Vue.js——十分鐘入門Vuex
一. 什麼是Vuex?

Vuex
Vuex是一個專門為Vue.js應用程式開發的狀態管理模式, 它採用集中式儲存管理所有元件的公共狀態, 並以相應的規則保證狀態以一種可預測的方式發生變化.
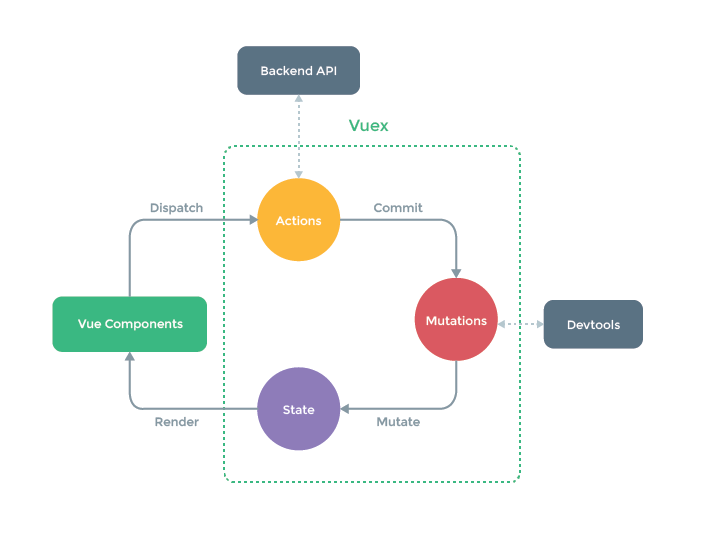
Vuex核心
上圖中綠色虛線包裹起來的部分就是Vuex的核心, state中儲存的就是公共狀態, 改變state的唯一方式就是通過mutations進行更改. 可能你現在看這張圖有點不明白, 等經過本文的解釋和案例演示, 再回來看這張圖, 相信你會有更好的理解.
二. 為什麼要使用Vuex?
試想這樣的場景, 比如一個Vue的根例項下面有一個根元件名為App.vue, 它下面有兩個子元件A.vue
B.vue, App.vue想要與A.vue或者B.vue通訊可以通過props傳值的方式, 但是如果A.vue和B.vue之間的通訊就很麻煩了, 他們需要共有的父元件通過自定義事件進行實現, A元件想要和B元件通訊往往是這樣的:
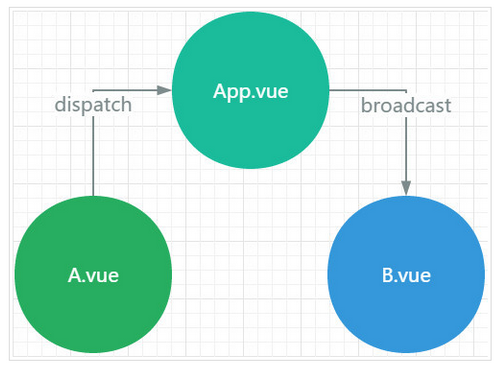
元件通訊
- A元件說: "報告老大, 能否幫我託個信給小弟B" => dispatch一個事件給App
- App老大說: "包在我身上, 它需要監聽A元件的dispatch的時間, 同時需要broadcast一個事件給B元件"
- B小弟說: "資訊已收到", 它需要on監聽App元件分發的事件
這只是一條通訊路徑, 如果父元件下有多個子元件, 子元件之間通訊的路徑就會變的很繁瑣, 父元件需要監聽大量的事件, 還需要負責分發給不同的子元件, 很顯然這並不是我們想要的元件化的開發體驗.
Vuex就是為了解決這一問題出現的
三.如何引入Vuex?
- 下載
vuex:npm install vuex --save - 在
main.js新增:
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use( Vuex );
const store = new Vuex.Store({
//待新增
})
new Vue({
el: '#app',
store,
render: h => h(App)
})
四. Vuex的核心概念?
