【OpenCV】透視變換 Perspective Transformation
透視變換的原理和矩陣求解請參見前一篇《透視變換 Perspective Transformation》。在OpenCV中也實現了透視變換的公式求解和變換函式。
求解變換公式的函式:
Mat getPerspectiveTransform(const Point2f src[], const Point2f dst[])
void perspectiveTransform
-
int main( )
-
{
-
Mat img=imread(
"boy.png"
-
int img_height = img.rows;
-
int img_width = img.cols;
-
vector<Point2f> corners(
4);
-
corners[
0] = Point2f(
0,
0);
-
corners[
1] = Point2f(img_width
-1,
0);
-
corners[
2] = Point2f(
0,img_height
-1);
-
corners[
3] = Point2f(img_width
-1,img_height
-1);
-
vector<Point2f> corners_trans(
4);
-
corners_trans[
0] = Point2f(
150,
250);
-
corners_trans[
1] = Point2f(
771,
0);
-
corners_trans[
2] = Point2f(
0,img_height
-1);
-
corners_trans[
3] = Point2f(
650,img_height
-1);
-
-
Mat transform = getPerspectiveTransform(corners,corners_trans);
-
cout<<transform<<
endl;
-
vector<Point2f> ponits, points_trans;
-
for(
int i=
0;i<img_height;i++){
-
for(
int j=
0;j<img_width;j++){
-
ponits.push_back(Point2f(j,i));
-
}
-
}
-
-
perspectiveTransform( ponits, points_trans, transform);
-
Mat img_trans = Mat::zeros(img_height,img_width,CV_8UC3);
-
int count =
0;
-
for(
int i=
0;i<img_height;i++){
-
uchar* p = img.ptr<uchar>(i);
-
for(
int j=
0;j<img_width;j++){
-
int y = points_trans[count].y;
-
int x = points_trans[count].x;
-
uchar* t = img_trans.ptr<uchar>(y);
-
t[x*
3] = p[j*
3];
-
t[x*
3+
1] = p[j*
3+
1];
-
t[x*
3+
2] = p[j*
3+
2];
-
count++;
-
}
-
}
-
imwrite(
"boy_trans.png",img_trans);
-
-
return
0;
-
}
得到變換之後的圖片:
注意這種將原圖變換到對應影象上的方式會有一些沒有被填充的點,也就是右圖中黑色的小點。解決這種問題一是用差值的方式,再一種比較簡單就是不用原圖的點變換後對應找新圖的座標,而是直接在新圖上找反向變換原圖的點。說起來有點繞口,具體見前一篇《透視變換 Perspective Transformation》的程式碼應該就能懂啦。
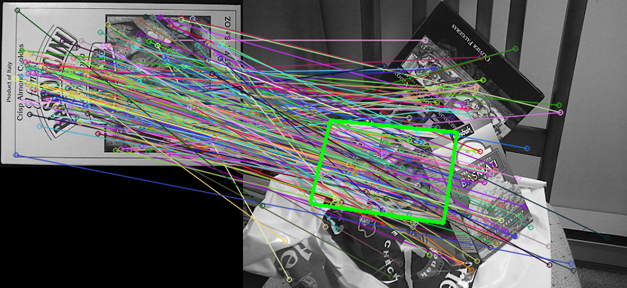
除了getPerspectiveTransform()函式,OpenCV還提供了findHomography()的函式,不是用點來找,而是直接用透視平面來找變換公式。這個函式在特徵匹配的經典例子中有用到,也非常直觀:
-
int main( int argc, char** argv )
-
{
-
Mat img_object = imread( argv[
1], IMREAD_GRAYSCALE );
-
Mat img_scene = imread( argv[
2], IMREAD_GRAYSCALE );
-
if( !img_object.data || !img_scene.data )
-
{
std::
cout<<
" --(!) Error reading images " <<
std::
endl;
return
-1; }
-
-
//-- Step 1: Detect the keypoints using SURF Detector
-
int minHessian =
400;
-
SurfFeatureDetector detector( minHessian );
-
std::
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_object, keypoints_scene;
-
detector.detect( img_object, keypoints_object );
-
detector.detect( img_scene, keypoints_scene );
-
-
//-- Step 2: Calculate descriptors (feature vectors)
-
SurfDescriptorExtractor extractor;
-
Mat descriptors_object, descriptors_scene;
-
extractor.compute( img_object, keypoints_object, descriptors_object );
-
extractor.compute( img_scene, keypoints_scene, descriptors_scene );
-
-
//-- Step 3: Matching descriptor vectors using FLANN matcher
-
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;
-
std::
vector< DMatch > matches;
-
matcher.match( descriptors_object, descriptors_scene, matches );
-
double max_dist =
0;
double min_dist =
100;
-
-
//-- Quick calculation of max and min distances between keypoints
-
for(
int i =
0; i < descriptors_object.rows; i++ )
-
{
double dist = matches[i].distance;
-
if( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist;
-
if( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist;
-
}
-
-
printf(
"-- Max dist : %f \n", max_dist );
-
printf(
"-- Min dist : %f \n", min_dist );
-
-
//-- Draw only "good" matches (i.e. whose distance is less than 3*min_dist )
-
std::
vector< DMatch > good_matches;
-
-
for(
int i =
0; i < descriptors_object.rows; i++ )
-
{
if( matches[i].distance <
3*min_dist )
-
{ good_matches.push_back( matches[i]); }
-
}
-
-
Mat img_matches;
-
drawMatches( img_object, keypoints_object, img_scene, keypoints_scene,
-
good_matches, img_matches, Scalar::all(
-1), Scalar::all(
-1),
-
vector<
char>(), DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS );
-
-
//-- Localize the object from img_1 in img_2
-
std::
vector<Point2f> obj;
-
std::
vector<Point2f> scene;
-
-
for(
size_t i =
0; i < good_matches.size(); i++ )
-
{
-
//-- Get the keypoints from the good matches
-
obj.push_back( keypoints_object[ good_matches[i].queryIdx ].pt );
-
scene.push_back( keypoints_scene[ good_matches[i].trainIdx ].pt );
-
}
-
-
Mat H = findHomography( obj, scene, RANSAC );
-
-
//-- Get the corners from the image_1 ( the object to be "detected" )
-
std::
vector<Point2f> obj_corners(
4);
-
obj_corners[
0] = Point(
0,
0); obj_corners[
1] = Point( img_object.cols,
0 );
-
obj_corners[
2] = Point( img_object.cols, img_object.rows ); obj_corners[
3] = Point(
0, img_object.rows );
-
std::
vector<Point2f> scene_corners(
4);
-
perspectiveTransform( obj_corners, scene_corners, H);
-
//-- Draw lines between the corners (the mapped object in the scene - image_2 )
-
Point2f offset( (float)img_object.cols, 0);
-
line( img_matches, scene_corners[
0] + offset, scene_corners[
1] + offset, Scalar(
0,
255,
0),
4 );
-
line( img_matches, scene_corners[
1] + offset, scene_corners[
2] + offset, Scalar(
0,
255,
0),
4 );
-
line( img_matches, scene_corners[
2] + offset, scene_corners[
3] + offset, Scalar(
0,
255,
0),
4 );
-
line( img_matches, scene_corners[
3] + offset, scene_corners[
0] + offset, Scalar(
0,
255,
0),
4 );
-
-
//-- Show detected matches
-
imshow(
"Good Matches & Object detection", img_matches );
-
waitKey(
0);
-
return
0;
-
}
程式碼執行效果:
findHomography()函式直接通過兩個平面上相匹配的特徵點求出變換公式,之後程式碼又對原圖的四個邊緣點進行變換,在右圖上畫出對應的矩形。這個圖也很好地解釋了所謂透視變換的“Viewing Plane”。
(轉載請註明作者和出處:http://blog.csdn.net/xiaowei_cqu 未經允許請勿用於商業用途)
透視變換的原理和矩陣求解請參見前一篇《透視變換 Perspective Transformation》。在OpenCV中也實現了透視變換的公式求解和變換函式。
求解變換公式的函式:
Mat getPerspectiveTransform(const Point2f src[], const Point2f dst[])
void perspectiveTransform(InputArray src, OutputArray dst, InputArray m)
-
int main( )
-
{
-
Mat img=imread(
"boy.png");
-
int img_height = img.rows;
-
int img_width = img.cols;
-
vector<Point2f> corners(
4);
-
corners[
0] = Point2f(
0,
0);
-
corners[
1] = Point2f(img_width
-1,
0);
-
corners[
2] = Point2f(
0,img_height
-1);
-
corners[
3] = Point2f(img_width
-1,img_height
-1);
-
vector<Point2f> corners_trans(
4);
-
corners_trans[
0] = Point2f(
150,
250);
-
corners_trans[
1] = Point2f(
771,
0);
-
corners_trans[
2] = Point2f(
0,img_height
-1);
-
corners_trans[
3] = Point2f(
650,img_height
-1);
-
-
Mat transform = getPerspectiveTransform(corners,corners_trans);
-
cout<<transform<<
endl;
-
vector<Point2f> ponits, points_trans;
-
for(
int i=
0;i<img_height;i++){
-
for(
int j=
0;j<img_width;j++){
-
ponits.push_back(Point2f(j,i));
-
}
-
}
-
-
perspectiveTransform( ponits, points_trans, transform);
-
Mat img_trans = Mat::zeros(img_height,img_width,CV_8UC3);
-
int count =
0;
-
for(
int i=
0;i<img_height;i++){
-
uchar* p = img.ptr<uchar>(i);
-
for(
int j=
0;j<img_width;j++){
-
int y = points_trans[count].y;
-
int x = points_trans[count].x;
-
uchar* t = img_trans.ptr<uchar>(y);
-
t[x*
3] = p[j*
3];
-
t[x*
3+
1] = p[j*
3+
1];
-
t[x*
3+
2] = p[j*
3+
2];
-
count++;
-
}
-
}
-
imwrite(
"boy_trans.png",img_trans);
-
-
return
0;
-
}
得到變換之後的圖片:
注意這種將原圖變換到對應影象上的方式會有一些沒有被填充的點,也就是右圖中黑色的小點。解決這種問題一是用差值的方式,再一種比較簡單就是不用原圖的點變換後對應找新圖的座標,而是直接在新圖上找反向變換原圖的點。說起來有點繞口,具體見前一篇《透視變換 Perspective Transformation》的程式碼應該就能懂啦。
除了getPerspectiveTransform()函式,OpenCV還提供了findHomography()的函式,不是用點來找,而是直接用透視平面來找變換公式。這個函式在特徵匹配的經典例子中有用到,也非常直觀:
-
int main( int argc, char** argv )
-
{
-
Mat img_object = imread( argv[
1], IMREAD_GRAYSCALE );
-
Mat img_scene = imread( argv[
2], IMREAD_GRAYSCALE );
-
if( !img_object.data || !img_scene.data )
-
{
std::
cout<<
" --(!) Error reading images " <<
std::
endl;
return
-1; }
-
-
//-- Step 1: Detect the keypoints using SURF Detector
-
int minHessian =
400;
-
SurfFeatureDetector detector( minHessian );
-
std::
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_object, keypoints_scene;
-
detector.detect( img_object, keypoints_object );
-
detector.detect( img_scene, keypoints_scene );
-
-
//-- Step 2: Calculate descriptors (feature vectors)
-
SurfDescriptorExtractor extractor;
-
Mat descriptors_object, descriptors_scene;
-
extractor.compute( img_object, keypoints_object, descriptors_object );
-
extractor.compute( img_scene, keypoints_scene, descriptors_scene );
-
-
//-- Step 3: Matching descriptor vectors using FLANN matcher
-
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;
-
std::
vector< DMatch > matches;
-
matcher.match( descriptors_object, descriptors_scene, matches );
-
double max_dist =
0;
double min_dist =
100;
-
-
//-- Quick calculation of max and min distances between keypoints
-
for(
int i =
0; i < descriptors_object.rows; i++ )
-
{
double dist = matches[i].distance;
-
if( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist;
-