mybatis原始碼-Mapper解析之SQL 語句節點解析(一條語句對應一個MappedStatement)
一起學 mybatis
你想不想來學習 mybatis? 學習其使用和原始碼呢?那麼, 在部落格園關注我吧!!
我自己打算把這個原始碼系列更新完畢, 同時會更新相應的註釋。快去 star 吧!!
在 mybatis 中, 對應 CRUD 的是四種節點: <select>, <insert>, <delete>, <update>。
在解析 Mapper.xml 檔案中, 會呼叫 XMLStatementBuilder 來 進行這幾個節點的解析。 解析完成後使用 MappedStatement 來表示一條條 SQL 語句。 完成的是這樣這個過程
0 <sql> 節點解析
在此之前, 需要先了解一下 <sql>。
<sql> 節點不僅僅是程式碼生成器生成時, 代表一些欄位而已, 其定義可重用的 SQL 語句的片段。 類似於我們在寫程式碼時, 抽象出一個方法。
/** * 解析 <sql> 節點 * * @param list * @param requiredDatabaseId * @throws Exception */ private void sqlElement(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) throws Exception { // 遍歷 <sql> 節點 for (XNode context : list) { // 獲取 databaseId 屬性 String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId"); // 獲取 id 屬性 String id = context.getStringAttribute("id"); // 為 id 新增名稱空間 id = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(id, false); // 檢查 sql 節點的 databaseId 與當前 Configuration 中的是否一致 if (databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, requiredDatabaseId)) { // 記錄到 XMLMapperBuider.sqlFragments(Map<String, XNode>)中儲存 // 其最終是指向了 Configuration.sqlFragments(configuration.getSqlFragments) 集合 sqlFragments.put(id, context); } } }
整體的過程就是獲取所有節點, 然後逐個解析。 然後以 id-> context 鍵值對的方式存放在 XMLMapperBuilder.sqlFragments 物件中, 後續會用到。
注意, 此時的 context 還是 XNode 物件, 其最終的解析還是在解析 include 時進行解析。
注意, id 使用了 MapperBuilderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace 進行了處理。 其是按照一定的規則在前面新增 namespace, 以便 id 在全域性具有唯一性。
1 解析流程
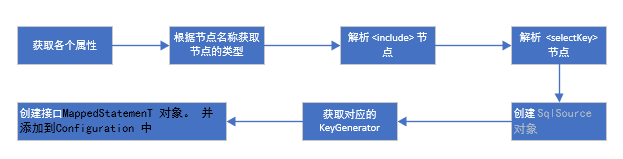
其整體的程式碼是這樣子的
public void parseStatementNode() { // 獲取 id 屬性 String id = context.getStringAttribute("id"); // 獲取 databaseid String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId"); //驗證databaseId是否匹配 if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this.requiredDatabaseId)) { return; } // 獲取各個屬性 Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize"); Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout"); String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap"); String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType"); Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType); String resultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap"); String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType"); String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang"); LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang); Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType); String