在介紹Vuex的核心概念之前, 我使用vue-cli初始化了一個demo, 準備以程式碼的形式來說明Vuex的核心概念, 大家可以在github上的ProductListOne.vue和ProductListTwo.vue, 在App.vue的datat中儲存著共有的商品列表, 程式碼和初始化的效果如下圖所示:
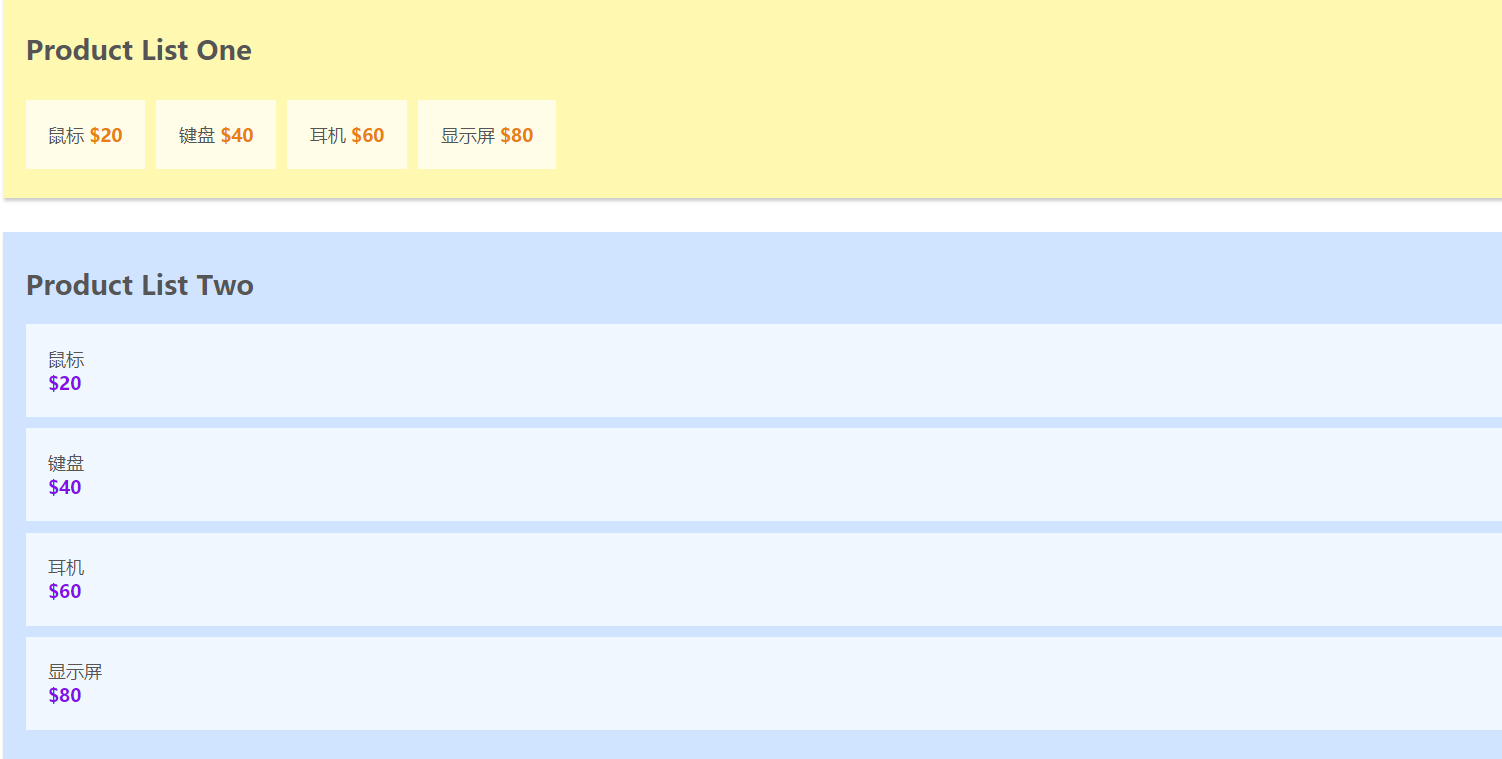
初始化效果
//App.vue中的初始化程式碼
<template>
<div id="app">
<product-list-one v-bind:products="products"></product-list-one>
<product-list-two v-bind:products="products"></product-list-two>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import ProductListOne from './components/ProductListOne.vue'
import ProductListTwo from './components/ProductListTwo.vue'
export default {
name: 'app',
components: {
'product-list-one': ProductListOne,
'product-list-two': ProductListTwo
},
data () {
return {
products: [
{name: '滑鼠', price: 20},
{name: '鍵盤', price: 40},
{name: '耳機', price: 60},
{name: '顯示屏', price: 80}
]
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
body{
font-family: Ubuntu;
color: #555;
}
</style>
//ProductListOne.vue
<template>
<div id="product-list-one">
<h2>Product List One</h2>
<ul>
<li v-for="product in products">
<span class="name">{{ product.name }}</span>
<span class="price">${{ product.price }}</span>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: ['products'],
data () {
return {
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
#product-list-one{
background: #FFF8B1;
box-shadow: 1px 2px 3px rgba(0,0,0,0.2);
margin-bottom: 30px;
padding: 10px 20px;
}
#product-list-one ul{
padding: 0;
}
#product-list-one li{
display: inline-block;
margin-right: 10px;
margin-top: 10px;
padding: 20px;
background: rgba(255,255,255,0.7);
}
.price{
font-weight: bold;
color: #E8800C;
}
</style>
//ProductListTwo.vue
<template>
<div id="product-list-two">
<h2>Product List Two</h2>
<ul>
<li v-for="product in products">
<span class="name">{{ product.name }}</span>
