kubernetes搭建rook-ceph
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-11-21
cpu databases ply scribe pac ont forward 回收 serve 簡介
- Rook官網:https://rook.io
- Rook是雲原生計算基金會(CNCF)的孵化級項目.
- Rook是Kubernetes的開源雲本地存儲協調器,為各種存儲解決方案提供平臺,框架和支持,以便與雲原生環境本地集成。
- 至於CEPH,官網在這:https://ceph.com/
- ceph官方提供的helm部署,至今我沒成功過,所以轉向使用rook提供的方案
有道筆記原文:http://note.youdao.com/noteshare?id=281719f1f0374f787effc90067e0d5ad&sub=0B59EA339D4A4769B55F008D72C1A4C0
環境
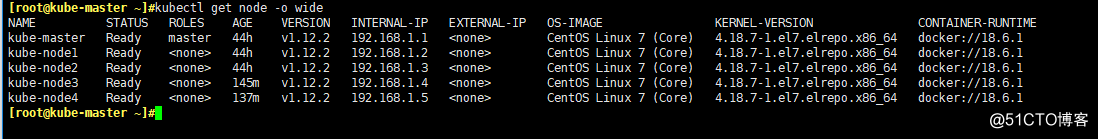
centos 7.5 kernel 4.18.7-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 docker 18.06 kubernetes v1.12.2 kubeadm部署: 網絡: canal DNS: coredns 集群成員: 192.168.1.1 kube-master 192.168.1.2 kube-node1 192.168.1.3 kube-node2 192.168.1.4 kube-node3 192.168.1.5 kube-node4 所有node節點準備一塊200G的磁盤:/dev/sdb
準備工作
- 所有節點開啟ip_forward
cat <<EOF > /etc/sysctl.d/ceph.conf
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
EOF
sysctl --system
開始部署Operator
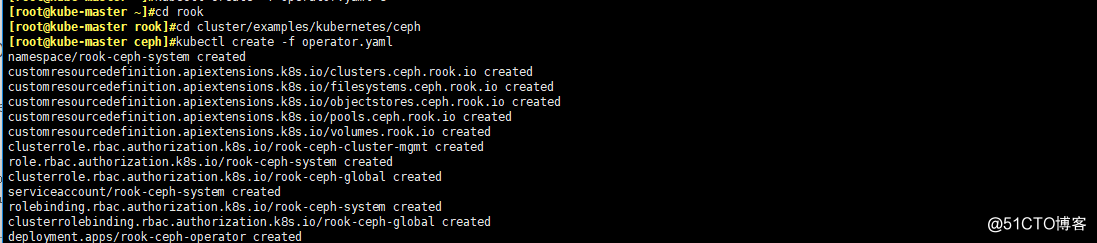
- 部署Rook Operator
#無另外說明,全部操作都在master操作 cd $HOME git clone https://github.com/rook/rook.git cd rook cd cluster/examples/kubernetes/ceph kubectl apply -f operator.yaml
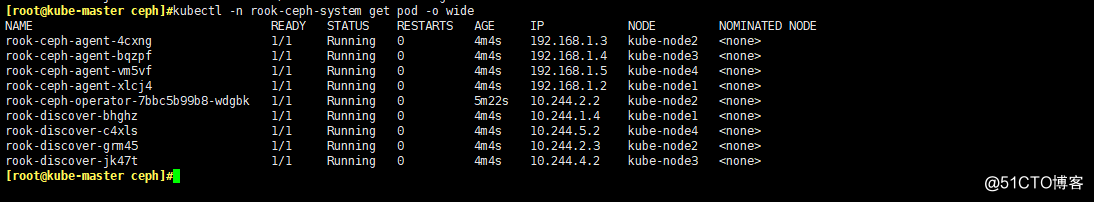
- 查看Operator的狀態
#執行apply之後稍等一會。
#operator會在集群內的每個主機創建兩個pod:rook-discover,rook-ceph-agent
kubectl -n rook-ceph-system get pod -o wide
給節點打標簽
- 運行ceph-mon的節點打上:ceph-mon=enabled
kubectl label nodes {kube-node1,kube-node2,kube-node3} ceph-mon=enabled
- 運行ceph-osd的節點,也就是存儲節點,打上:ceph-osd=enabled
kubectl label nodes {kube-node1,kube-node2,kube-node3} ceph-osd=enabled
- 運行ceph-mgr的節點,打上:ceph-mgr=enabled
#mgr只能支持一個節點運行,這是ceph跑k8s裏的局限
kubectl label nodes kube-node1 ceph-mgr=enabled
配置cluster.yaml文件
-
官方配置文件詳解:https://rook.io/docs/rook/v0.8/ceph-cluster-crd.html
-
文件中有幾個地方要註意:
- dataDirHostPath: 這個路徑是會在宿主機上生成的,保存的是ceph的相關的配置文件,再重新生成集群的時候要確保這個目錄為空,否則mon會無法啟動
- useAllDevices: 使用所有的設備,建議為false,否則會把宿主機所有可用的磁盤都幹掉
- useAllNodes:使用所有的node節點,建議為false,肯定不會用k8s集群內的所有node來搭建ceph的
- databaseSizeMB和journalSizeMB:當磁盤大於100G的時候,就註釋這倆項就行了
- 本次實驗用到的 cluster.yaml 文件內容如下:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: rook-ceph
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: rook-ceph-cluster
namespace: rook-ceph
---
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: rook-ceph-cluster
namespace: rook-ceph
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["configmaps"]
verbs: [ "get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "delete" ]
---
# Allow the operator to create resources in this cluster‘s namespace
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: rook-ceph-cluster-mgmt
namespace: rook-ceph
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: rook-ceph-cluster-mgmt
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: rook-ceph-system
namespace: rook-ceph-system
---
# Allow the pods in this namespace to work with configmaps
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: rook-ceph-cluster
namespace: rook-ceph
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: rook-ceph-cluster
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: rook-ceph-cluster
namespace: rook-ceph
---
apiVersion: ceph.rook.io/v1beta1
kind: Cluster
metadata:
name: rook-ceph
namespace: rook-ceph
spec:
cephVersion:
# The container image used to launch the Ceph daemon pods (mon, mgr, osd, mds, rgw).
# v12 is luminous, v13 is mimic, and v14 is nautilus.
# RECOMMENDATION: In production, use a specific version tag instead of the general v13 flag, which pulls the latest release and could result in different
# versions running within the cluster. See tags available at https://hub.docker.com/r/ceph/ceph/tags/.
image: ceph/ceph:v13
# Whether to allow unsupported versions of Ceph. Currently only luminous and mimic are supported.
# After nautilus is released, Rook will be updated to support nautilus.
# Do not set to true in production.
allowUnsupported: false
# The path on the host where configuration files will be persisted. If not specified, a kubernetes emptyDir will be created (not recommended).
# Important: if you reinstall the cluster, make sure you delete this directory from each host or else the mons will fail to start on the new cluster.
# In Minikube, the ‘/data‘ directory is configured to persist across reboots. Use "/data/rook" in Minikube environment.
dataDirHostPath: /var/lib/rook
# The service account under which to run the daemon pods in this cluster if the default account is not sufficient (OSDs)
serviceAccount: rook-ceph-cluster
# set the amount of mons to be started
# count可以定義ceph-mon運行的數量,這裏默認三個就行了
mon:
count: 3
allowMultiplePerNode: true
# enable the ceph dashboard for viewing cluster status
# 開啟ceph資源面板
dashboard:
enabled: true
# serve the dashboard under a subpath (useful when you are accessing the dashboard via a reverse proxy)
# urlPrefix: /ceph-dashboard
network:
# toggle to use hostNetwork
# 使用宿主機的網絡進行通訊
# 使用宿主機的網絡貌似可以讓集群外的主機掛載ceph
# 但是我沒試過,有興趣的兄弟可以試試改成true
# 反正這裏只是集群內用,我就不改了
hostNetwork: false
# To control where various services will be scheduled by kubernetes, use the placement configuration sections below.
# The example under ‘all‘ would have all services scheduled on kubernetes nodes labeled with ‘role=storage-node‘ and
# tolerate taints with a key of ‘storage-node‘.
placement:
# all:
# nodeAffinity:
# requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
# nodeSelectorTerms:
# - matchExpressions:
# - key: role
# operator: In
# values:
# - storage-node
# podAffinity:
# podAntiAffinity:
# tolerations:
# - key: storage-node
# operator: Exists
# The above placement information can also be specified for mon, osd, and mgr components
# mon:
# osd:
# mgr:
# nodeAffinity:通過選擇標簽的方式,可以限制pod被調度到特定的節點上
# 建議限制一下,為了讓這幾個pod不亂跑
mon:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: ceph-mon
operator: In
values:
- enabled
osd:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: ceph-osd
operator: In
values:
- enabled
mgr:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: ceph-mgr
operator: In
values:
- enabled
resources:
# The requests and limits set here, allow the mgr pod to use half of one CPU core and 1 gigabyte of memory
# mgr:
# limits:
# cpu: "500m"
# memory: "1024Mi"
# requests:
# cpu: "500m"
# memory: "1024Mi"
# The above example requests/limits can also be added to the mon and osd components
# mon:
# osd:
storage: # cluster level storage configuration and selection
useAllNodes: false
useAllDevices: false
deviceFilter:
location:
config:
# The default and recommended storeType is dynamically set to bluestore for devices and filestore for directories.
# Set the storeType explicitly only if it is required not to use the default.
# storeType: bluestore
# databaseSizeMB: "1024" # this value can be removed for environments with normal sized disks (100 GB or larger)
# journalSizeMB: "1024" # this value can be removed for environments with normal sized disks (20 GB or larger)
# Cluster level list of directories to use for storage. These values will be set for all nodes that have no `directories` set.