resultSetType = context.getStringAttribute("resultSetType"); StatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf(context.getStringAttribute("statementType", StatementType.PREPARED.toString())); ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = resolveResultSetType(resultSetType); // 獲取節點的型別 String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName(); SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH)); boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT; boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache", !isSelect); boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache", isSelect); boolean resultOrdered = context.getBooleanAttribute("resultOrdered", false); // Include Fragments before parsing // 引入include 解析出的 sql 節點內容 XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration, builderAssistant); includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode()); // Parse selectKey after includes and remove them. // 處理 selectKey processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver); // Parse the SQL (pre: <selectKey> and <include> were parsed and removed) SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass); String resultSets = context.getStringAttribute("resultSets"); String keyProperty = context.getStringAttribute("keyProperty"); String keyColumn = context.getStringAttribute("keyColumn"); KeyGenerator keyGenerator; // 設定主鍵自增的方式 String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX; keyStatementId = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(keyStatementId, true); if (configuration.hasKeyGenerator(keyStatementId)) { keyGenerator = configuration.getKeyGenerator(keyStatementId); } else { keyGenerator = context.getBooleanAttribute("useGeneratedKeys", configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType)) ? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE; } builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType, fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass, resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered, keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets); }
但去除一些獲取節點屬性的程式碼, 去除一些反射的程式碼。 其流程可以用下圖表示
2
在其他的內容解析之前, 會先解析 <incliude>節點, 用對應 id 的重用 SQL 語句將該節點替換掉。
先看看約束的定義
<!ELEMENT include (property+)?>
<!ATTLIST include
refid CDATA #REQUIRED
>可以看出, <incliude> 節點中可以包含有 property 一個或多個, 必須包含有 refid。 refid 是對應 <sql> 節點的 id。
2.1 解析流程
解析時, 通過 XMLIncludeTransformer.applyIncludes 方法進行解析。
/**
* 從 parseStatementNode 方法進入時, Node 還是 (select|insert|update|delete) 節點
*/
public void applyIncludes(Node source) {
Properties variablesContext = new Properties();
// 獲取的是 mybatis-config.xml 所定義的屬性
Properties configurationVariables = configuration.getVariables();
if (configurationVariables != null) {
variablesContext.putAll(configurationVariables);
}
// 處理 <include> 子節點
applyIncludes(source, variablesContext, false);
}獲取 Coniguration.variables 中的所有屬性, 這些屬性後續在將 ${XXX} 替換成真實的引數時會用到。 然後遞迴解析所有的 include 節點。 具體的實現過程如下:
/**
* Recursively apply includes through all SQL fragments.
* 遞迴的包含所有的 SQL 節點
*
* @param source Include node in DOM tree
* @param variablesContext Current context for static variables with values
*/
private void applyIncludes(Node source, final Properties variablesContext, boolean included) {
// 下面是處理 include 子節點
if (source.getNodeName().equals("include")) {
// 查詢 refid 屬性指向 <sql> 節點
Node toInclude = findSqlFragment(getStringAttribute(source, "refid"), variablesContext);
// 解析 <include> 節點下的 <property> 節點, 將得到的鍵值對新增到 variablesContext 中
// 並形成 Properties 物件返回, 用於替換佔位符
Properties toIncludeContext = getVariablesContext(source, variablesContext);
// 遞迴處理 <include> 節點, 在 <sql> 節點中可能會 <include> 其他 SQL 片段
applyIncludes(toInclude, toIncludeContext, true);
if (toInclude.getOwnerDocument() != source.getOwnerDocument()) {
toInclude = source.getOwnerDocument().importNode(toInclude, true);
}
// 將 <include> 節點替換成 <sql>
source.getParentNode().replaceChild(toInclude, source);
while (toInclude.hasChildNodes()) {
toInclude.getParentNode().insertBefore(toInclude.getFirstChild(), toInclude);
}
toInclude.getParentNode().removeChild(toInclude);
} else if (source.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
if (included && !variablesContext.isEmpty()) {
// replace variables in attribute values
// 獲取所有的屬性值, 並使用 variablesContext 進行佔位符的解析
NamedNodeMap attributes = source.getAttributes();
for (int i = 0; i < attributes.getLength(); i++) {
Node attr = attributes.item(i);
attr.setNodeValue(PropertyParser.parse(attr.getNodeValue(), variablesContext));
}
}
// 獲取所有的子類, 並遞迴解析
NodeList children = source.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < children.getLength(); i++) {
applyIncludes(children.item(i), variablesContext, included);
}
} else if (included && source.getNodeType() == Node.TEXT_NODE
&& !variablesContext.isEmpty()) {
// replace variables in text node