<span class="price">${{ product.price }}</span>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: ['products'],
data () {
return {
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
#product-list-two{
background: #D1E4FF;
box-shadow: 1px 2px 3px rgba(0,0,0,0.2);
margin-bottom: 30px;
padding: 10px 20px;
}
#product-list-two ul{
padding: 0;
list-style-type: none;
}
#product-list-two li{
margin-right: 10px;
margin-top: 10px;
padding: 20px;
background: rgba(255,255,255,0.7);
}
.price{
font-weight: bold;
color: #860CE8;
display: block;
}
</style>
核心概念1: State
state就是Vuex中的公共的狀態, 我是將state看作是所有元件的data, 用於儲存所有元件的公共資料.
- 此時我們就可以把
App.vue中的兩個元件共同使用的data抽離出來, 放到state中,程式碼如下:
//main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use( Vuex )
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
products: [
{name: '滑鼠', price: 20},
{name: '鍵盤', price: 40},
{name: '耳機', price: 60},
{name: '顯示屏', price: 80}
]
}
})
new Vue({
el: '#app',
store,
render: h => h(App)
})
- 此時,
ProductListOne.vue和ProductListTwo.vue也需要做相應的更改
//ProductListOne.vue
export default {
data () {
return {
products : this.$store.state.products //獲取store中state的資料
}
}
}
//ProductListTwo.vue
export default {
data () {
return {
products: this.$store.state.products //獲取store中state的資料
}
}
}
-
此時的頁面如下圖所示, 可以看到, 將公共資料抽離出來後, 頁面沒有發生變化.
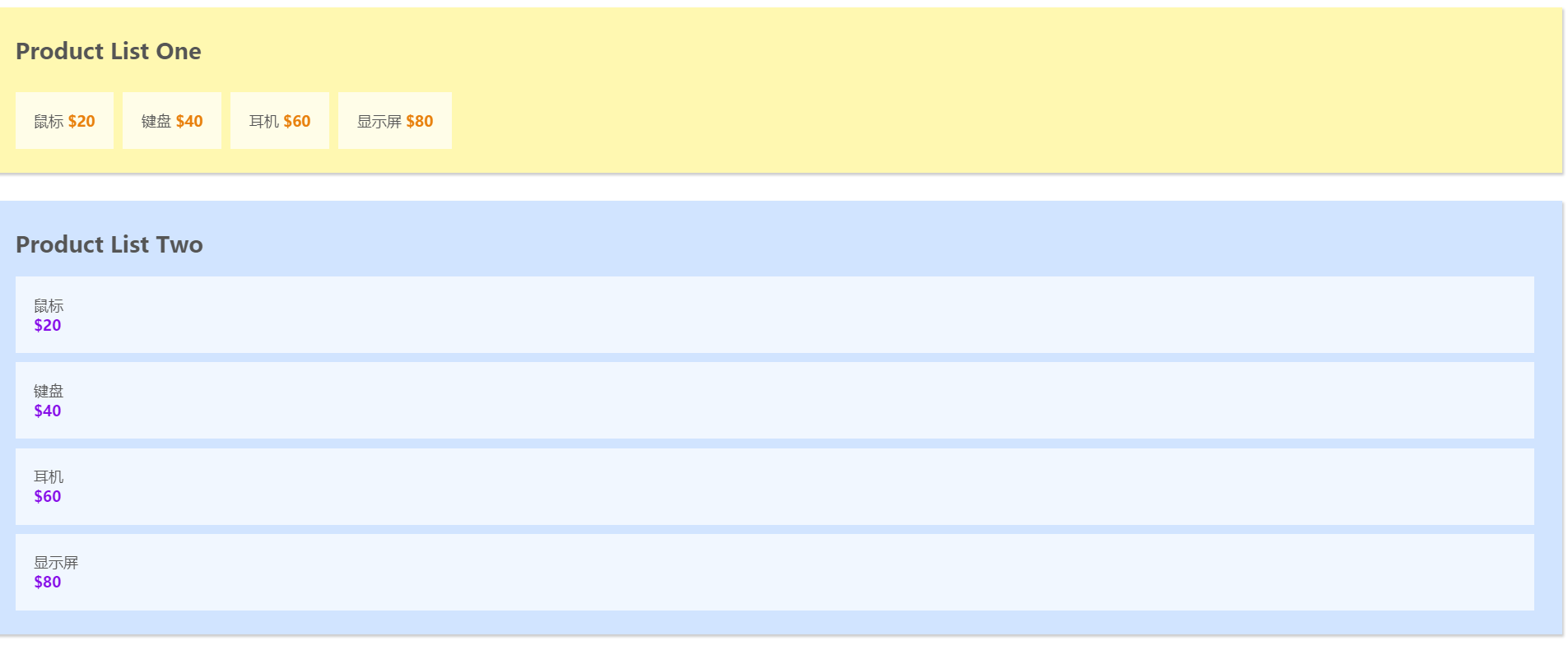
state效果
到此處的Github倉庫中程式碼為: 分支code01
核心概念2: Getters
我將getters屬性理解為所有元件的computed屬性, 也就是計算屬性. vuex的官方文件也是說到可以將getter理解為store的計算屬性, getters的返回值會根據它的依賴被快取起來,且只有當它的依賴值發生了改變才會被重新計算。
- 此時,我們可以在
main.js中新增一個getters屬性, 其中的saleProducts物件將state中的價格減少一半(除以2)
//main.js
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
products: [
{name: '滑鼠', price: 20},
{name: '鍵盤', price: 40},
{name: '耳機', price: 60},
{name: '顯示屏', price: 80}
]
},
getters:{ //新增getters
saleProducts: (state) => {