# directories:
# - path: /rook/storage-dir
# Individual nodes and their config can be specified as well, but ‘useAllNodes‘ above must be set to false. Then, only the named
# nodes below will be used as storage resources. Each node‘s ‘name‘ field should match their ‘kubernetes.io/hostname‘ label.
#建議磁盤配置方式如下:
#name: 選擇一個節點,節點名字為kubernetes.io/hostname的標簽,也就是kubectl get nodes看到的名字
#devices: 選擇磁盤設置為OSD
# - name: "sdb":將/dev/sdb設置為osd
nodes:
- name: "kube-node1"
devices:
- name: "sdb"
- name: "kube-node2"
devices:
- name: "sdb"
- name: "kube-node3"
devices:
- name: "sdb"
# directories: # specific directories to use for storage can be specified for each node
# - path: "/rook/storage-dir"
# resources:
# limits:
# cpu: "500m"
# memory: "1024Mi"
# requests:
# cpu: "500m"
# memory: "1024Mi"
# - name: "172.17.4.201"
# devices: # specific devices to use for storage can be specified for each node
# - name: "sdb"
# - name: "sdc"
# config: # configuration can be specified at the node level which overrides the cluster level config
# storeType: filestore
# - name: "172.17.4.301"
# deviceFilter: "^sd."
開始部署ceph
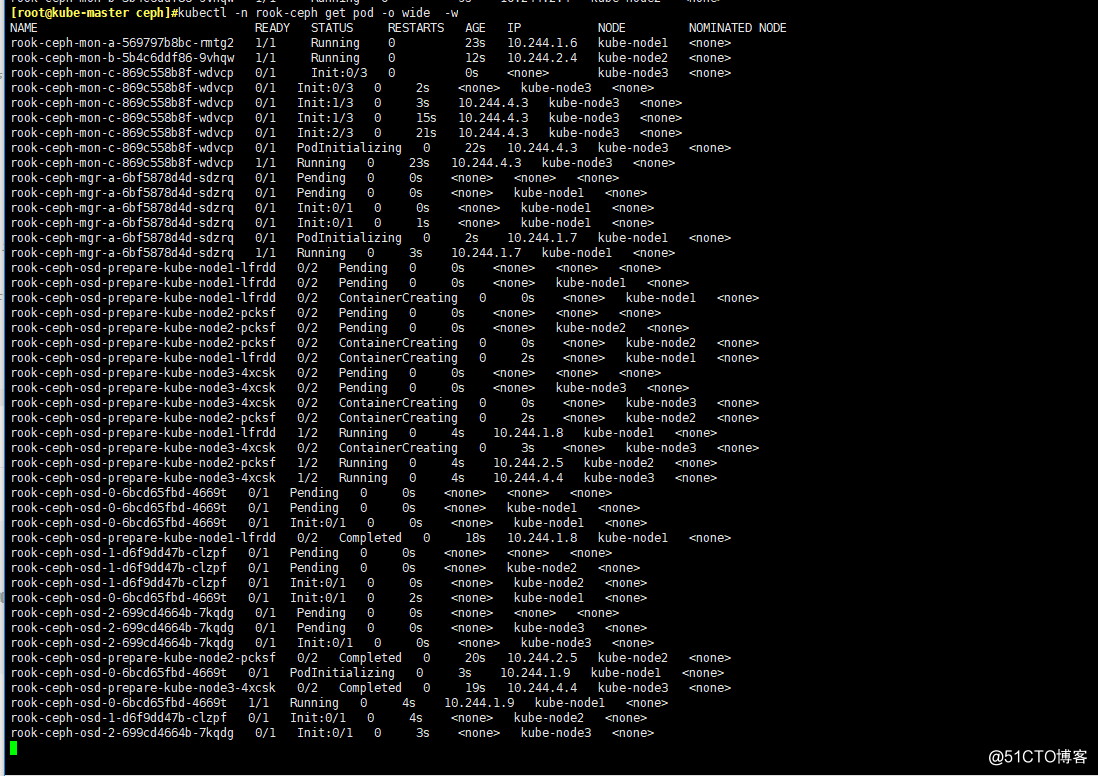
- 部署ceph
kubectl apply -f cluster.yaml
# cluster會在rook-ceph這個namesapce創建資源
# 盯著這個namesapce的pod你就會發現,它在按照順序創建Pod
kubectl -n rook-ceph get pod -o wide -w
# 看到所有的pod都Running就行了
# 註意看一下pod分布的宿主機,跟我們打標簽的主機是一致的
kubectl -n rook-ceph get pod -o wide
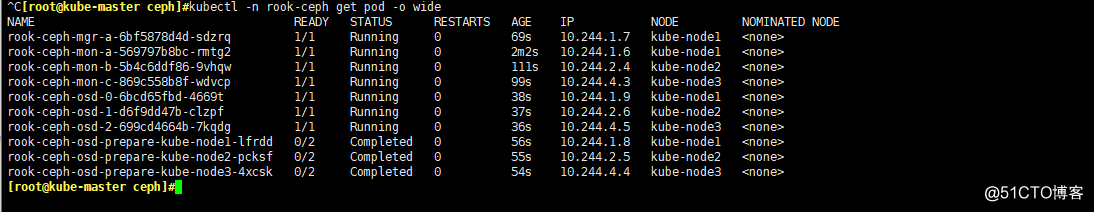
-
切換到其他主機看一下磁盤
- 切換到kube-node1
lsblk
- 切換到kube-node3
lsblk
配置ceph dashboard
- 看一眼dashboard在哪個service上
kubectl -n rook-ceph get service
#可以看到dashboard監聽了8443端口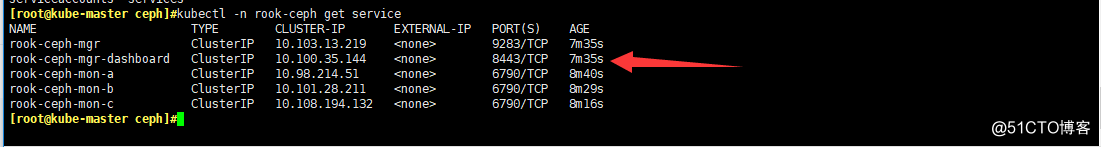
- 創建個nodeport類型的service以便集群外部訪問
kubectl apply -f dashboard-external-https.yaml
# 查看一下nodeport在哪個端口
ss -tanl
kubectl -n rook-ceph get service
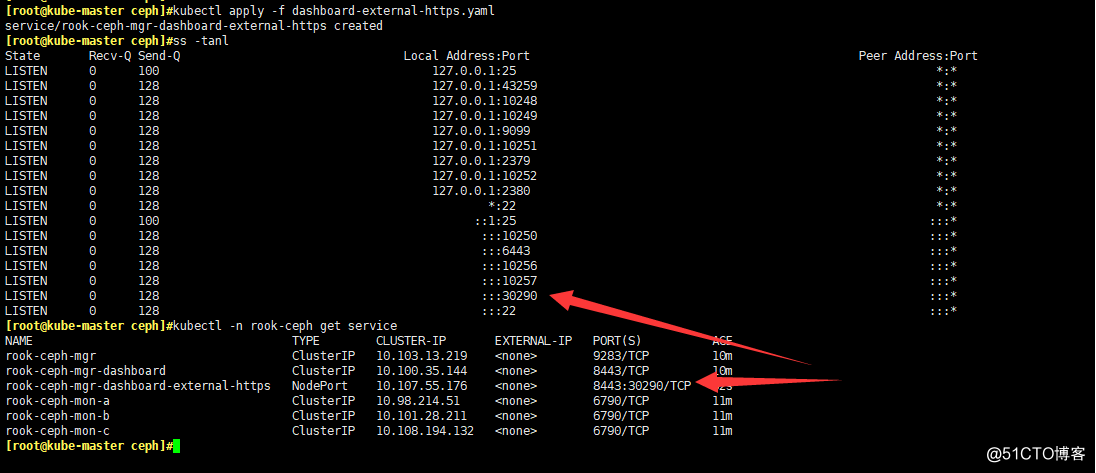
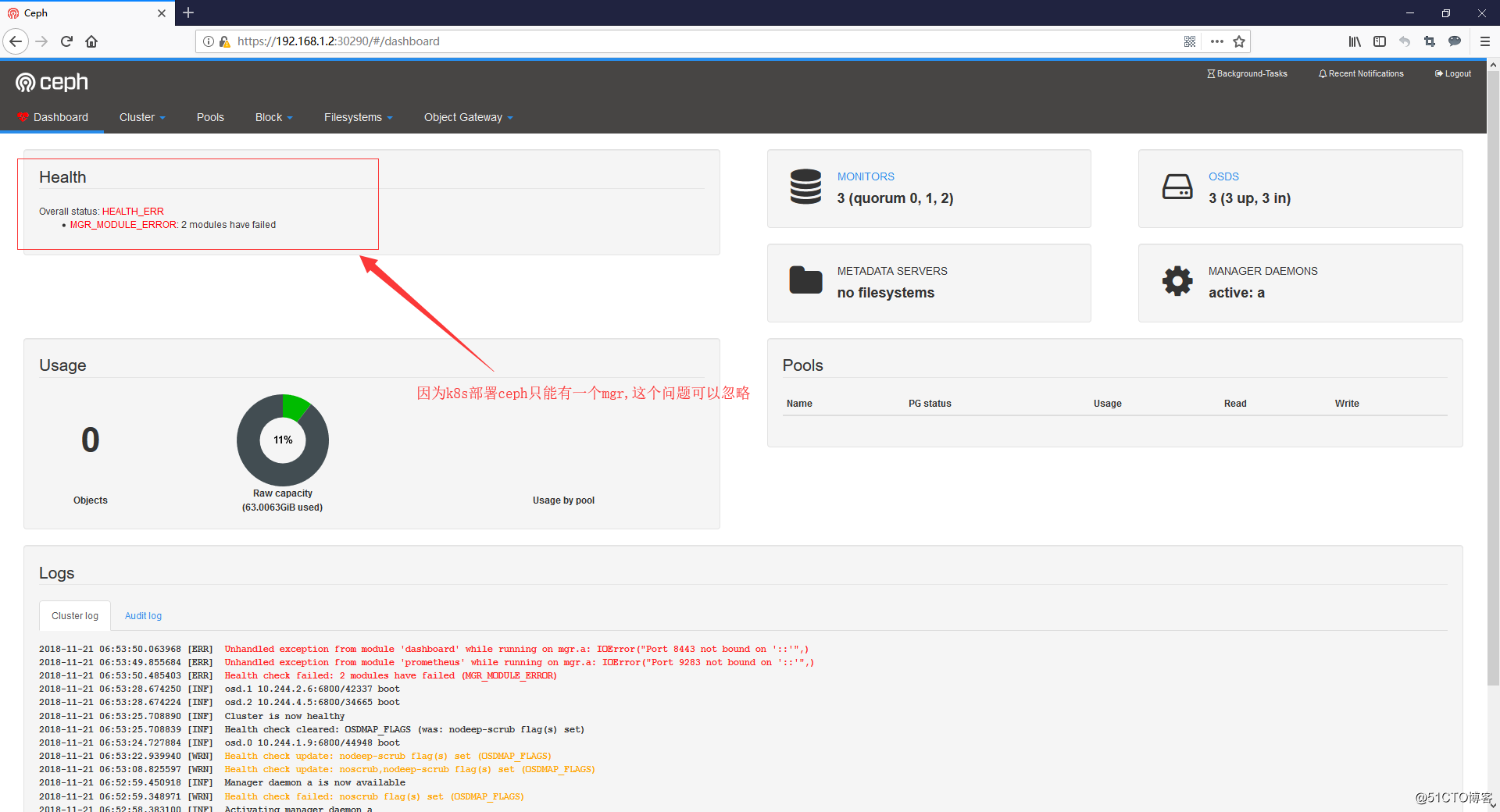
- 找出Dashboard的登陸賬號和密碼
MGR_POD=`kubectl get pod -n rook-ceph | grep mgr | awk ‘{print $1}‘`
kubectl -n rook-ceph logs $MGR_POD | grep password
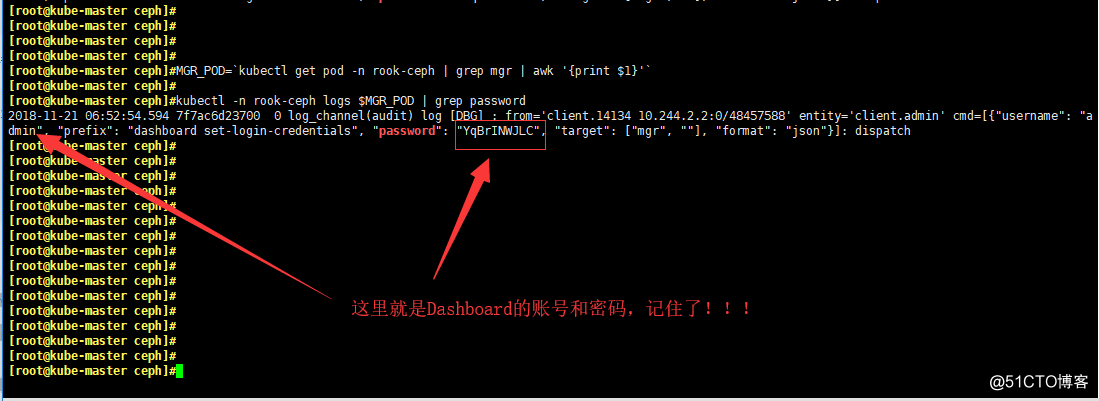
- 打開瀏覽器輸入任意一個Node的IP+nodeport端口
- 這裏我的就是:https://192.168.1.2:30290
配置ceph為storageclass
- 官方給了一個樣本文件:storageclass.yaml
- 這個文件使用的是 RBD 塊存儲
- pool創建詳解:https://rook.io/docs/rook/v0.8/ceph-pool-crd.html
apiVersion: ceph.rook.io/v1beta1
kind: Pool
metadata:
#這個name就是創建成ceph pool之後的pool名字
name: replicapool
namespace: rook-ceph
spec:
replicated:
size: 1
# size 池中數據的副本數,1就是不保存任何副本
failureDomain: osd
# failureDomain:數據塊的故障域,
# 值為host時,每個數據塊將放置在不同的主機上
# 值為osd時,每個數據塊將放置在不同的osd上
---
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: ceph
# StorageClass的名字,pvc調用時填的名字
provisioner: ceph.rook.io/block
parameters:
pool: replicapool
# Specify the namespace of the rook cluster from which to create volumes.
# If not specified, it will use `rook` as the default namespace of the cluster.
# This is also the namespace where the cluster will be
clusterNamespace: rook-ceph
# Specify the filesystem type of the volume. If not specified, it will use `ext4`.
fstype: xfs
# 設置回收策略默認為:Retain
reclaimPolicy: Retain
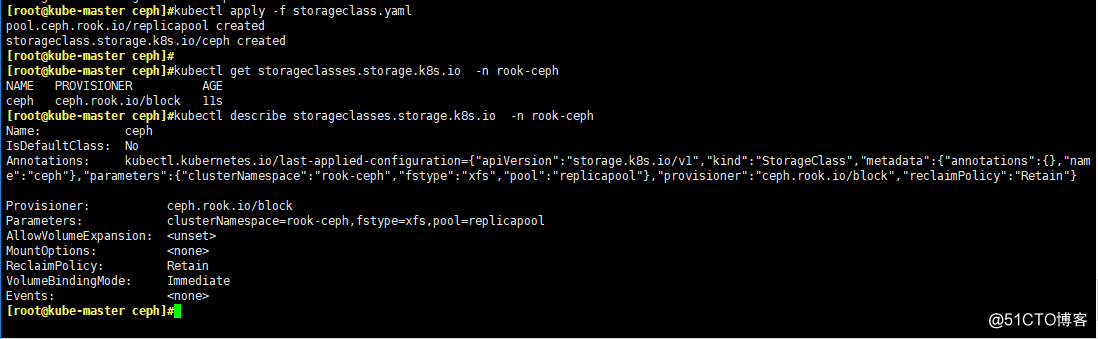
- 創建StorageClass
kubectl apply -f storageclass.yaml
kubectl get storageclasses.storage.k8s.io -n rook-ceph
kubectl describe storageclasses.storage.k8s.io -n rook-ceph
- 創建個nginx pod嘗試掛載
cat << EOF > nginx.yaml
