實戰Java高併發程式設計(3.1同步控制)
3.1重入鎖
重入鎖使用java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock來實現
public class Test implements Runnable { public static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); public static int i = 0; @Override public void run() { for (int j = 0; j < 1000000; j++) { lock.lock(); try { i++; }finally { lock.unlock(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Test t1 = new Test(); Thread thread1 = new Thread(t1); Thread thread2 = new Thread(t1); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); thread1.join(); thread2.join(); System.out.println(i); } }
重入鎖與synchronized相比有明顯的操作過程,開發人員必須指定何時加鎖,何時解鎖。同時,重入鎖是可以反覆新增的。一個縣城可以連續兩次獲得同一把鎖。
lock.lock();
lock.lock();
try {
i++;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
lock.unlock();
}3.1.1重入鎖可以被中斷
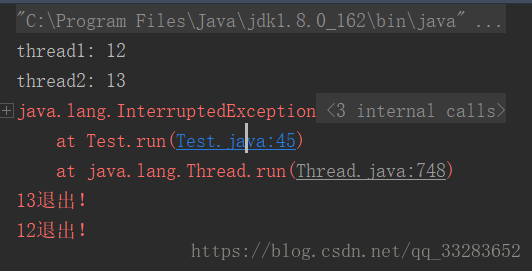
public class Test implements Runnable { public static ReentrantLock lock1 = new ReentrantLock(); public static ReentrantLock lock2 = new ReentrantLock(); int lock; /** * 控制加鎖順序,方便構成死鎖 * * @param lock */ public Test(int lock) { this.lock = lock; } @Override public void run() { try { if (lock == 1) { lock1.lockInterruptibly(); // 以可以響應中斷的方式加鎖 try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } lock2.lockInterruptibly(); } else { lock2.lockInterruptibly(); // 以可以響應中斷的方式加鎖 try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } lock1.lockInterruptibly(); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (lock1.isHeldByCurrentThread()) { lock1.unlock(); } if (lock2.isHeldByCurrentThread()) { lock2.unlock(); } System.err.println(Thread.currentThread().getId() + "退出!"); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Test t1 = new Test(1); Test t2 = new Test(2); Thread thread1 = new Thread(t1); Thread thread2 = new Thread(t2); System.out.println("thread1: "+thread1.getId()); System.out.println("thread2: "+thread2.getId()); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); Thread.sleep(1000); thread2.interrupt();//③給t2執行緒狀態標記為中斷 } }
t1、t2執行緒開始執行時,會分別持有lock1和lock2而請求lock2和lock1,這樣就發生了死鎖。但是,在③處給t2執行緒狀態標記為中斷後,持有重入鎖lock2的執行緒t2會響應中斷,並不再繼續等待lock1,同時釋放了其原本持有的lock2,這樣t1獲取到了lock2,正常執行完成。t2也會退出,但只是釋放了資源並沒有完成工作。
3.1.2鎖申請等待限時
可以使用 tryLock()或者tryLock(long timeout, TimeUtil unit) 方法進行一次限時的鎖等待。
前者不帶引數,這時執行緒嘗試獲取鎖,如果獲取到鎖則繼續執行,如果鎖被其他執行緒持有,則立即返回 false ,也就是不會使當前執行緒等待,所以不會產生死鎖。
後者帶有引數,表示在指定時長內獲取到鎖則繼續執行,如果等待指定時長後還沒有獲取到鎖則返回false。
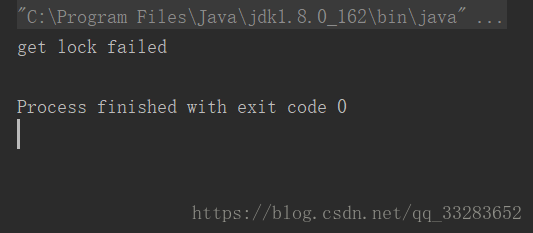
public class Test implements Runnable {
public static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
@Override
public void run() {
try {
if (lock.tryLock(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)){
Thread.sleep(6000);
}else {
System.out.println("get lock failed");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (lock.isHeldByCurrentThread()){
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test test = new Test();
Thread t1 = new Thread(test);
Thread t2 = new Thread(test);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}tryLock()方法接受的兩個引數,一個表示等待時長,另一個表示計時單位。在本例中,由於佔用鎖的程序持有鎖長達6秒,另一個執行緒無法再5秒的等待時間中得到鎖,會返回false。
3.2公平鎖
在大多數情況下,鎖的申請並不是公平的,先申請的執行緒並不一定在鎖可用時先使用。要實現公平鎖需要系統維護一個有序數列,效能較低,因此,預設情況下,鎖都是非公平的。
public class Test implements Runnable {
/**
* 預設為false,表示為非公平鎖
*/
public static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(true);
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
try {
lock.lock();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"獲得鎖");
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test test = new Test();
Thread t1 = new Thread(test);
Thread t2 = new Thread(test);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}兩個執行緒會交替輸出。如果是非公平鎖:
執行緒1顯示一大堆,然後執行緒2顯示一大堆。一個執行緒會傾向於再次獲取已經持有的鎖。
3.3Condition條件
await()方法會使當前執行緒等待,同時釋放當前鎖,當其他執行緒使用signal()或者signalAll()方法時,執行緒會重新獲得鎖並執行。
public class Test implements Runnable {
public static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public static Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
@Override
public void run() {
try {
lock.lock();
condition.await();
System.out.println("Thread is going on");
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException{
Test test = new Test();
Thread t1 = new Thread(test);
t1.start();
Thread.sleep(2000);
//通知執行緒繼續執行
lock.lock();
condition.signal();
lock.unlock();
}
}3.4訊號量(Semaphore)
訊號量可以指導多個執行緒同時訪問某一資源。
acquire()方法嘗試獲取一個准入許可,若無法獲得,則執行緒等待。
tryAcquire()方法嘗試獲取一個許可,成功返回true,失敗返回false,不會等待。