let saleProducts = state.products.map( product => {
return {
name: product.name,
price: product.price / 2
}
})
return saleProducts;
}
}
})
- 將
productListOne.vue中的products的值更換為this.$store.getters.saleProducts
export default {
data () {
return {
products : this.$store.getters.saleProducts
}
}
}
- 現在的頁面中,Product List One中的每項商品的價格都減少了一半

getters效果
到此處的Github倉庫中程式碼為: 分支code02
核心概念3: Mutations
我將mutaions理解為store中的methods, mutations物件中儲存著更改資料的回撥函式,該函式名官方規定叫type, 第一個引數是state, 第二引數是payload, 也就是自定義的引數.
- 下面,我們在
main.js中新增mutations屬性,其中minusPrice這個回撥函式用於將商品的價格減少payload這麼多, 程式碼如下:
//main.js
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
products: [
{name: '滑鼠', price: 20},
{name: '鍵盤', price: 40},
{name: '耳機', price: 60},
{name: '顯示屏', price: 80}
]
},
getters:{
saleProducts: (state) => {
let saleProducts = state.products.map( product => {
return {
name: product.name,
price: product.price / 2
}
})
return saleProducts;
}
},
mutations:{ //新增mutations
minusPrice (state, payload ) {
let newPrice = state.products.forEach( product => {
product.price -= payload
})
}
}
})
- 在
ProductListTwo.vue中新增一個按鈕,為其新增一個點選事件, 給點選事件觸發minusPrice方法
//ProductListTwo.vue
<template>
<div id="product-list-two">
<h2>Product List Two</h2>
<ul>
<li v-for="product in products">
<span class="name">{{ product.name }}</span>
<span class="price">${{ product.price }}</span>
</li>
<button @click="minusPrice">減少價格</button> //新增按鈕
</ul>
</div>
</template>
- 在
ProductListTwo.vue中註冊minusPrice方法, 在該方法中commitmutations中的minusPrice這個回撥函式
注意:呼叫mutaions中回撥函式, 只能使用store.commit(type, payload)
//ProductListTwo.vue
export default {
data () {
return {
products: this.$store.state.products
}
},
methods: {
minusPrice() {
this.$store.commit('minusPrice', 2); //提交`minusPrice,payload為2
}
}
}
- 新增按鈕, 可以發現, Product List Two中的價格減少了2, 當然你可以自定義
payload,以此自定義減少對應的價格.
