ffmpeg transcode (ffmpeg轉碼程式)
大家都知道,ffmpeg是一個強大的轉碼程式,但是ffmpeg功能實在太多了,以至於我們讀ffmpeg.c都覺得特別頭疼!其實你我都只是想看看mp4轉ts,或avi轉mkv怎麼做的~
好吧,其實ffmpeg的原始碼裡有sample code,是簡化版的轉碼程式,讀起來就容易多了!
具體位置:ffmpeg/doc/examples/transcoding.c。
我把這個程式碼拉出來,修改了一下,單獨編譯成一個程式。也很好用。
為了讓更多的朋友瞭解,我決定博此一文,說說這個轉碼程式!
1 原始碼+詳細註釋
#include <libavcodec/avcodec.h> 2 詳細解析
看了程式碼,可能你還意猶未盡。
那麼,我先來說說程式碼的流程。
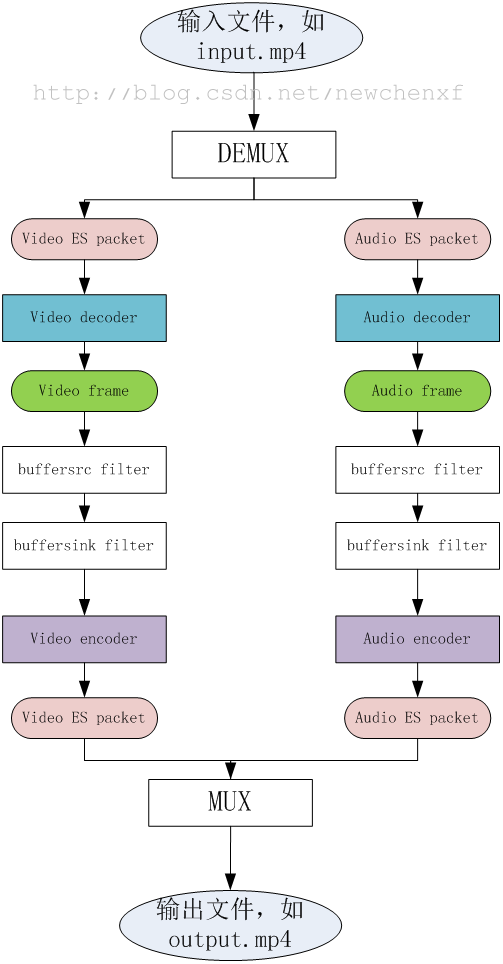
既然是轉碼,那整理流程就是,先把一個原始檔,比如input.mp4,拆包(DEMUX),獲得編碼過的資料packet,然後把packet送給decoder解碼,獲得audio/video的原始資料frame,再把frame送給encoder編碼,又變成編碼過的資料packet,然後把packet打包(MUX)成另一種格式,比如output.ts。
程式流程圖就不說了,程式碼量那麼少,一看就知道。
3 關於PTS
本例最難懂的就是PTS的計算。
time_base
time_base稱為時間基準,在不同的階段(結構體),每個time_base具體的值不一樣,ffmpeg提供函式av_packet_rescale_ts()在各個time_base中進行切換。
time_base主要在2個結構體最常用,一個是AVStream。
//libavformat/avformat.h
typedef struct AVStream {
AVCodecContext *codec;
/**
* This is the fundamental unit of time (in seconds) in terms
* of which frame timestamps are represented.
*
* decoding: set by libavformat
* encoding: May be set by the caller before avformat_write_header() to
* provide a hint to the muxer about the desired timebase. In
* avformat_write_header(), the muxer will overwrite this field
* with the timebase that will actually be used for the timestamps
* written into the file (which may or may not be related to the
* user-provided one, depending on the format).
*/
AVRational time_base;
//......
}一個是AVCodecContext
//libavcodec/avcodec.h
typedef struct AVCodecContext {
const AVClass *av_class;
enum AVMediaType codec_type; /* see AVMEDIA_TYPE_xxx */
const struct AVCodec *codec;
/**
* This is the fundamental unit of time (in seconds) in terms
* of which frame timestamps are represented. For fixed-fps content,
* timebase should be 1/framerate and timestamp increments should be
* identically 1.
* This often, but not always is the inverse of the frame rate or field rate
* for video. 1/time_base is not the average frame rate if the frame rate is not
* constant.
*
* Like containers, elementary streams also can store timestamps, 1/time_base
* is the unit in which these timestamps are specified.
* As example of such codec time base see ISO/IEC 14496-2:2001(E)
* vop_time_increment_resolution and fixed_vop_rate
* (fixed_vop_rate == 0 implies that it is different from the framerate)
*
* - encoding: MUST be set by user.
* - decoding: the use of this field for decoding is deprecated.
* Use framerate instead.
*/
AVRational time_base;AVRational 本身很簡單,定義是
typedef struct AVRational{
int num; ///< numerator
int den; ///< denominator
} AVRational;什麼意思呢?
以video為例子。
在AVStream的階段,也就是還沒解碼之前的原始資料,假設是mp4檔案,FPS = 15,那麼
time_base={1, 15},那麼
懂第一幀到開始,每一ES packet的PTS就是1, 2, 3,。。。。
為何呢?
簡單啊,比如第一幀,packet.pts=1,實際的packet.pts = 1/15 = 0.0666s
同理第二幀,packet.pts=2,實際的packet.pts = 2/15 = 0.1333s
到第15幀,packet.pts=15,實際的packet.pts = 15/15 = 1s
也符合我們的預想嘛!