// 使用 variablesContext 進行佔位符的解析
source.setNodeValue(PropertyParser.parse(source.getNodeValue(), variablesContext));
}
}它分三種節點進行解析
- include
- Node.ELEMENT_NODE
- Node.TEXT_NODE
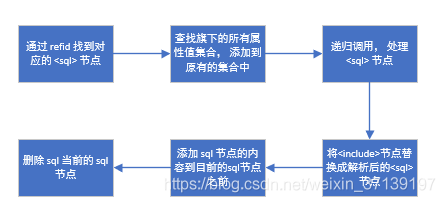
2.2 <include> 節點的解析
這個是節點為 <include> 時才進行解析的, 其解析的流程大體如下
2.3 Node.ELEMENT_NODE 型別解析
什麼時候回出現這種情況呢? 節點是非 <include> 的 Node.ELEMENT_NODE 型別的節點時, 如 sql 節點, (select | insert | update | delete) 節點的時候。 這些節點的特點就是都有可能含有 <include> 節點。
這個的流程很簡單, 就是遞迴呼叫解析所有的 <include> 子節點。
// 獲取所有的子類, 並遞迴解析
NodeList children = source.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < children.getLength(); i++) {
applyIncludes(children.item(i), variablesContext, included);
}2.4 Node.TEXT_NODE
Node.TEXT_NODE 就是文字節點, 當時該型別的節點時, 就會使用 PropertyParser.parse 方法來進行解析。 其大體就是將 ${xxx} 替換成相應的值。
由於有 included 條件的現在, 其只有是在 include 所包含的子節點時才會如此。
舉例
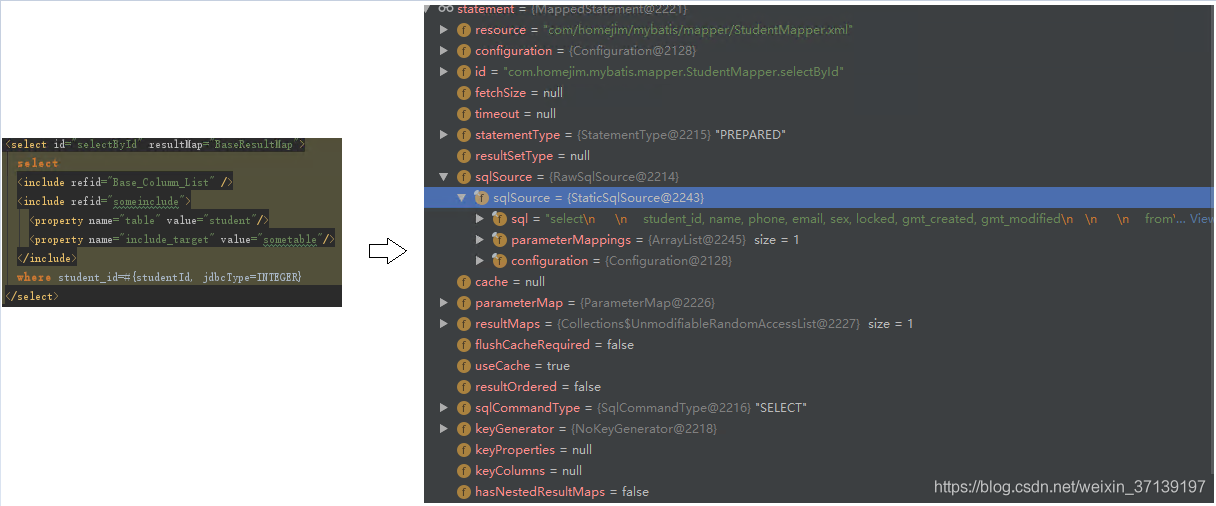
該過程中涉及到了多層遞迴, 同時還有多種節點型別, 還需要進行佔位符的處理, 理解上還是比較費勁的, 舉個栗子吧
<!--全部欄位-->
<sql id="Base_Column_List">
student_id, name, phone, email, sex, locked, gmt_created, gmt_modified
</sql>
<!--表名-->
<sql id="sometable">
${table}
</sql>
<!--refid可以使用${}-->
<sql id="someinclude">
from
<include refid="${include_target}"/>
</sql>
<!--SQL-->
<select id="selectById" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select
<include refid="Base_Column_List" />
<include refid="someinclude">
<property name="table" value="student"/>
<property name="include_target" value="sometable"/>
</include>
where student_id=#{studentId, jdbcType=INTEGER}
</select>其流程大體如下
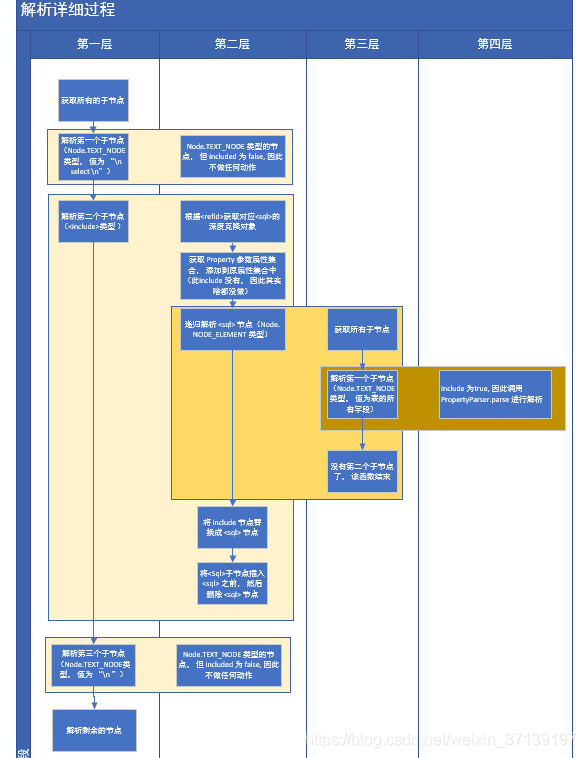
看的時候, 請對照程式碼來看, 詳細講解了前面三個節點的解析過程。 後面的類似, 可能有的遞迴層次加深了, 並大體的思路並沒有改變。
3
<insert>、<update>可以定義<selectKey>節點來獲取主鍵。
/**
* 真正解析 selectKey 的函式
*/
private void parseSelectKeyNode(String id, XNode nodeToHandle, Class<?> parameterTypeClass, LanguageDriver langDriver, String databaseId) {
// 開始時獲取各個屬性
String resultType = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("resultType");
Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType);
StatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf(nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("statementType", StatementType.PREPARED.toString()));
String keyProperty = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("keyProperty");
String keyColumn = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("keyColumn");
boolean executeBefore = "BEFORE".equals(nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("order", "AFTER"));
