Object Detection (4)Faster RCNN Keras 原理+程式碼 第二部分
目錄
- Object Detection (1)VOC2007資料集製作
- Object Detection (2)Faster RCNN詳解
- Object Detection (3)Faster RCNN Keras 原理+程式碼 第一部分
- Object Detection (4)Faster RCNN Keras 原理+程式碼 第二部分
- Object Detection (5)Faster RCNN Keras 釋出為api
本文基於git專案做二次開發:
改造後git地址:https://github.com/xvshu/keras-frcnn-web
原git地址:https://github.com/yhenon/keras-frcnn
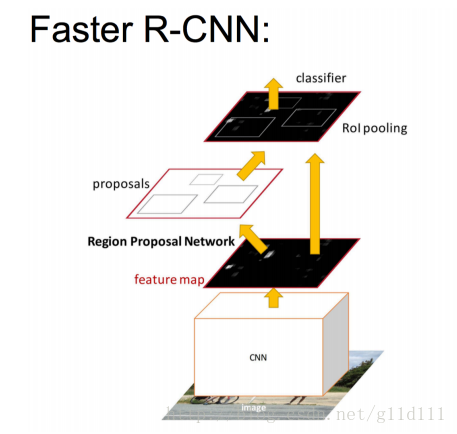
前面,我們分析了RPN,得到了一些框和背景。按照下圖,把RPN的輸出輸入給RoI pooling進行一系列操作。
① 定義輸入資料RPN,將RPN的輸出輸入到RoI
#coding:UTF-8 from __future__ import division import random import pprint import sys import time import numpy as np from optparse import OptionParser import pickle from keras import backend as K from keras.optimizers import Adam, SGD, RMSprop from keras.layers import Input from keras.models import Model from keras_frcnn import config, data_generators from keras_frcnn import losses as losses import keras_frcnn.roi_helpers as roi_helpers from keras.utils import generic_utils # 輸入尺度(以backend為Tensorflow為例) input_shape_img = (None, None, 3) img_input = Input(shape=input_shape_img) # 關於rpn函式的內容,請檢視Faster-RCNN程式碼+理論——1 rpn = nn.rpn(shared_layers, num_anchors) # 定義model_rpn model_rpn = Model(img_input, rpn[:2]) ... # 簡化的訓練過程(這裡相比keras程式碼的內容進行了簡化) num_epochs = 2000 for epoch_num in range(num_epochs): # Progbar是生成進度條(這是一個武大的兄弟告訴我的,表示感謝) progbar = generic_utils.Progbar(epoch_length) print('Epoch {}/{}'.format(epoch_num + 1, num_epochs)) while True: # data_gen_train是一個迭代器。返回的是 np.copy(x_img), [np.copy(y_rpn_cls), np.copy(y_rpn_regr)], img_data_aug(我們這裡假設資料沒有進行水平翻轉等操作。那麼,x_img = img_data_aug),y_rpn_cls和y_rpn_regr是RPN的兩個損失函式。 X, Y, img_data = next(data_gen_train) loss_rpn = model_rpn.train_on_batch(X, Y) P_rpn = model_rpn.predict_on_batch(X) # 得到了region proposals,接下來另一個重要的思想就是ROI, # 可將不同shape的特徵圖轉化為固定shape,送到全連線層進行最終的預測。 # rpn_to_roi接收的是每張圖片的預測輸出,返回的R = [boxes, probs] R = roi_helpers.rpn_to_roi(P_rpn[0], P_rpn[1], C, K.image_dim_ordering(), use_regr=True, overlap_thresh=0.7, max_boxes=300) # note: calc_iou converts from (x1,y1,x2,y2) to (x,y,w,h) format # 通過calc_iou()找出剩下的不多的region對應ground truth裡重合度最高的bbox,從而獲得model_classifier的資料和標籤。 # X2保留所有的背景和match bbox的框; Y1 是類別one-hot轉碼; Y2是對應類別的標籤及迴歸要學習的座標位置; IouS是debug用的。 X2, Y1, Y2, IouS = roi_helpers.calc_iou(R, img_data, C, class_mapping)
下面簡單敘述一下rpn_to_roi和calc_iou的作用。
② 函式rpn_to_roi & calc_iou分析
從上面的程式碼可以看出,rpn_to_roi輸出作為calc_iou的輸入。那麼按照順序先來分析一下rpn_to_roi,此函式的主要作用是:把由RPN輸出的所有可能的框過濾掉重合度高的框,降低計算複雜度。
其中,涉及到一個演算法:non_max_suppression(非極大值抑制)
下面關於非極大值抑制這個演算法的介紹來自參考資料[1]
因為經過RPN之後,可能會從一張圖片中找出很多個可能是物體的矩形框,然後為每個矩形框為做類別分類概率:
以上面的圖片為例,目標是要定位一個車輛,最後演算法就找出了一堆的方框,我們需要判別哪些矩形框是沒用的。非極大值抑制的意思就是:先假設有6個矩形框,根據分類器類別分類概率做排序,從小到大分別屬於車輛的概率分別為A、B、C、D、E、F。
(1)從最大概率矩形框F開始,分別判斷A~E與F的重疊度IOU是否大於某個設定的閾值;
(2)假設B、D與F的重疊度超過閾值,那麼就扔掉B、D;並標記第一個矩形框F,是我們保留下來的。
(3)從剩下的矩形框A、C、E中,選擇概率最大的E,然後判斷E與A、C的重疊度,重疊度大於一定的閾值,那麼就扔掉;並標記E是我們保留下來的第二個矩形框。
就這樣一直重複,找到所有被保留下來的矩形框。
而calc_iou的作用是,通過calc_iou()找出剩下的不多的region對應ground truth裡重合度最高的bbox,從而獲得model_classifier的資料和標籤。
X2保留所有的背景和match bbox的框; Y1 是類別one-hot轉碼; Y2是對應類別的標籤及迴歸要學習的座標位置; IouS是debug用的。X2, Y1, Y2, IouS = roi_helpers.calc_iou(R, img_data, C, class_mapping)
# 通過calc_iou()找出剩下的不多的region對應ground truth裡重合度最高的bbox,
# 從而獲得model_classifier的目標和標籤。
def calc_iou(R, img_data, C, class_mapping):
bboxes = img_data['bboxes']
(width, height) = (img_data['width'], img_data['height'])
# get image dimensions for resizing
(resized_width, resized_height) = data_generators.get_new_img_size(width, height, C.im_size)
# 這裡跟calc_rpn基本一致
gta = np.zeros((len(bboxes), 4))
for bbox_num, bbox in enumerate(bboxes):
# get the GT box coordinates, and resize to account for image resizing
gta[bbox_num, 0] = int(round(bbox['x1'] * (resized_width / float(width))/C.rpn_stride))
gta[bbox_num, 1] = int(round(bbox['x2'] * (resized_width / float(width))/C.rpn_stride))
gta[bbox_num, 2] = int(round(bbox['y1'] * (resized_height / float(height))/C.rpn_stride))
gta[bbox_num, 3] = int(round(bbox['y2'] * (resized_height / float(height))/C.rpn_stride))
x_roi = []
y_class_num = []
y_class_regr_coords = []
y_class_regr_label = []
IoUs = [] # for debugging only
# R = [boxes, probs]
for ix in range(R.shape[0]):
(x1, y1, x2, y2) = R[ix, :]
x1 = int(round(x1))
y1 = int(round(y1))
x2 = int(round(x2))
y2 = int(round(y2))
best_iou = 0.0
best_bbox = -1
for bbox_num in range(len(bboxes)):
# x1 x2 y1 y2是生成的框,gta是相對於原圖縮小比例的bbox
curr_iou = data_generators.iou([gta[bbox_num, 0], gta[bbox_num, 2], gta[bbox_num, 1], gta[bbox_num, 3]], [x1, y1, x2, y2])
if curr_iou > best_iou:
best_iou = curr_iou
best_bbox = bbox_num
# 如果對於某個框,其匹配現有的bbox重疊率小於0.3,那麼這個框就扔掉
if best_iou < C.classifier_min_overlap:
continue
else:
w = x2 - x1
h = y2 - y1
x_roi.append([x1, y1, w, h])
IoUs.append(best_iou)
if C.classifier_min_overlap <= best_iou < C.classifier_max_overlap:
# hard negative example
cls_name = 'bg'
elif C.classifier_max_overlap <= best_iou:
cls_name = bboxes[best_bbox]['class']
cxg = (gta[best_bbox, 0] + gta[best_bbox, 1]) / 2.0
cyg = (gta[best_bbox, 2] + gta[best_bbox, 3]) / 2.0
cx = x1 + w / 2.0
cy = y1 + h / 2.0
tx = (cxg - cx) / float(w)
ty = (cyg - cy) / float(h)
tw = np.log((gta[best_bbox, 1] - gta[best_bbox, 0]) / float(w))
th = np.log((gta[best_bbox, 3] - gta[best_bbox, 2]) / float(h))
else:
print('roi = {}'.format(best_iou))
raise RuntimeError
# 找到class對應的類別的數字標籤:0,1,2...
class_num = class_mapping[cls_name]
# One-Hot
class_label = len(class_mapping) * [0]
class_label[class_num] = 1
y_class_num.append(copy.deepcopy(class_label))
coords = [0] * 4 * (len(class_mapping) - 1)
labels = [0] * 4 * (len(class_mapping) - 1)
if cls_name != 'bg':
label_pos = 4 * class_num
sx, sy, sw, sh = C.classifier_regr_std
# coords: 座標調整:相當於coords是迴歸要學習的內容
coords[label_pos:4+label_pos] = [sx*tx, sy*ty, sw*tw, sh*th]
labels[label_pos:4+label_pos] = [1, 1, 1, 1]
y_class_regr_coords.append(copy.deepcopy(coords))
y_class_regr_label.append(copy.deepcopy(labels))
else:
y_class_regr_coords.append(copy.deepcopy(coords))
y_class_regr_label.append(copy.deepcopy(labels))
if len(x_roi) == 0:
return None, None, None, None
# X保留所有的背景和match bbox的框; Y1 是類別one-hot轉碼; Y2是對應類別的標籤及迴歸要學習的座標位置
X = np.array(x_roi)
Y1 = np.array(y_class_num)
Y2 = np.concatenate([np.array(y_class_regr_label),np.array(y_class_regr_coords)],axis=1)
# expand_dims:增加一個通道
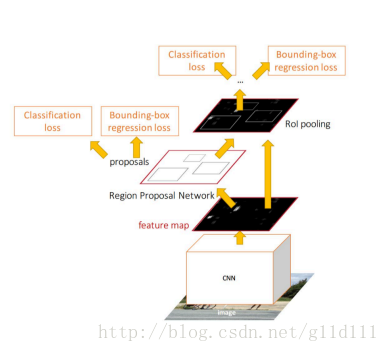
return np.expand_dims(X, axis=0), np.expand_dims(Y1, axis=0), np.expand_dims(Y2, axis=0), IoUs③ 總訓練(結合四個損失函式)
如圖,因為Faster-RCNN有四個損失函式:
• RPN calssification(anchor good.bad)
• RPN regression(anchor->propoasal)
• Fast R-CNN classification(over classes)
• Fast R-CNN regression(proposal ->box)
現在,我們結合第②步的輸出和原始輸入,來訓練總的網路。
# sel_samples表示所有匹配Bbox的框(pos)及背景(neg)
sel_samples = selected_pos_samples + selected_neg_samples
loss_class = model_classifier.train_on_batch([X, X2[:, sel_samples, :]], [Y1[:, sel_samples, :], Y2[:, sel_samples, :]])這裡,
# 輸入
roi_input = Input(shape=(None, 4)) # roi框的位置,故為4
input_shape_img = (None, None, 3)
img_input = Input(shape=input_shape_img)
# classifier是什麼?
# classes_count {} 每一個類的數量:{'cow': 4, 'dog': 10, ...}
# C.num_rois每次取的感興趣區域,預設為32
# roi_input = Input(shape=(None, 4)) 框框
# classifier是faster rcnn的兩個損失函式[out_class, out_reg]
# shared_layers是Faster-RCNN程式碼+理論——1裡面vgg的輸出feature map
classifier = nn.classifier(shared_layers, roi_input, C.num_rois, nb_classes=len(classes_count), trainable=True)
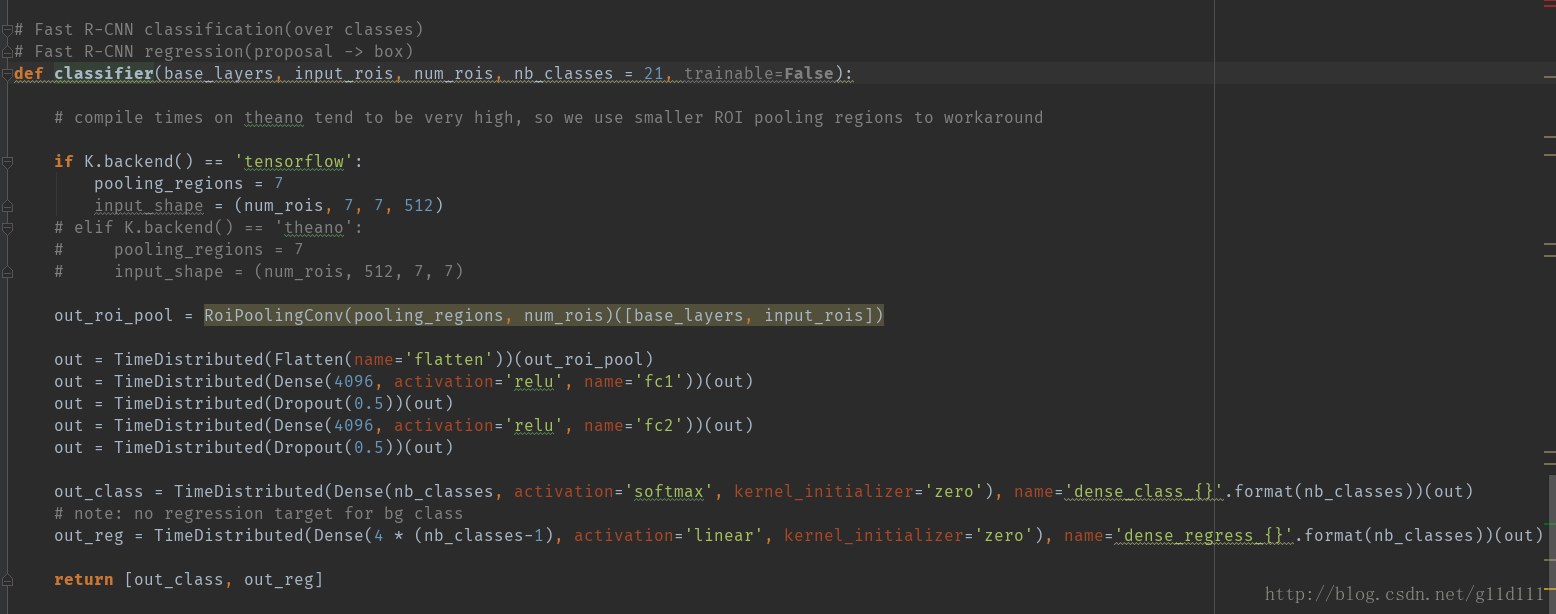
model_classifier = Model([img_input, roi_input], classifier)那麼,這個nn.classifier()是什麼呢?請看下圖:
這裡,RoiPoolingConv一個自定義的keras layer,下面大家可能會問,為什麼用TimeDistributed這個DD呢?這個不是用在RNN裡面的嗎?
答:
在最後Faster RCNN的結構中進行類別判斷和bbox框的迴歸時,需要對設定的num_rois個感興趣區域進行迴歸處理,由於每一個區域的處理是相對獨立的,便等價於此時的時間步為num_rois,因此用TimeDistributed來wrap。
最後,產生num_rois個out_class和out_reg。也就是上面的四個損失函式中的下面兩個:Fast R-CNN classification和Fast R-CNN regression(proposal ->box)。
總結
這裡,我將結合圖片來解釋一下流程:
① 輸入資料:
| 圖片地址 | 左上角橫座標 | 左上角縱座標 | 右下角橫座標 | 右下角縱座標 | Label |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| xxx.jpg | x11 | y11 | x21 | y21 | dog |
| xxx.jpg | x12 | y12 | x22 | y22 | cat |
② 經過VGG/Resnet等分類模型產生特徵圖後,進行RPN網路的訓練:
注意:這裡重點來了,RPN網路的輸入X
是原圖:xxx.jpg;而其對應的labelY
則是由 keras程式碼
data_generators裡面對應的get_anchor_gt生產的新的label,而不僅僅是①中的兩個Bbox。
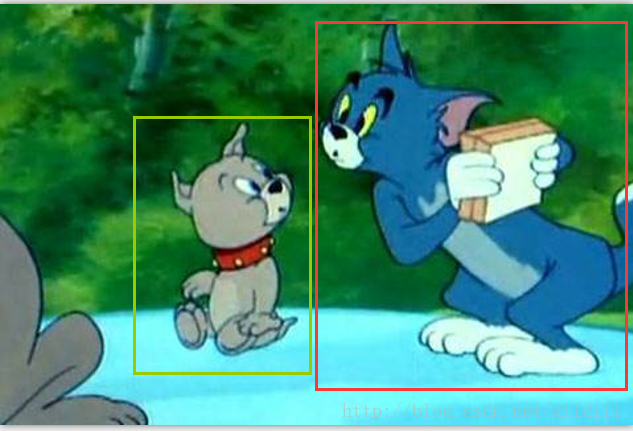
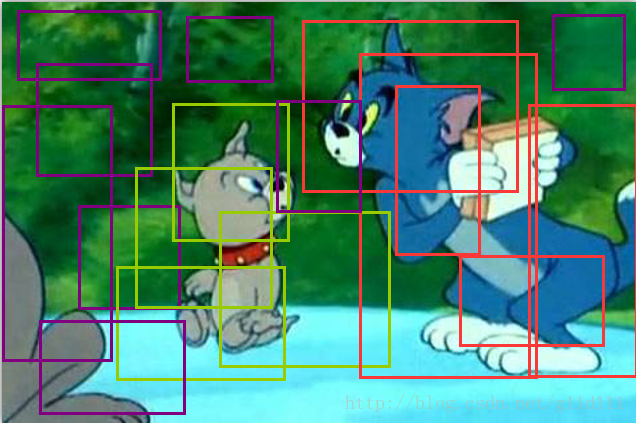
這步產生的輸出可能是:(其中:綠色代表狗,紅色代表貓,紫色代表背景。)
注意:RPN的迴歸是迴歸這些亂78糟的由錨點生產的框,而不是迴歸原始label對應的框!
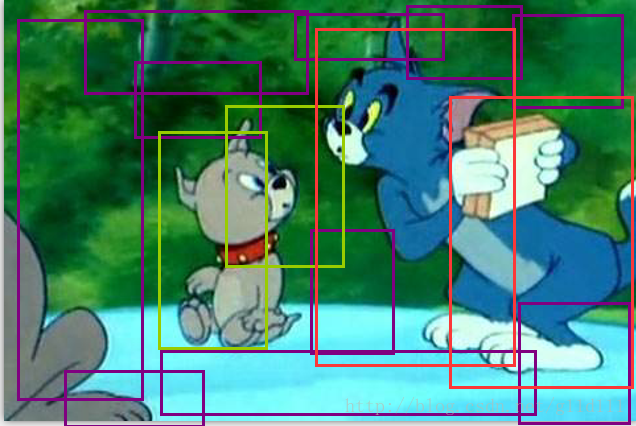
③ 經過一系列處理(包括非極大值抑制),得到合適的框和標籤:
這一步見之前函式calc_iou的返回值。
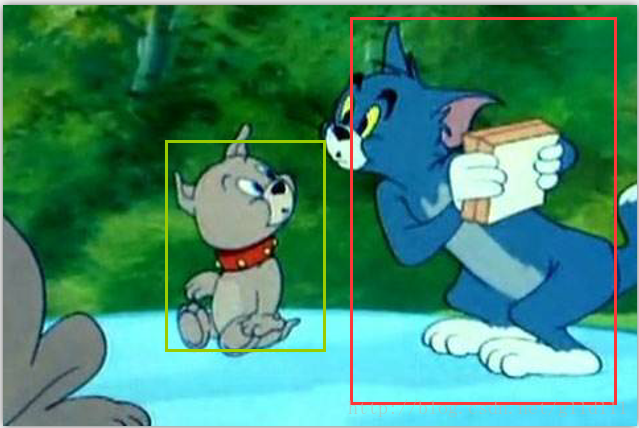
④ 最後經過把rpn和roiPoolingConv合併起來的Faster-RCNN來進行判別和修正:
此步將不展示背景:
關於損失函式和RoiPoolingConv等內容,這裡不再細述。希望這兩篇文章對大家有幫助!