release()用於執行緒訪問完資源後,釋放許可。
public class Test implements Runnable {
final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(5);
@Override
public void run() {
try {
semaphore.acquire();
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getId()+" done");
semaphore.release();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException{
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(20);
final Test test = new Test();
for (int i = 0;i<20;i++){
executorService.submit(test);
}
}
}5個執行緒為一組同時訪問資源,但執行緒的順序隨機。
3.5ReadWriteLock讀寫鎖
讀寫鎖允許多個執行緒同時讀,但寫寫操作和讀寫操作間依然需要相互等待及持有鎖。
public class Test {
private static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private static ReentrantReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
private static Lock readLock = readWriteLock.readLock();
private static Lock writeLock = readWriteLock.writeLock();
private int value;
// 模擬讀操作
public Object handleRead(Lock lock)throws InterruptedException{
try {
lock.lock();
// 讀操作耗時越多,讀寫鎖的優勢越明顯
Thread.sleep(1000);
return value;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 模擬寫操作
public void handleWrite(Lock lock,int index) throws InterruptedException{
try {
lock.lock();
Thread.sleep(1000);
value = index;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Test test = new Test();
Runnable readRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
test.handleRead(readLock);
// test.handleRead(lock);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
Runnable writeRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
test.handleWrite(writeLock,new Random().nextInt());
// test.handleWrite(lock,new Random().nextInt());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
for (int i = 0;i<18;i++){
new Thread(readRunnable).start();
}
for (int i = 18;i<20;i++){
new Thread(writeRunnable).start();
}
}
}讀執行緒和寫執行緒可以並行,寫會阻塞讀,所以這段程式碼執行2秒多就結束,如果不用讀寫鎖,則需要20多秒。
3.6倒計時器:CountDownLatch
例如火箭發射倒計時,完成10項檢查才能發射火箭。
public class Test implements Runnable {
// 標明要完成10個任務
static final CountDownLatch end = new CountDownLatch(10);
static final Test test = new Test();
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(10) * 1000);
System.out.println("check template");
end.countDown();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException{
// 建立10個任務
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
service.submit(test);
}
// 等待檢查,要求主執行緒完成所有任務後才能執行
end.await();
System.out.println("Fire!");
service.shutdown();
}
}3.7迴圈柵欄:CyclicBarrier
假設司令下達命令,要求10個士兵一起去完成一項任務。士兵需要先集合,再去完成任務。
public class Test {
public static class Soldier implements Runnable {
private String soldier;
private final CyclicBarrier cyclic;
Soldier(CyclicBarrier cyclic, String soldierName) {
this.cyclic = cyclic;
this.soldier = soldierName;
}
void doWork() {
try {
Thread.sleep(Math.abs(new Random().nextInt() % 10000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(soldier + " 任務完成");
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// 確定是否都集合完畢
cyclic.await();
doWork();
// 確定是否都完成工作
cyclic.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static class BarrierRun implements Runnable {
boolean flag;
int N;
public BarrierRun(boolean flag, int N) {
this.flag = flag;
this.N = N;
}
@Override
public void run() {
if (flag) {
System.out.println("司令:[士兵" + N + "個,任務完成]");
} else {
System.out.println("司令:[士兵" + N + "個,集合完畢]");
flag = true;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
final int N = 10;
Thread[] allSoldier = new Thread[N];
boolean flag = false;
//迴圈呼叫這個計時器
CyclicBarrier cyclic = new CyclicBarrier(N, new BarrierRun(flag, N));
System.out.println("集合隊伍!");
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
System.out.println("士兵" + i + "報道");
allSoldier[i] = new Thread(new Soldier(cyclic, "士兵" + i));
allSoldier[i].start();
}
}
}3.8執行緒阻塞工具類:LockSupport
LockSupport可以線上程中的任何位置讓執行緒阻塞。
public class Test {
public static Object u = new Object();
static ChangeObjectThread t1 = new ChangeObjectThread("t1");
static ChangeObjectThread t2 = new ChangeObjectThread("t2");
public static class ChangeObjectThread extends Thread{
public ChangeObjectThread(String name) {
super.setName(name);
}
@Override
public void run(){
synchronized (u){
System.out.println("in "+getName());
LockSupport.park();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException{
t1.start();
Thread.sleep(100);
t2.start();
LockSupport.unpark(t1);
LockSupport.unpark(t2);
t1.join();
t2.join();
}
}