//defaults
boolean useCache = false;
boolean resultOrdered = false;
KeyGenerator keyGenerator = NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
Integer fetchSize = null;
Integer timeout = null;
boolean flushCache = false;
String parameterMap = null;
String resultMap = null;
ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = null;
// 生成對應的 SqlSource
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, nodeToHandle, parameterTypeClass);
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.SELECT;
// 使用 SqlSource 建立 MappedStatement 物件
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, null);
id = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
MappedStatement keyStatement = configuration.getMappedStatement(id, false);
// 新增到 Configuration 中, 並通過 executeBefore 還覺得是在sql之前執行還是之後執行
configuration.addKeyGenerator(id, new SelectKeyGenerator(keyStatement, executeBefore));
}其中涉及到
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, nodeToHandle, parameterTypeClass);這個過程。
LanguageDriver 類有兩個實現類
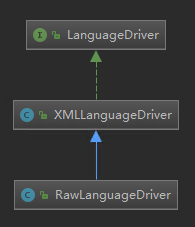
預設是 XMLLanguageDriver。 可以通過 Configuration 的建構函式得出。
languageRegistry.setDefaultDriverClass(XMLLanguageDriver.class);在 langDriver.createSqlSource 函式中, 會呼叫 parseScriptNode 函式
/**
* 解析動態節點
* @return
*/
public SqlSource parseScriptNode() {
// 首先判斷是不是動態節點
MixedSqlNode rootSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(context);
SqlSource sqlSource = null;
if (isDynamic) {
sqlSource = new DynamicSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode);
} else {
sqlSource = new RawSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode, parameterType);
}
return sqlSource;
}而其中, 需要判定是否為動態SQL, 其中, 有 $ 和動態 sql 的節點, 都會認為是動態SQL。
/**
* 解析動態節點
* @param node
* @return
*/
protected MixedSqlNode parseDynamicTags(XNode node) {
List<SqlNode> contents = new ArrayList<>();
// 獲取節點下的所有子節點
NodeList children = node.getNode().getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < children.getLength(); i++) {
// 獲取節點
XNode child = node.newXNode(children.item(i));
if (child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.CDATA_SECTION_NODE || child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.TEXT_NODE) {
// 如果有 $ , 則為動態sql節點
String data = child.getStringBody("");
TextSqlNode textSqlNode = new TextSqlNode(data);
if (textSqlNode.isDynamic()) {
contents.add(textSqlNode);
isDynamic = true;// 標記為動態節點
} else {
contents.add(new StaticTextSqlNode(data));
}
} else if (child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) { // issue #628
// 子節點是標籤, 則一定是動態sql節點。 根據nodeName, 生產不同的 NodeHandler
String nodeName = child.getNode().getNodeName();
NodeHandler handler = nodeHandlerMap.get(nodeName);
if (handler == null) {
throw new BuilderException("Unknown element <" + nodeName + "> in SQL statement.");
}
handler.handleNode(child, contents);
isDynamic = true;
}
}
return new MixedSqlNode(contents);
}NodeHandler 有以下幾個實現類
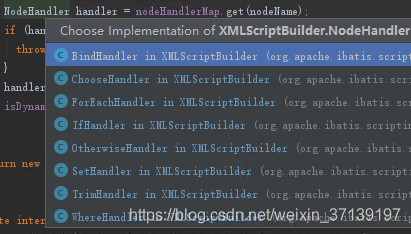
是不是似曾相識? 就是動態 SQL 的幾個節點所對應的。
在該過程之後, selectById 就變成了:
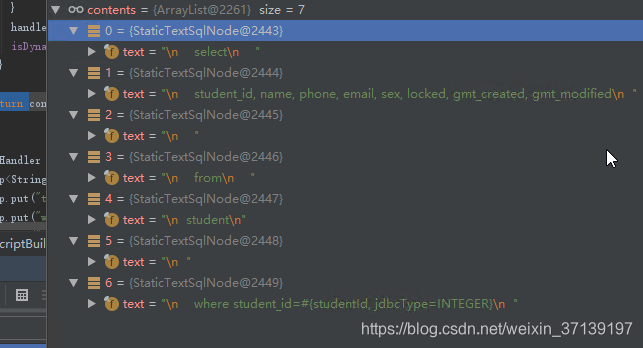
4 建立 SqlSource
該過程與上面的過程相似, 經過 include 節點的解析之後, 會建立對應的 SqlSourceNode 物件。
關於 SqlSource, 會在後續的文章中詳細展開講解。
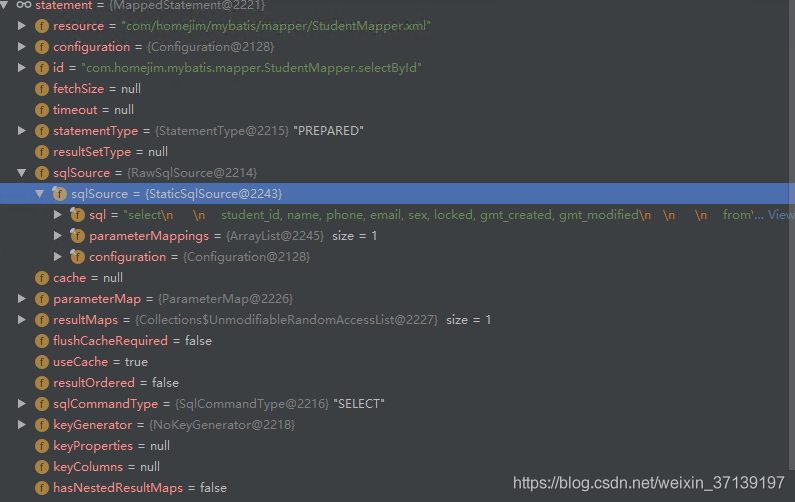
在該過程之後, selectById 變成了
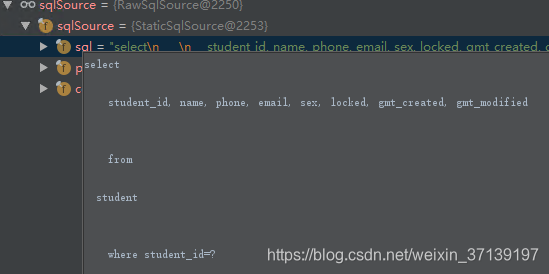
對應引數及其型別被儲存起來, 同時引數的佔位符 #{xxx, JdbcType=yyy} 變成了問號。 在呼叫 RawSqlSource 建構函式時, 會完成該過程
public RawSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String sql, Class<?> parameterType) {
SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration);
Class<?> clazz = parameterType == null ? Object.class : parameterType;
sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(sql, clazz, new HashMap<String, Object>());
}
public SqlSource parse(String originalSql, Class<?> parameterType, Map<String, Object> additionalParameters) {
// 佔位符處理器
ParameterMappingTokenHandler handler = new ParameterMappingTokenHandler(configuration, parameterType, additionalParameters);
GenericTokenParser parser = new GenericTokenParser("#{", "}", handler);
String sql = parser.parse(originalSql);
return new StaticSqlSource(configuration, sql, handler.getParameterMappings());
}
// SQL 中的佔位符處理。
@Override
public String handleToken(String content) {
parameterMappings.add(buildParameterMapping(content));
return "?";
}5 獲取對應的 KeyGenerator
KeyGenerator為鍵生成器。 在我們使用主鍵自動生成時, 會生成一個對應的主鍵生成器例項。
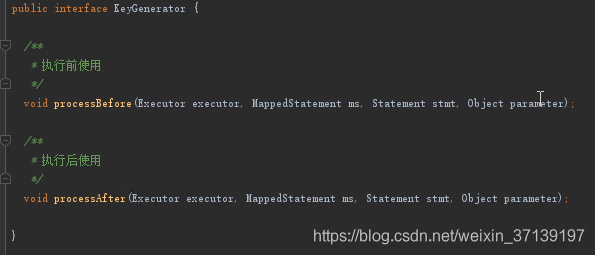
該介面主要定義了生成器的在 SQL 在查詢前執行還是之後執行。 其有如下的實現類
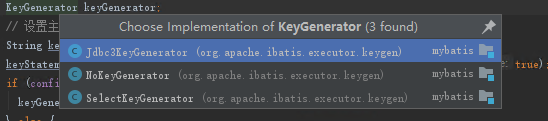
- Jdbc3KeyGenerator:用於處理資料庫支援自增主鍵的情況,如MySQL的auto_increment。
- NoKeyGenerator:空實現,不需要處理主鍵。沒有主鍵生成器, 如不是 INSERT, 也沒有使用主鍵生成器的時候, 就是該型別。
- SelectKeyGenerator:配置了 <selectKey> 之後, 就是該型別。 用於處理資料庫不支援自增主鍵的情況,比如Oracle,postgres的sequence序列。
6 建立並新增 MappedStatement
在完成以上步驟的處理之後, 通過
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets);進行 MappedStatement 物件的生成, 並新增到 Configuration 中。
以上的 selectById 最後再存在 Configuration中: