個新的字元陣列
byte[] getBytes(); //將此字串轉化為byte陣列
-
StringBuilder類和StringBuffer類
- 當對字串進行修改的時候,需要使用 StringBuffer 和 StringBuilder 類。
和 String 類不同的是,StringBuffer 和 StringBuilder 類的物件能夠被多次的修改,並且不產生新的未使用物件。
StringBuilder 的方法不是執行緒安全的(不能同步訪問)。在應用程式要求執行緒安全的情況下,則必須使用 StringBuffer 類。
建議在涉及大量字串操作時使用StringBuffer。
public class StringBuffer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "abcde";
String str2 = "abcde";
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(str1.hashCode()));//列印地址
str1 = str1 + "fg";
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(str1.hashCode()));
System.out.println("-----------------");
java.lang.StringBuffer stringBuffer = new java.lang.StringBuffer("hello");
System.out.println(stringBuffer);
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(stringBuffer.hashCode()));
stringBuffer.append("world");//追加
System.out.println(stringBuffer);
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(stringBuffer.hashCode()));
}
}
執行結果:
584f463
b8197464
————————————
hello
154617c
helloworld
154617c
StringBuffer的常用方法
a、append方法
public StringBuffer append(boolean b)
該方法的作用是追加內容到當前StringBuffer物件的末尾,類似於字串的連線。呼叫該方法以後,StringBuffer物件的內容也發生改變,例如:
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(“abc”);
sb.append(true); 則物件sb的值將變成”abctrue”。
使用該方法進行字串的連線,將比String更加節約內容。
b、deleteCharAt方法
public StringBuffer deleteCharAt(int index)
該方法的作用是刪除指定位置的字元,然後將剩餘的內容形成新的字串。
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(“Test”);
sb. deleteCharAt(1);public StringBuffer delete(int start,int end)
該方法的作用是刪除指定區間以內的所有字元,包含start,不包含end索引值的區間。
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(“TestString”);
sb. delete (1,4);該程式碼的作用是刪除索引值1(包括)到索引值4(不包括)之間的所有字元,剩餘的字元形成新的字串。則物件sb的值是”TString”
c、insert方法
public StringBuffer insert(int offset, boolean b)
該方法的作用是在StringBuffer物件中插入內容,然後形成新的字串。
tringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(“TestString”);
sb.insert(4,true);該示例程式碼的作用是在物件sb的索引值4的位置插入true值,形成新的字串,則執行以後物件sb的值是”TestyrueString”。
d、reverse方法
public StringBuffer reverse()
該方法的作用是將StringBuffer物件中的內容反轉,然後形成新的字串。
sb.reverse();
轉以後物件sb中的內容將變為”cba” .
e、setCharAt方法
public void setCharAt(int index, char ch)
該方法的作用是修改物件中索引值為index位置的字元為新的字元ch
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(“abc”);
sb.setCharAt(1,’D’); 物件sb的值將變成”aDc”。
StringBuilder類和StringBuffer類功能基本相似,方法也差不多,主要區別在於StringBuffer類的方法是多執行緒安全的,而StringBuilder是StringBuffer的一個簡易替換,用在字串緩衝區被單個執行緒使用的時候,不是執行緒安全的,相比Buffer而言,StringBuilder具有更高的效能,會略微快一點。
總結
執行緒安全:
StringBuffer:執行緒安全
StringBuilder:執行緒不安全
使用環境:
操作少量的資料使用 String;
單執行緒操作大量資料使用 StringBuilder;
多執行緒操作大量資料使用 StringBuffer。
例子1:
public static void main1(String[] args) {
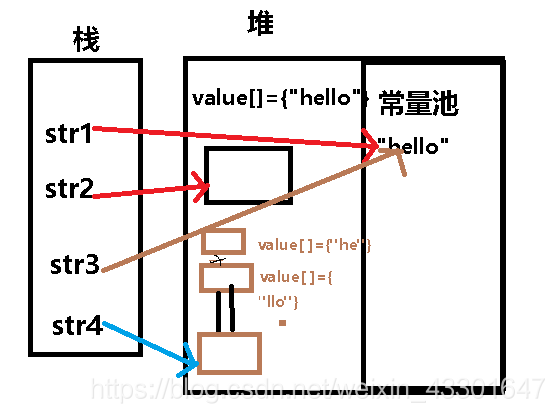
String str1 = "hello";
String str2 = new String("hello");
String str3 = "he"+"llo";//"hello"
String str4 = new String("he")+new String("llo");
System.out.println(str1 == str2);
System.out.println(str3 == str1);
System.out.println(str3 == str2);
System.out.println(str4 == str3);
}
}
例子2:
public static void main(String[] args) {
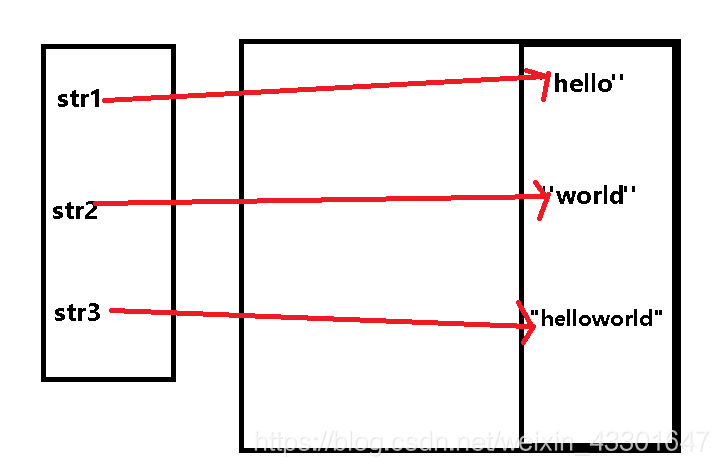
String str1 = "hello";
String str2 = "world";
String str3 = "helloworld";
System.out.println(str1+str2);
System.out.println(str3);
System.out.println(str3 == (str1+str2));
System.out.println(str3 == ("hello"+"world"));
}

例子3、
public static void main(String[] args) {
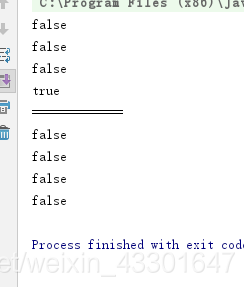
String str1 = new String("hello");
String str2 = "hello";
System.out.println(str1 == str2);//false
String str3 = "he"+new String("llo");
System.out.println(str1 == str3);
System.out.println(str2 == str3);
String str4 = "he"+"llo";
System.out.println(str4 == str2);
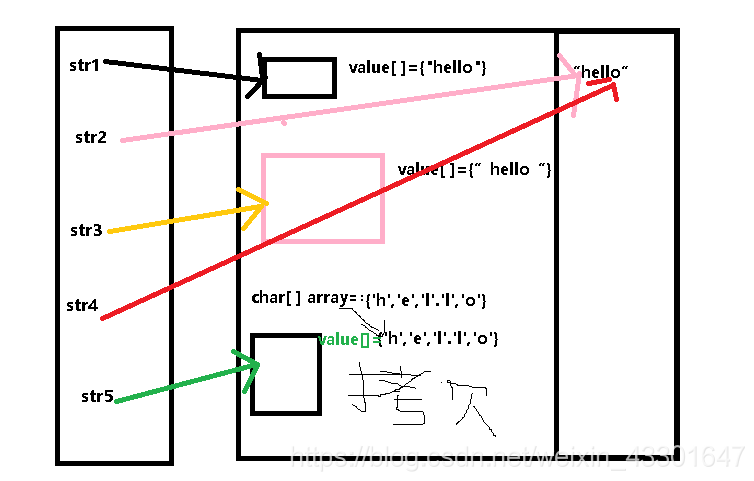
char[] array = {'h','e','l','l','o'};
String str5 = new String(array);
System.out.println("=============");
System.out.println(str1 == str5);
System.out.println(str2 == str5);
System.out.println(str3 == str5);
System.out.println(str4 == str5);
}
例子4:
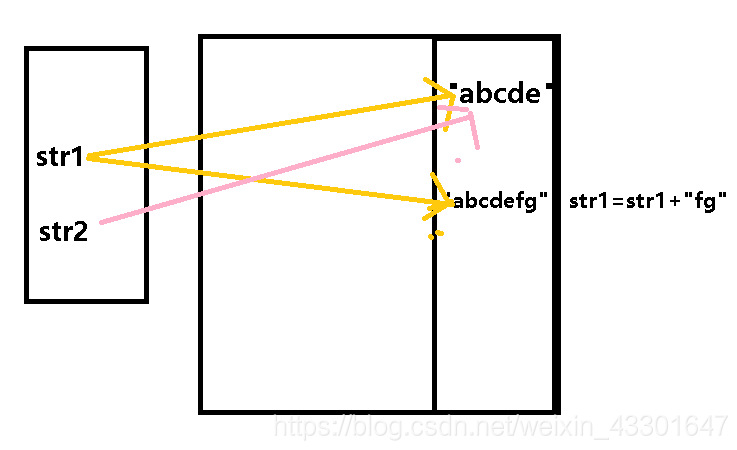