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: nginx-pvc
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
storageClassName: ceph
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx
spec:
selector:
app: nginx
ports:
- port: 80
name: nginx-port
targetPort: 80
protocol: TCP
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
name: nginx
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /html
name: http-file
volumes:
- name: http-file
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: nginx-pvc
EOF
kubectl apply -f nginx.yaml
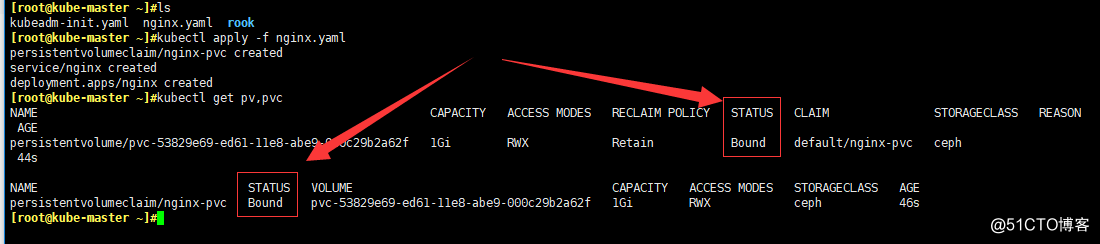
- 查看pv,pvc是否創建了
kubectl get pv,pvc
# 看一下nginx這個pod也運行了
kubectl get pod
- 刪除這個pod,看pv是否還存在
kubectl delete -f nginx.yaml
