Netty入門(4) - 附帶的ChannelHandler和Codec
使用SSL/TLS建立安全的Netty程式
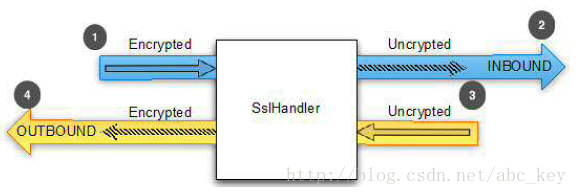
Java提供了抽象的SslContext和SslEngine,實際上SslContext可以用來獲取SslEngine來進行加密和解密。Netty拓展了Java的SslEngine,稱SslHandler,用來對網路資料進行加密和解密。
1、製作自簽證書
#keytool -genkey -keysize 2048 -validity 365 -keyalg RSA -dnam e "CN=gornix.com" -keypass 654321 -storepass 123456 -keystore gornix.jks
keytool為JDK提供的生成證書工具
- -keysize 2048 金鑰長度2048位(這個長度的金鑰目前可認為無法被暴力破解)
- -validity 365 證書有效期365天
- -keyalg RSA 使用RSA非對稱加密演算法
- -dname "CN=gornix.com" 設定Common Name為gornix.com,這是我的域名
- -keypass 654321 金鑰的訪問密碼為654321
- -storepass 123456 金鑰庫的訪問密碼為123456(其實這兩個密碼也可以設定一樣,通常都設定一樣,方便記)
- -keystore gornix.jks 指定生成的金鑰庫檔案為gornix.jks
2、服務端程式
public class SocketServerHelper { private static int WORKER_GROUP_SIZE = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() * 2; private static EventLoopGroup bossGroup; private static EventLoopGroup workerGroup; private static Class<? extends ServerChannel> channelClass;public static void startSpiderServer() throws Exception { ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap(); b.childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true) .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true) .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_REUSEADDR, true) .childOption(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, new PooledByteBufAllocator(false)) .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, 1048576) .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_SNDBUF, 1048576); bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1); workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(WORKER_GROUP_SIZE); channelClass = NioServerSocketChannel.class; System.out.println("workerGroup size:" + WORKER_GROUP_SIZE); System.out.println("preparing to start spider server..."); b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup); b.channel(channelClass); KeyManagerFactory keyManagerFactory = null; KeyStore keyStore = KeyStore.getInstance("JKS"); keyStore.load(new FileInputStream("G:\\ssl.jks"), "123456".toCharArray()); keyManagerFactory = KeyManagerFactory.getInstance("SunX509"); keyManagerFactory.init(keyStore,"123456".toCharArray()); SslContext sslContext = SslContextBuilder.forServer(keyManagerFactory).build(); b.childHandler(new SslChannelInitializer(sslContext)); b.bind(9912).sync(); System.out.println("spider server start sucess, listening on port " + 9912 + "."); } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { SocketServerHelper.startSpiderServer(); } public static void shutdown() { System.out.println("preparing to shutdown spider server..."); bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); System.out.println("spider server is shutdown."); } }
public class SslChannelInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> { private final SslContext context; public SslChannelInitializer(SslContext context) { this.context = context; } @Override protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception { SSLEngine engine = context.newEngine(ch.alloc()); engine.setUseClientMode(false); ch.pipeline().addFirst("ssl", new SslHandler(engine)); ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast("frameDecoder", new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, 4, 0, 4)); pipeline.addLast("frameEncoder", new LengthFieldPrepender(4)); //最大16M pipeline.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder(Charset.forName("UTF-8"))); pipeline.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder(Charset.forName("UTF-8"))); pipeline.addLast("spiderServerBusiHandler", new SpiderServerBusiHandler()); } }
3、客戶端程式
public class SocketClientHelper { public static void main(String[] args) { Channel channel = SocketClientHelper.createChannel("localhost",9912); try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } SocketHelper.writeMessage(channel, "ssh over tcp test 1"); SocketHelper.writeMessage(channel, "ssh over tcp test 2"); SocketHelper.writeMessage(channel, "ssh over tcp test 3"); SocketHelper.writeMessage(channel, "ssh over tcp test 4"); SocketHelper.writeMessage(channel, "ssh over tcp test 5"); } public static Channel createChannel(String host, int port) { Channel channel = null; Bootstrap b = getBootstrap(); try { channel = b.connect(host, port).sync().channel(); System.out.println(MessageFormat.format("connect to spider server ({0}:{1,number,#}) success for thread [" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "].", host , port)); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return channel; } public static Bootstrap getBootstrap(){ EventLoopGroup group; Class<? extends Channel> channelClass = NioSocketChannel.class; group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap(); b.group(group).channel(channelClass); b.option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true); b.