數字影象處理——形態學處理
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-11-21
形態學處理:利用數學形態學作為工具從影象中提取對於表達和描述區域形狀有用的影象分量。
數學形態學的語言:二值影象的集合論。顯示時黑色表示為1,白色表示為0!
基本處理:
1.擴張/膨脹dilation
將模板中心(結構原點)對準待處理畫素,逐點掃描模板下的畫素,如果模板中的畫素有一點以上和模板下的對應畫素的1點相同,則待處理畫素為1,否則為0;
2.腐蝕erosion
將模板中心(結構原點)對準待處理畫素,逐點掃描模板下的畫素,如果模板中的所有1點畫素都和模板下的對應畫素相同,則待處理畫素為1,否則為0;
3.開變換open
先腐蝕再擴張,斷開狹窄的連線和消除細小的突出物,平滑較大物體邊界的同時而不明顯改變其面積。開變換可以去除面積較小的並噪聲。
4.閉變換close
先擴張再腐蝕,消除狹窄的間斷和細小的鴻溝,填補輪廓線中的斷裂。閉變換可以去除面積較小的差噪聲。
5.擊中擊不中變換HIT-MISS
從影象A中探測結構元素B=(w,b)的位置,需要兩個結構單元w和b,w探測影象內部,b探測影象外部。w對A腐蝕,b對A的補腐蝕,二者的結果相與,即可找到B的位置。
Matlab程式碼:
function f_dilate = dilate(f,se,origin) % dilation operation on binary image % f --binary image % se --structure element % origin --the origin of se [h,w] = size(f); [h_se,w_se] = size(se); ox = origin(1);oy = origin(2); % 假設模板的最大尺寸為5x5 f_ext = zeros(h+4,w+4); % 擴充背景 f_ext(3:h+2,3:w+2) = f; f_ext = logical(f_ext); f_dilate = logical(zeros(h,w)); % 初始化擴張後的影象 % 掃描畫素,對每個畫素進行處理 for i = 3:h+2 for j = 3:w+2 temp = f_ext(i-ox+1:i+h_se-ox,j-oy+1:j+w_se-oy)&se; if sum(temp(:))>0 f_dilate(i-2,j-2) = 1; else f_dilate(i-2,j-2) = 0; end end end end
function f_erode = erode(f,se,origin) % erosion operation on binary image % f --binary image % se --structure element % origin --the origin of se [h,w] = size(f); [h_se,w_se] = size(se); ox = origin(1);oy = origin(2); % 假設模板的最大尺寸為5x5 f_ext = zeros(h+4,w+4); % 擴充背景 f_ext(3:h+2,3:w+2) = f; f_ext = logical(f_ext); f_erode = logical(zeros(h,w)); % 腐蝕後的影象 % 掃描影象,對每個畫素進行處理 for i = 3:h+2 for j = 3:w+2 temp = f_ext(i-ox+1:i+h_se-ox,j-oy+1:j+w_se-oy)&se; if temp==se f_erode(i-2,j-2) = 1; else f_erode(i-2,j-2) = 0; end end end end
測試程式碼:
clc,clear
f = [0 0 0 0 0 0 0;
0 0 1 1 0 0 0;
0 0 0 1 0 0 0;
0 0 0 1 1 0 0;
0 0 1 1 1 1 0;
0 0 1 1 1 0 0;
0 1 0 1 0 1 0;
0 0 0 0 0 0 0];
f = logical(f);
se1 = [1 1 1];
se2 = [1 1;0 1];
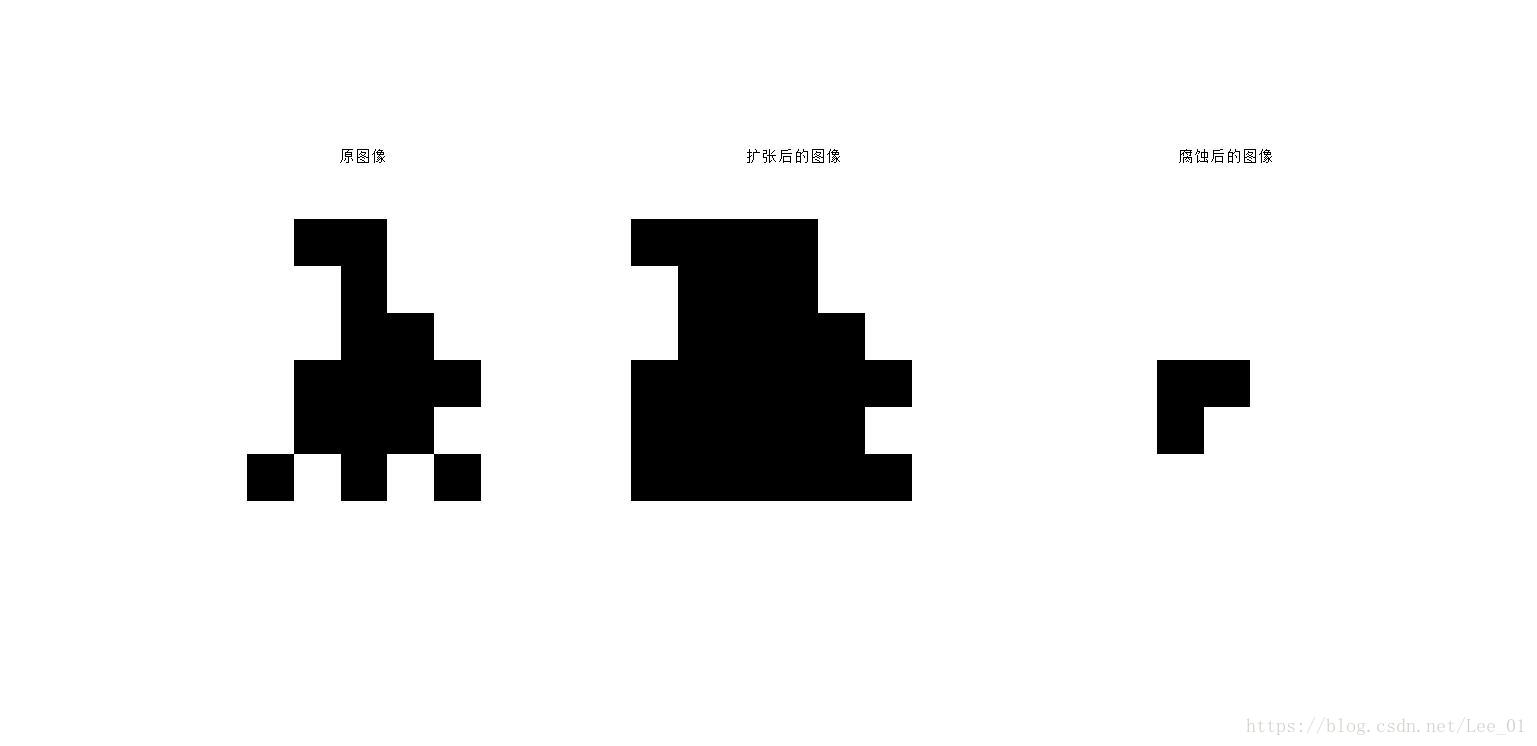
f_dilate1 = dilate(f,se1,[1,1]);
f_erode1 = erode(f,se1,[1,1]);
figure;
subplot(1,3,1),imshow(~f),title('原影象');
subplot(1,3,2),imshow(~f_dilate1),title('擴張後的影象');
subplot(1,3,3),imshow(~f_erode1),title('腐蝕後的影象');
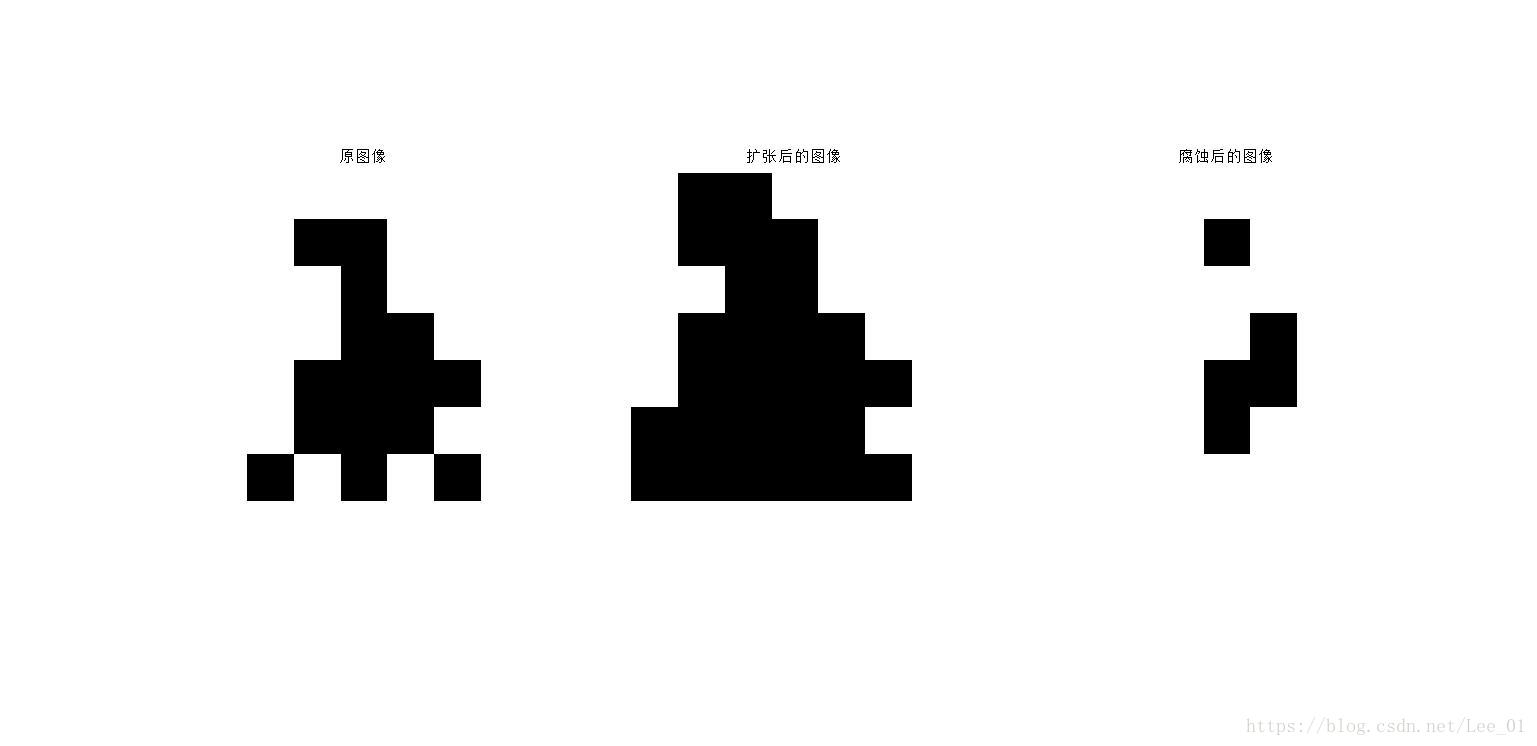
f_dilate2 = dilate(f,se2,[1,1]);
f_erode2 = erode(f,se2,[1,2]);
figure;
subplot(1,3,1),imshow(~f),title('原影象');
subplot(1,3,2),imshow(~f_dilate2),title('擴張後的影象');
subplot(1,3,3),imshow(~f_erode2),title('腐蝕後的影象');
f_open1 = dilate(f_erode1,se1,[1,1]); % 開變換,先腐蝕後擴張
f_close1 = erode(f_dilate1,se1,[1,1]); % 閉變換,先擴張後腐蝕
figure;
subplot(1,3,1),imshow(~f),title('原影象');
subplot(1,3,2),imshow(~f_open1),title('開變換後的影象');
subplot(1,3,3),imshow(~f_close1),title('閉變換後的影象');
f_open2 = dilate(f_erode2,se2,[1,2]); % 開變換,先腐蝕後擴張
f_close2 = erode(f_dilate2,se2,[1,2]); % 閉變換,先擴張後腐蝕
figure;
subplot(1,3,1),imshow(~f),title('原影象');
subplot(1,3,2),imshow(~f_open2),title('開變換後的影象');
subplot(1,3,3),imshow(~f_close2),title('閉變換後的影象');執行結果:
結構元素為se1:
結構元素為se2: