CF445B DZY Loves Chemistry
題意翻譯
DZY熱愛化學.他有n種物質,其中m對會反應.他把它們一種一種倒到燒杯裡.有一個危險值,一開始等於1.如果一種物質倒到燒杯裡之後至少有一種物質能和它反應,則危險值乘以二;否則危險值不變.求所有物質倒到燒杯裡之後最大的危險值.
By @Fuko_Ibuki
題目描述
DZY loves chemistry, and he enjoys mixing chemicals.
DZY has n n n chemicals, and m m m pairs of them will react. He wants to pour these chemicals into a test tube, and he needs to pour them in one by one, in any order.
Let's consider the danger of a test tube. Danger of an empty test tube is 1 1 1 . And every time when DZY pours a chemical, if there are already one or more chemicals in the test tube that can react with it, the danger of the test tube will be multiplied by 2 2 2 . Otherwise the danger remains as it is.
Find the maximum possible danger after pouring all the chemicals one by one in optimal order.
輸入輸出格式
輸入格式:
The first line contains two space-separated integers n n n and m m m 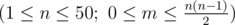 .
.
Each of the next m m m lines contains two space-separated integers xi x_{i} xi and yi y_{i} yi (1<=xi<yi<=n) (1<=x_{i}<y_{i}<=n) (1<=xi<yi<=n) . These integers mean that the chemical xi x_{i} xi will react with the chemical yi y_{i} yi . Each pair of chemicals will appear at most once in the input.
Consider all the chemicals numbered from 1 1 1 to n n n in some order.
輸出格式:
Print a single integer — the maximum possible danger.
輸入輸出樣例
輸入樣例#1: 複製
1 0
輸出樣例#1: 複製
1
輸入樣例#2: 複製
2 1 1 2
輸出樣例#2: 複製
2
輸入樣例#3: 複製
3 2 1 2 2 3
輸出樣例#3: 複製
4
說明
In the first sample, there's only one way to pour, and the danger won't increase.
In the second sample, no matter we pour the 1 1 1 st chemical first, or pour the 2 2 2 nd chemical first, the answer is always 2 2 2 .
In the third sample, there are four ways to achieve the maximum possible danger: 2-1-3, 2-3-1, 1-2-3 and 3-2-1 (that is the numbers of the chemicals in order of pouring).
用並查集維護即可;
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<bitset>
#include<ctime>
#include<deque>
#include<stack>
#include<functional>
#include<sstream>
//#include<cctype>
//#pragma GCC optimize("O3")
using namespace std;
#define maxn 100005
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define INF 999999999999999
#define rdint(x) scanf("%d",&x)
#define rdllt(x) scanf("%lld",&x)
#define rdlf(x) scanf("%lf",&x)
#define rdstr(x) scanf("%s",x)
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef unsigned int U;
#define ms(x) memset((x),0,sizeof(x))
const long long int mod = 1e9 + 7;
#define Mod 20100403
#define sq(x) (x)*(x)
#define eps 1e-5
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
#define pi acos(-1.0)
const int N = 1005;
#define REP(i,n) for(int i=0;i<(n);i++)
inline ll rd() {
ll x = 0;
char c = getchar();
bool f = false;
while (!isdigit(c)) {
if (c == '-') f = true;
c = getchar();
}
while (isdigit(c)) {
x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48);
c = getchar();
}
return f ? -x : x;
}
ll gcd(ll a, ll b) {
return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a%b);
}
ll sqr(ll x) { return x * x; }
int n, m;
ll ans;
int fa[maxn];
void init() {
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)fa[i] = i;
}
int findfa(int x) {
if(x == fa[x])return x;
return fa[x] = findfa(fa[x]);
}
void merge(int x, int y) {
if (findfa(x) != findfa(y)) {
fa[findfa(x)] = findfa(y);
}
}
int main()
{
//ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
rdint(n); rdint(m);
init(); ll ans = 1;
while (m--) {
int x, y;
rdint(x); rdint(y);
merge(x, y);
}
int tot = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (fa[i] == i)tot++;
}
cout << ((ll)1 << (n - tot)) << endl;
return 0;
}
