鎖和多執行緒:執行緒建立3種方式(一)
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-11-20
執行緒
鎖Synchronized
可以保證不存在多賣情況.
搞明白 執行緒 鎖和多執行緒系列
1.執行緒建立
執行緒建立常見的三種方式:
-
繼承Thread類
-
實現Runnable介面
-
實現Callable介面
第三種方式有非同步呼叫效果,類似js中的ajax可以接收返回值,其餘兩種不能.
package thread;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import 2.執行緒安全
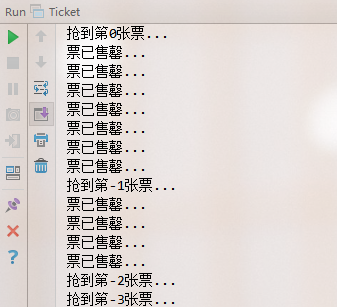
多執行緒下訪問資料會有執行緒安全問題.比如買火車票,只有10張票20人買,那就要確保不能賣重,不能多賣.看下面例子:
package thread;
/**
* @Author lyf
* @Date 2018/11/17 0017 14:13
*/
public class Ticket {
private int num = 10;
public void buy() {
if (num > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep((long) (Math.random() * 100));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("搶到第" + num-- + "張票...");
} else {
System.out.println("票已售罄...");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Ticket ticket = new Ticket();
for (int i = 0; i < 200; i++) {
new Thread(() -> { ticket.buy(); }).start();
}
}
}

多執行緒操作下,就會出現多賣的情況.如果要解決,可以通過加鎖synchronized方式來實現.把上邊的程式碼修改如下:
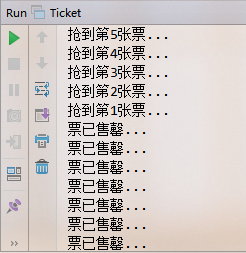
public synchronized void buy() {
...
}

可以保證不存在多賣情況.
