Python3自學筆記
文章目錄
- 一些優秀的博主
- 首先是掌握基本語法!
- 內建的運算子函式
- math庫
- 天天向上程式碼
- 基本的字串操作符
- random庫的常用函式
- 列表型別特有的函式或方法
- 異常處理程式碼
- 單例模式
- 讀寫模式
- python3的文字處理
- jieba庫的使用
- Python 中的 if __name__ == '__main__' 該如何理解
- python環境搭建和pycharm的安裝配置及漢化(零基礎小白版)
- PyCharm和git安裝教程
- 爬蟲
一些優秀的博主
首先是掌握基本語法!
先來幾個程式碼
str1 = input("請輸入一個人的名字:") str2 = input("請輸入一個國家的名字:") print("世界這麼大,{}想去看看{}:".format(str1,str2))
1到N求和
n = input("請輸入一個整數:")
sum = 0
for i in range(int(n)):
sum += i + 1
print("1到N求和的結果:",sum)
乘法口訣表
for i in range(1,10):
for j in range(1,i +1):
print("{}*{}={:2} ".format(j,i,i*j),end = '')
print('')
列印1! + 2! + 3! + …10!
sum , tem = 0, 1 for i in range(1,4): print("{}".format(i)) for i in range(1,4): tem = i * tem sum += tem print("{}".format(sum))
猴子吃桃問題!
n = 1
for i in range(5,0,-1):
n = (n + 1) << 1
print(n)
攝氏度和華氏度溫度轉換
TempStr = input("")
if TempStr[0] in ['F','f']:
C = (eval(TempStr) -32 ) /1.8
print("{:.2f}C".format(C))
elif TempStr[0] in ['C','c']:
F = 1.8 * eval(TempStr) + 32
print("{:.2f}F".format(F))
else:
print("輸入格式錯誤")
內建的運算子函式
https://www.cnblogs.com/xiao1/p/5856890.html
math庫
- math.pi
數學常數π= 3.141592……
- math.e
數學常數e = 2.718281….
- math.tau
數學常數τ= 6.283185……
- math.ceil(x)
返回x的上限,返回最小的整數A (A>=x)。如math.ceil(3.14)返回的整數為4官網math庫
- math.fabs(x)
返回絕對值x。
- math.factorial(x)
返回 x!。如果x不是積分或者是負的,就會產生ValueError。
- math.floor(x)
返回x的下限,返回一個值最大整數A (A<=x)。如math.floor(3.14)返回的整數為3
-
math.exp(x)
返回 ex也就是 math.e**x
-
math . pow(x,y)
- math.sqrt(x)
返回√x
- math.degrees(x)
將角x從弧度轉換成角度。
- math.radians(x)
把角x從度轉換成弧度。
- math.acos(x)
返回 x 的反餘弦
- math.asin(x)
返回 x 的反正弦。
- math.atan(x)
返回 x 的反正切。
- math.cos(x)
返回 x 的餘弦。
- math.sin(x)
返回 x 的正弦。
- math.tan(x)
返回 x 的正切。
- math.log(x,a)
 ,若不寫a 內定 e
,若不寫a 內定 e
python官網math庫連結
天天向上程式碼
import math
dayup = math.pow((1.0 + 0.005), 365)
daydown = math.pow((1.0 - 0.005),365)
print("向上:{:.2f},向下:{:.2f}.".format(dayup,daydown))
def dayUP(df):
dayup = 0.01
for i in range(365):
if i % 7 in [6,0]:
dayup = dayup * (1 - 0.01)
else:
dayup = dayup * (1 + df)
return dayup
dayfactor = 0.01
while(dayUP(dayfactor) < 37.78):
dayfactor += 0.001
print("每天努力引數是:{:.3f}.".format(dayfactor))
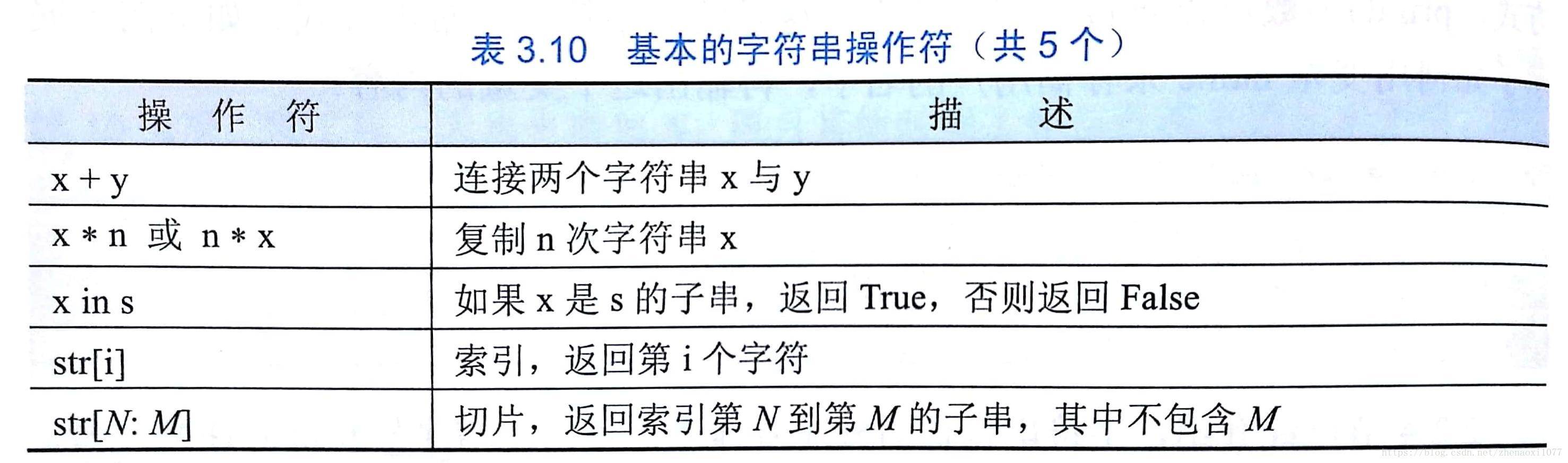
基本的字串操作符
2.內建字串處理函式(6個)
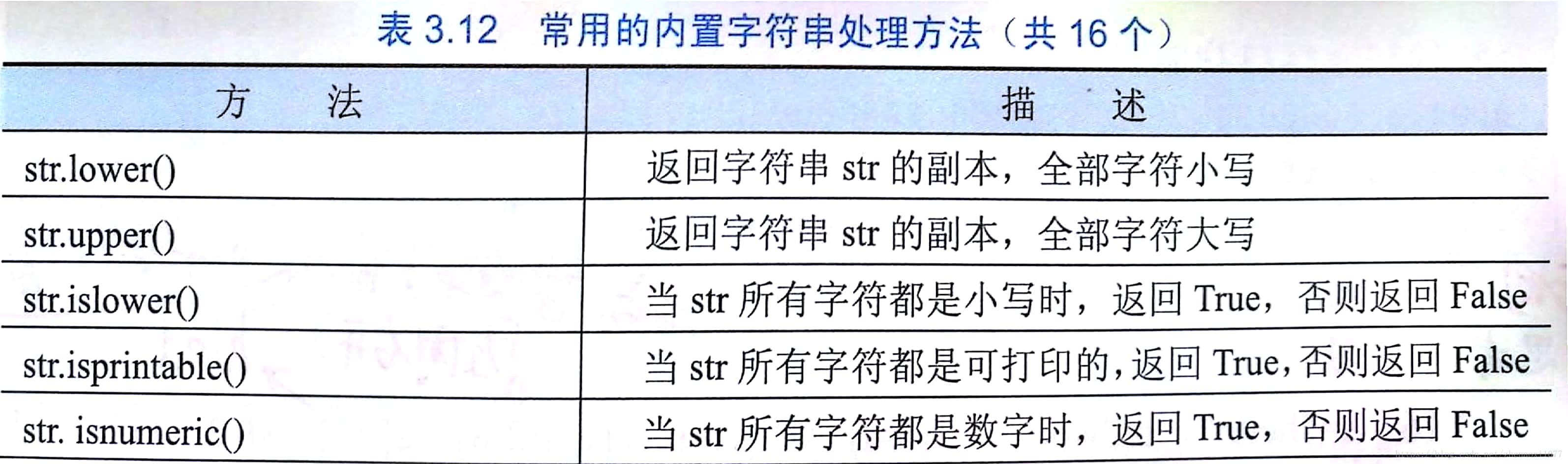
2.常用的內建字串處理方法(16個)
3.特殊的格式化控制字元
4.format()方法的格式控制
random庫的常用函式
列表型別特有的函式或方法
異常處理程式碼
try:
<body>
except <ErrorType1>:
<handler1>
except <ErrorType2>:
<handler2>
except:
<handler0>
else:
<process_else>
finally:
<process_finally>
單例模式
class Singleton(object):
class _A(object):
def __init__(self):
pass
def display(self):
return id(self)
_instance = None
def __init__(self):
if Singleton._instance is None:
Singleton._instance = Singleton._A()
def __getattr__(self, attr):
return getattr(self._instance, attr)
if __name__ == '__main__':
s1 = Singleton()
s2 = Singleton()
print(id(s1), s1.display())
print(id(s2), s2.display())
程式碼的解釋
def getattr(self, attr):
return getattr(self._instance, attr)
# 例如這裡有一個類 A ,,有兩個屬性
>>> class A:
... test1 = "this test1"
... test2 = "this test2"
...
>>>
# 然後例項化一個物件
>>> a = A()
# 就可以用 getattr 直接去獲取物件 a 的屬性值
>>> getattr(a, "test1")
'this test1'
>>>
>>> getattr(a, "test2")
'this test2'
>>>
讀寫模式
https://www.cnblogs.com/c-x-m/articles/7756498.html
#1. 開啟檔案的模式有(預設為文字模式):
r ,只讀模式【預設模式,檔案必須存在,不存在則丟擲異常】
w,只寫模式【不可讀;不存在則建立;存在則清空內容】
a, 之追加寫模式【不可讀;不存在則建立;存在則只追加內容】
#2. 對於非文字檔案,我們只能使用b模式,“b"表示以位元組的方式操作(而所有檔案也都是以位元組的形式儲存的,使用這種模式無需考慮文字檔案的字元編碼、圖片檔案的jgp格式、視訊檔案的avi格式)
rb
wb
ab
注:以b方式開啟時,讀取到的內容是位元組型別,寫入時也需要提供位元組型別,不能指定編碼
#”+" 表示
可以同時讀寫某個檔案
r+, 讀寫【可讀,可寫】
w+,寫讀【可讀,可寫】
a+, 寫讀【可讀,可寫】
x, 只寫模式【不可讀;不存在則建立,存在則報錯】
x+ ,寫讀【可讀,可寫】
xb
python讀寫操作的簡單模板
fo = open("baidu.txt", "w+")
ls ="Hello world"
fo.write(ls)
fo.close()
如果說想把print的內容寫到檔案該怎麼做?
fo = open("baidu.txt", "w+")
print("Hello world",file=fo)
fo.close()
python3的文字處理
jieba庫的使用
pip3 install jieba
統計hamlet.txt文字中高頻詞的個數
講解視訊
[email protected]:~/python$ cat ClaHamlet.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding=utf-8
#e10.1CalHamlet.py
def getText():
txt = open("hamlet.txt", "r").read()
txt = txt.lower()
for ch in '!"#$%&()*+,-./:;<=>[email protected][\\]^_‘{|}~':
txt = txt.replace(ch, " ") #將文字中特殊字元替換為空格
return txt
hamletTxt = getText()
words = hamletTxt.split()
counts = {}
for word in words:
counts[word] = counts.get(word,0) + 1
items = list(counts.items())
items.sort(key=lambda x:x[1], reverse=True)
for i in range(10):
word, count = items[i]
print ("{0:<10}{1:>5}".format(word, count))
統計三國演義任務高頻次數
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding=utf-8
#e10.1CalHamlet.py
def getText():
txt = open("hamlet.txt", "r").read()
txt = txt.lower()
for ch in '!"#$%&()*+,-./:;<=>[email protected][\\]^_‘{|}~':
txt = txt.replace(ch, " ") #將文字中特殊字元替換為空格
return txt
hamletTxt = getText()
words = hamletTxt.split()
counts = {}
for word in words:
counts[word] = counts.get(word,0) + 1
items = list(counts.items())
items.sort(key=lambda x:x[1], reverse=True)
for i in range(10):
word, count = items[i]
print ("{0:<10}{1:>5}".format(word, count))
Python 中的 if name == ‘main’ 該如何理解
http://blog.konghy.cn/2017/04/24/python-entry-program/
python環境搭建和pycharm的安裝配置及漢化(零基礎小白版)
https://blog.csdn.net/ling_mochen/article/details/79314118#commentBox
PyCharm和git安裝教程
https://blog.csdn.net/csdn_kou/article/details/83720765
爬蟲
學習資源是中國大學mooc的爬蟲課程。《嵩天老師》
下面寫幾個簡單的程式碼!熟悉這幾個程式碼的書寫以後基本可以完成需求!
簡單例子1
import requests
r = requests.get("https://www.baidu.com")
fo = open("baidu.txt", "w+")
r.encoding = 'utf-8'
str = r.text
line = fo.write( str )
簡單例子2
import requests
url = "https://item.jd.com/2967929.html"
try:
r = requests.get(url)
r.raise_for_status()//如果不是200就會報錯
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding//轉utf-8格式
print(r.text[:1000])//只有前1000行
except:
print("False")
fo.close()
BeautifulSoup的使用1
fo = open("jingdong.md","w")
url = "https://item.jd.com/2967929.html"
try:
r = requests.get(url)
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
demo = r.text
soup = BeautifulSoup(demo,"html.parser")
fo.write(soup.prettify())
fo.writelines(soup.prettify())
except:
print("False")
fo.close()
BeautifulSoup的使用1
fo = open("baidu.md","w")
try:
r = requests.get("https://www.baidu.com")
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
demo = r.text
soup = BeautifulSoup(demo,"html.parser")
fo.write(soup.prettify())
fo.writelines(soup.prettify())
except:
print("False")
fo.close()