mutations效果
(Product List One中的價格沒有發生變化, 是因為getters將價格進行了快取)
到此處的Github倉庫中程式碼為: 分支code03
核心概念4: Actions
actions 類似於 mutations,不同在於:
-
actions提交的是mutations而不是直接變更狀態 -
actions中可以包含非同步操作,mutations中絕對不允許出現非同步 -
actions中的回撥函式的第一個引數是context, 是一個與store例項具有相同屬性和方法的物件 -
此時,我們在
store中新增actions屬性, 其中minusPriceAsync採用setTimeout來模擬非同步操作,延遲2s執行 該方法用於非同步改變我們剛才在mutaions中定義的minusPrice
//main.js
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
products: [
{name: '滑鼠', price: 20},
{name: '鍵盤', price: 40},
{name: '耳機', price: 60},
{name: '顯示屏', price: 80}
]
},
getters:{
saleProducts: (state) => {
let saleProducts = state.products.map( product => {
return {
name: product.name,
price: product.price / 2
}
})
return saleProducts;
}
},
mutations:{
minusPrice (state, payload ) {
let newPrice = state.products.forEach( product => {
product.price -= payload
})
}
},
actions:{ //新增actions
minusPriceAsync( context, payload ) {
setTimeout( () => {
context.commit( 'minusPrice', payload ); //context提交
}, 2000)
}
}
})
- 在
ProductListTwo.vue中新增一個按鈕,為其新增一個點選事件, 給點選事件觸發minusPriceAsync方法
<template>
<div id="product-list-two">
<h2>Product List Two</h2>
<ul>
<li v-for="product in products">
<span class="name">{{ product.name }}</span>
<span class="price">${{ product.price }}</span>
</li>
<button @click="minusPrice">減少價格</button>
<button @click="minusPriceAsync">非同步減少價格</button> //新增按鈕
</ul>
</div>
</template>
- 在
ProductListTwo.vue中註冊minusPriceAsync方法, 在該方法中dispatchactions中的minusPriceAsync這個回撥函式
export default {
data () {
return {
products: this.$store.state.products
}
},
methods: {
minusPrice() {
this.$store.commit('minusPrice', 2);
},
minusPriceAsync() {
this.$store.dispatch('minusPriceAsync', 5); //分發actions中的minusPriceAsync這個非同步函式
}
}
}
-
新增按鈕, 可以發現, Product List Two中的價格延遲2s後減少了5

actions效果
到此處的Github倉庫中程式碼為: 分支code04
核心概念5: Modules
由於使用單一狀態樹,應用的所有狀態會集中到一個比較大的物件。當應用變得非常複雜時,store 物件就有可能變得相當臃腫。為了解決以上問題,Vuex 允許我們將 store 分割成模組(module)。每個模組擁有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是巢狀子模組——從上至下進行同樣方式的分割
const moduleA = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... },
getters: { ... }
}
const moduleB = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... }
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
a: moduleA,
b: moduleB
}
})
store.state.a // -> moduleA 的狀態
store.state.b // -> moduleB 的狀態
【相關連結】
- 本文程式碼地址: https://github.com/Lee-Tanghui/Vuex-Demo
- Vuex官方文件: https://vuex.vuejs.org/zh-cn/intro.html
- Vuex官方案例演示原始碼: https://github.com/vuejs/vuex/tree/dev/examples
作者:Lee_tanghui
連結:https://www.jianshu.com/p/a804606ad8e9
來源:簡書
