c語言數字影象處理(九):邊緣檢測
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-11-19
背景知識
邊緣畫素是影象中灰度突變的畫素,而邊緣是連線邊緣畫素的集合。邊緣檢測是設計用來檢測邊緣畫素的區域性影象處理方法。
孤立點檢測
使用<https://www.cnblogs.com/GoldBeetle/p/9744625.html>中介紹的拉普拉斯運算元
輸出影象為
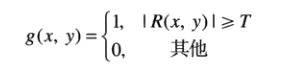
卷積模板
之前有過程式碼實現,這篇文章中不再進行測試
基本邊緣檢測
影象梯度
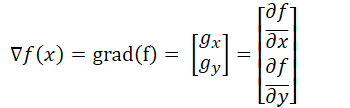
梯度向量大小

在影象處理過程中,因平方和和開方運算速度較慢,因此簡化為如下計算方法
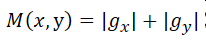
梯度向量方向與x軸夾角

對應與不同的偏導數計算方法,得出邊緣檢測的不同模板
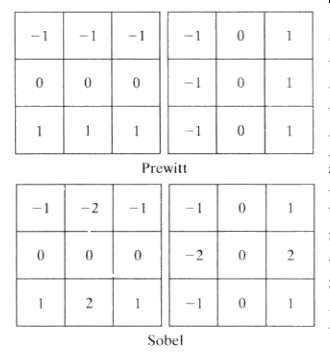
檢測垂直或水平邊緣
原圖
使用Sobel模板檢測水平邊緣

使用Sobel模板檢測垂直邊緣

兩者相加

程式碼實現
1 void edge_detection(short** in_array, short** out_array, long height, long width) 2 { 3 short gx = 0, gy = 0; 4 short** a_soble1; 5 short** a_soble2; 6 7 a_soble1 = allocate_image_array(3, 3); 8 a_soble2 = allocate_image_array(3, 3); 9 for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++){ 10 for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++){ 11 a_soble1[i][j] = soble1[i][j]; 12 a_soble2[i][j] = soble2[i][j]; 13 } 14 } 15 for (int i = 0; i < height; i++){ 16 for (int j = 0; j < width; j++){ 17 gx = convolution(in_array, i, j, height, width, a_soble1, 3); 18 gy = convolution(in_array, i, j, height, width, a_soble2, 3); 19 // out_array[i][j] = gx; 20 // out_array[i][j] = gy; 21 out_array[i][j] = gx + gy; 22 if (out_array[i][j] < 0) 23 out_array[i][j] = 0; 24 else if (out_array[i][j] > 0xff) 25 out_array[i][j] = 0xff; 26 } 27 } 28 free_image_array(a_soble1, 3); 29 free_image_array(a_soble2, 3); 30 }
檢測對角邊緣
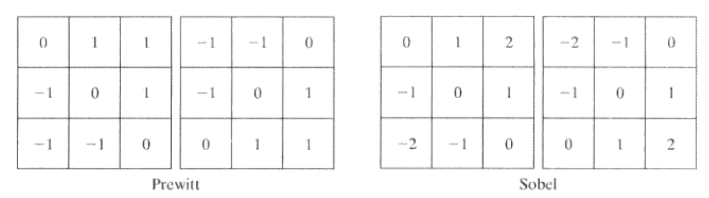
Sobel 45°檢測模板

Sobel -45°檢測模板

兩者相加

程式碼實現通上,只需替換模板值即可
Marr-Hildreth邊緣檢測演算法
1. 對二維高斯函式進行取樣,得高斯低通濾波器,對輸入影象濾波,濾波器模板大小為大於等於6*σ的最小奇整數
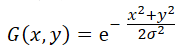
演算法實現
1 void generate_gaussian_filter(double** gaussian_filter, long sigma) 2 { 3 double x, y; 4 long filter_size = 6 * sigma + 1; 5 6 for (int i = 0; i < filter_size; i++){ 7 for (int j = 0; j < filter_size; j++){ 8 x = i - filter_size / 2; 9 y = j - filter_size / 2; 10 gaussian_filter[i][j] = exp(-1.0 * ((pow(x, 2) + pow(y, 2)) / 2 * sigma * sigma)); 11 } 12 } 13 }
2. 計算第一步得到影象的拉普拉斯,利用如下模板

演算法實現
1 void laplace(short** in_array, short** out_array, long height, long width) 2 { 3 short** a_sharpen; 4 5 a_sharpen = allocate_image_array(3, 3); 6 for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++){ 7 for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++){ 8 a_sharpen[i][j] = sharpen[i][j]; 9 } 10 } 11 for (int i = 0; i < height; i++){ 12 for (int j = 0; j < width; j++){ 13 out_array[i][j] = convolution(in_array, i, j, height, width, a_sharpen, 3); 14 } 15 } 16 free_image_array(a_sharpen, 3); 17 }
執行結果

3. 尋找零交叉,對任意畫素p,測試上/下,左/右,兩個對角線四個位置,當有兩對符號不同並且絕對值差大於某一閾值時為零交叉點
演算法實現
1 int is_cross(short** in_array, long row, long column) 2 { 3 int cross_num = 0; 4 5 if (in_array[row-1][column-1] * in_array[row+1][column+1] < 0 && 6 abs(abs(in_array[row-1][column-1]) - abs(in_array[row+1][column+1])) > 0x66) 7 cross_num++; 8 if (in_array[row-1][column] * in_array[row+1][column] < 0&& 9 abs(abs(in_array[row-1][column]) - abs(in_array[row+1][column])) > 0x66) 10 cross_num++; 11 if (in_array[row-1][column+1] * in_array[row+1][column-1] < 0&& 12 abs(abs(in_array[row-1][column+1]) - abs(in_array[row+1][column-1])) > 0x66) 13 cross_num++; 14 if (in_array[row][column-1] * in_array[row][column+1] < 0&& 15 abs(abs(in_array[row][column-1]) - abs(in_array[row][column+1])) > 0x66) 16 cross_num++; 17 18 if (cross_num >= 2) 19 return 1; 20 else 21 return 0; 22 }
最終執行結果

可以看出,該演算法檢測出的邊緣更加符合物體的真實邊緣,但是這些邊緣是由離散的點構成的,因此需要進行邊緣連線來進一步加工,本文對此不再進行詳述,讀者有興趣可以進行更加深入的研究。