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true); b.option(ChannelOption.SO_REUSEADDR, true); b.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, 5000); TrustManagerFactory tf = null; try { KeyStore keyStore = KeyStore.getInstance("JKS"); keyStore.load(new FileInputStream("G:\\ssl.jks"), "123456".toCharArray()); tf = TrustManagerFactory.getInstance("SunX509"); tf.init(keyStore); SslContext sslContext = SslContextBuilder.forClient().trustManager(tf).build(); b.handler(new SslChannelInitializer(sslContext)); return b; } catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } }
public class SslChannelInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> { private final SslContext context; public SslChannelInitializer(SslContext context) { this.context = context; } @Override protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception { SSLEngine engine = context.newEngine(ch.alloc()); engine.setUseClientMode(true); ch.pipeline().addFirst("ssl", new SslHandler(engine)); ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast("frameDecoder", new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, 4, 0, 4)); pipeline.addLast("frameEncoder", new LengthFieldPrepender(4)); //最大16M pipeline.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder(Charset.forName("UTF-8"))); pipeline.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder(Charset.forName("UTF-8"))); pipeline.addLast("spiderClientBusiHandler", new SpiderClientBusiHandler()); } }
可見SSL也沒什麼神祕的,就是在普通的TCP連線基礎上包了一層處理而已(但如果要自己實現這層處理那可是相當複雜的),這層處理體現在Netty中就是一個SslHandler,把這個SslHandler加入到TCP連線的處理管線中即可。
PS:我們也可以使用基於認證和報文頭加密的方式實現安全性。
處理空閒和超時
IdleStateHandler:當一個通道沒有進行讀寫或者運行了一段時間後發出IdleStateEvent
ReadTimeoutHandler:在指定時間沒沒有接收到任何資料將丟擲ReadTimeoutException
WriteTimeoutHandler:在指定時間內沒有寫入資料將丟擲WriteTimeoutException
public class IdleStateHandlerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> { @Override protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast(new IdleStateHandler(0, 0, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS)); pipeline.addLast(new HeartbeatHandler()); } public static final class HeartbeatHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { private static final ByteBuf HEARTBEAT_SEQ = Unpooled.unreleasableBuffer(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("HEARTBEAT", CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); @Override public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception { if (evt instanceof IdleStateEvent) { ctx.writeAndFlush(HEARTBEAT_SEQ.duplicate()).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE); } else { super.userEventTriggered(ctx, evt); } } } }
分隔符協議
DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder,解碼器,接收ByteBuf由一個或者多個分隔符拆分,如NUL或者換行符。
LineBasedFrameDecoder,解碼器,接收ByteBuf以分隔符結束,如"\n"和"\r\n"
public class LineBasedHandlerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> { @Override protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception { ch.pipeline().addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(65*1024), new FrameHandler()); } public static final class FrameHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf> { @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext arg0, ByteBuf arg1) throws Exception { // do something } } }
長度為基礎的協議
FixedLengthFrameDecoder:解碼器,固定長度提取幀
LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder:解碼器,讀取頭部長度並提取幀的長度
public class LengthBasedInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> { @Override protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception { ch.pipeline().addLast(new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(65*1024, 0, 8)) .addLast(new FrameHandler()); } public static final class FrameHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf> { @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg) throws Exception { // do something } } }
寫大資料
寫大量的資料的一個有效的方法就是使用非同步框架,如果記憶體和網路都處於爆滿負荷狀態,你需要停止寫,Netty提供zero-memory-copy機制,這種方法在將檔案內容寫到網路堆疊空間時可以獲得最大的效能:
public class WriteBigData extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { File file = new File(""); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); FileRegion region = new DefaultFileRegion(fis.getChannel(), 0, file.length()); Channel channel = ctx.channel(); channel.writeAndFlush(region).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() { @Override public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception { if (!future.isSuccess()) { Throwable cause = future.cause(); // do something } } }); } }
如果只想傳送指定的資料塊,可以使用ChunkedFile、ChunkedNioFile、ChunkedStream、ChunkedNioStream等。
Protobuf序列化傳輸
ProtobufDecoder、ProtobufEncoder、ProtobufVarint32FrameDecoder、ProtobufVarint32LengthPrepender,使用Protobuf需要映入protobuf-java-2.5.0.jar
1、下載編譯器,將protoc.exe配置到環境變數:https://github.com/google/protobuf/releases
2、編寫.proto檔案,參考:https://blog.csdn.net/hry2015/article/details/70766603
syntax = "proto3"; // 宣告可以選擇protobuf的編譯器版本(v2和v3) option java_outer_classname = "MessageProto"; // 指定生成的java類的類名 message Message { // 相當於c語言中的struct語句,表示定義一個資訊,其實也就是類。 string id = 1; // 要傳輸的欄位了,子段後面需要有一個數字編號,從1開始遞增 string content = 2; }
3、CMD執行編譯操作
protoc ./Message.proto --java_out=./
4、引入maven
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.google.protobuf/protobuf-java --> <dependency> <groupId>com.google.protobuf</groupId> <artifactId>protobuf-java</artifactId> <version>3.5.1</version> </dependency>
5、服務端
public class ServerPoHandlerProto extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) { MessageProto.Message message = (MessageProto.Message) msg; if (ConnectionPool.getChannel(message.getId()) == null) { ConnectionPool.putChannel(message.getId(), ctx); } System.err.println("server:" + message.getId()); ctx.writeAndFlush(message); } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) { cause.printStackTrace(); ctx.close(); } }
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { // 實體類傳輸資料,protobuf序列化 ch.pipeline().addLast("decoder", new ProtobufDecoder(MessageProto.Message.getDefaultInstance())); ch.pipeline().addLast("encoder", new ProtobufEncoder()); ch.pipeline().addLast(new ServerPoHandlerProto()); } }) .option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128) .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
6、客戶端
public class ClientPoHandlerProto extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) { MessageProto.Message message = (MessageProto.Message) msg; System.out.println("client:" + message.getContent()); } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) { cause.printStackTrace(); ctx.close(); } }
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap(); b.group(workerGroup); b.channel(NioSocketChannel.class); b.option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true); b.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { // 實體類傳輸資料,protobuf序列化 ch.pipeline().addLast("decoder", new ProtobufDecoder(MessageProto.Message.getDefaultInstance())); ch.pipeline().addLast("encoder", new ProtobufEncoder()); ch.pipeline().addLast(new ClientPoHandlerProto()); } });
單元測試
package com.netty.learn.demo6; import java.util.List; import java.util.Random; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline; import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler; import io.netty.channel.embedded.EmbeddedChannel; import io.netty.handler.codec.ByteToMessageDecoder; public class EmbeddedChannelInboundTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Random r = new Random(); ByteBuf byteBuf = Unpooled.buffer(); for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { int one = r.nextInt(); byteBuf.writeInt(one); System.out.println("generate one: " + one); } EmbeddedChannel embeddedChannel = new EmbeddedChannel(); // 獲取channelPipeLine ChannelPipeline channelPipeline = embeddedChannel.pipeline(); channelPipeline.addFirst(new DecodeTest()); channelPipeline.addLast(new SimpleChannelInBoundHandlerTest()); // 寫入測試資料 embeddedChannel.writeInbound(byteBuf); embeddedChannel.finish(); // 驗證測試資料 System.out.println("embeddedChannel readInbound:" + embeddedChannel.readInbound()); System.out.println("embeddedChannel readInbound:" + embeddedChannel.readInbound()); System.out.println("embeddedChannel readInbound:" + embeddedChannel.readInbound()); } } // 解碼器 class DecodeTest extends ByteToMessageDecoder { @Override protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception { if (in.readableBytes() >= 4) { out.add(in.readInt()); } } } // channelHandler @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") class SimpleChannelInBoundHandlerTest extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler { @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { System.out.println("Received message:" + msg); ctx.fireChannelRead(msg); } }