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "abcde";
String str2 = "abcde";
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(str1.hashCode()));
str1 = str1+"fg";
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(str1.hashCode()));
System.out.println("===========================");
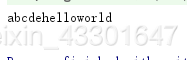
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer("hello");
System.out.println(stringBuffer);
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(stringBuffer.hashCode()));
stringBuffer.append("world");//追加
System.out.println(stringBuffer);
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(stringBuffer.hashCode()));
System.out.println("=============stringBuilder==============");
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(xigong");/xigongworld"
System.out.println(stringBuilder);
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(stringBuilder.hashCode()));
stringBuilder.append("world");//追加
System.out.println(stringBuilder);
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(stringBuilder.hashCode()));
}
 #### 例子5、
#### 例子5、
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "abcde";
String str2 = "hello";
String str3 = str1+str2+"world";
System.out.println(str3);
}
intern()方法
intern() 方法返回字串物件的規範化表示形式。
它遵循以下規則:對於任意兩個字串 s 和 t,當且僅當 s.equals(t) 為 true 時,s.intern() == t.intern() 才為 true。
語法
public String intern()
引數:無
返回值:一個字串,內容與此字串相同,但一定取自具有唯一字串的池。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("ab")+new String("cdef");
str1.intern();
String str2 = "abcdef";
str1.intern();
System.out.println(str1 == str2);
}
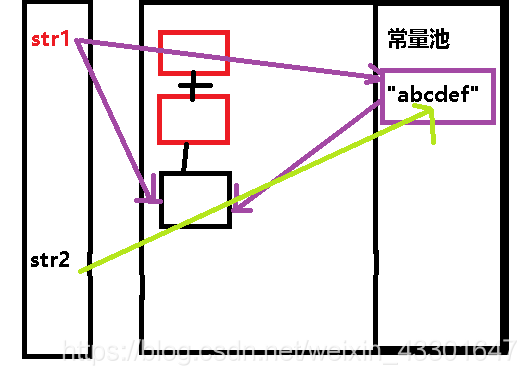
當呼叫 str1.intern()時,在常量池中沒有"abcdef"這個常量,所以,此時就會在常量池中生成堆中物件的引用,所以,常量池的引用和str1的引用的地址一樣。
拷貝:
public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] array = {'a','b','c','d','e'};
String str1 = new String(array,2,3);
System.out.println(str1);//cde
String str2 = "abcdef";
String str3 = str2.substring(0,3);//不包含3號下標
System.out.println(str3);