kubectl get pv,pvc
# 可以看到,pod和pvc都已經被刪除了,但是pv還在!!!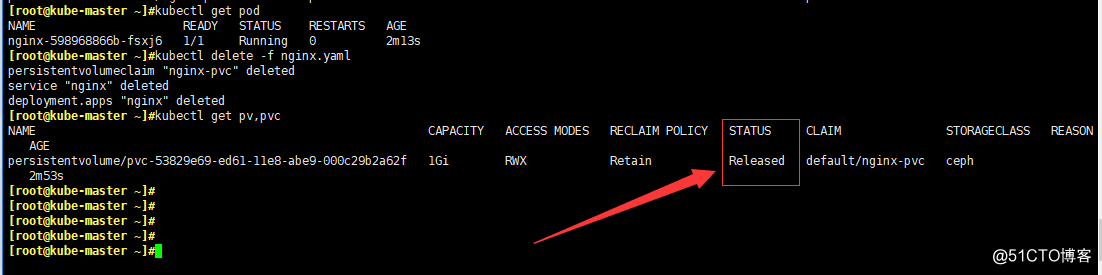
添加新的OSD進入集群
- 這次我們要把node4添加進集群,先打標簽
kubectl label nodes kube-node4 ceph-osd=enabled
- 重新編輯cluster.yaml文件
# 原來的基礎上添加node4的信息
cd $HOME/rook/cluster/examples/kubernetes/ceph/
vi cluster.yam
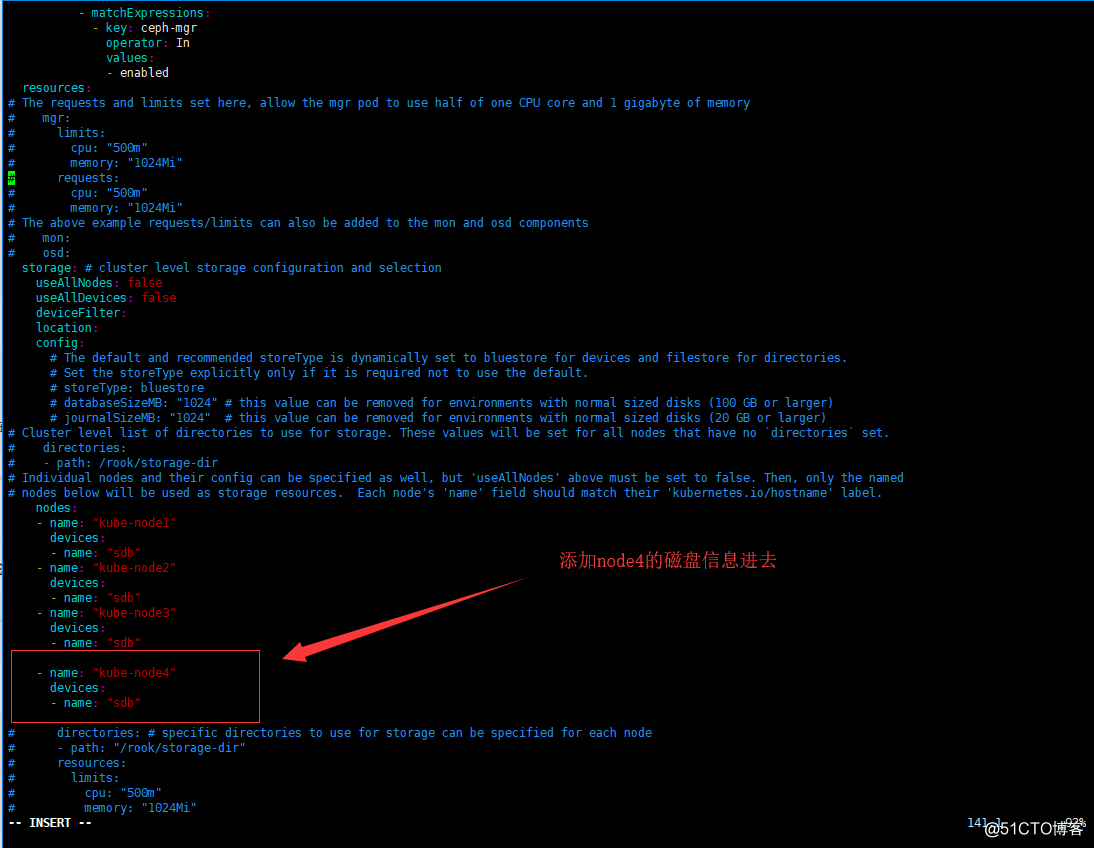
- apply一下cluster.yaml文件
kubectl apply -f cluster.yaml
# 盯著rook-ceph名稱空間,集群會自動添加node4進來
kubectl -n rook-ceph get pod -o wide -w
kubectl -n rook-ceph get pod -o wide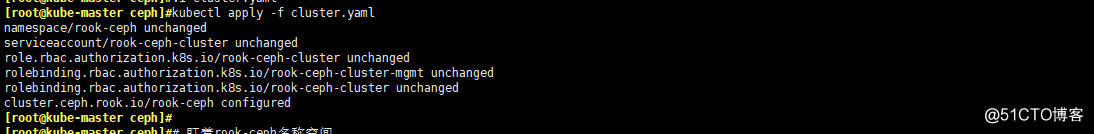
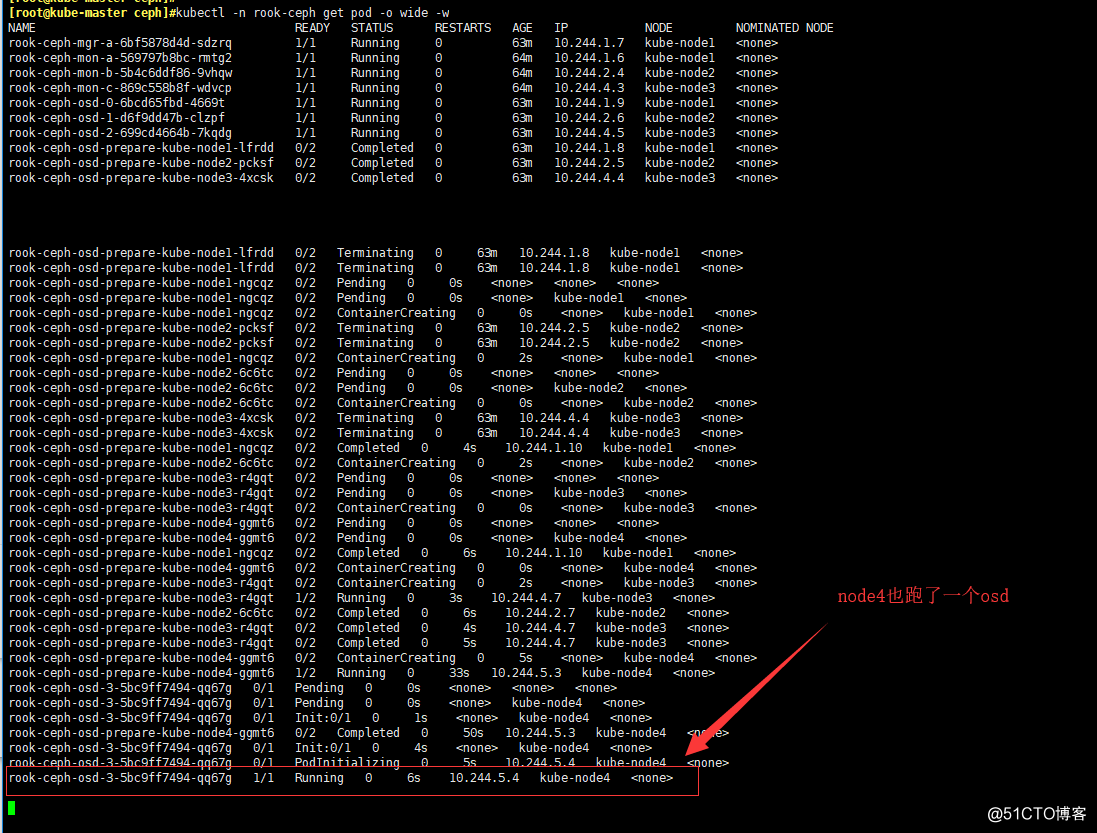
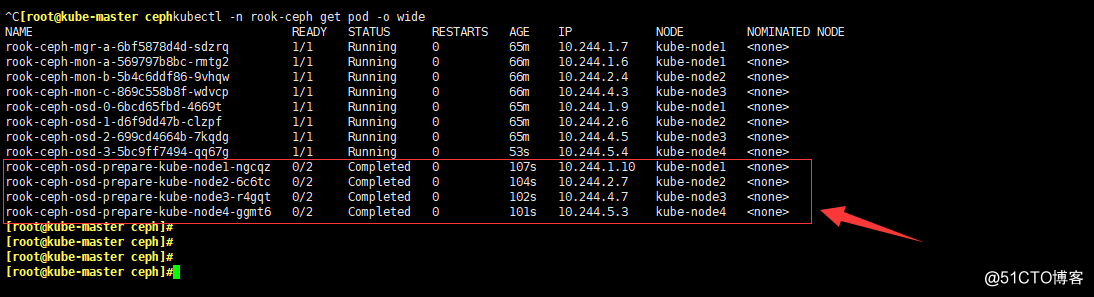
- 去node4節點看一下磁盤
lsblk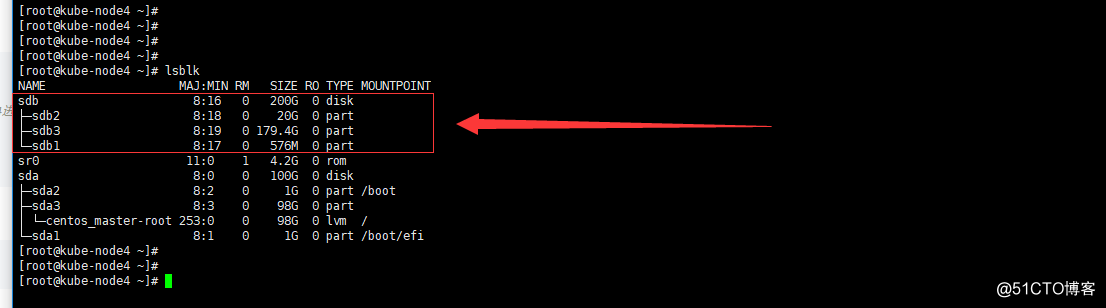
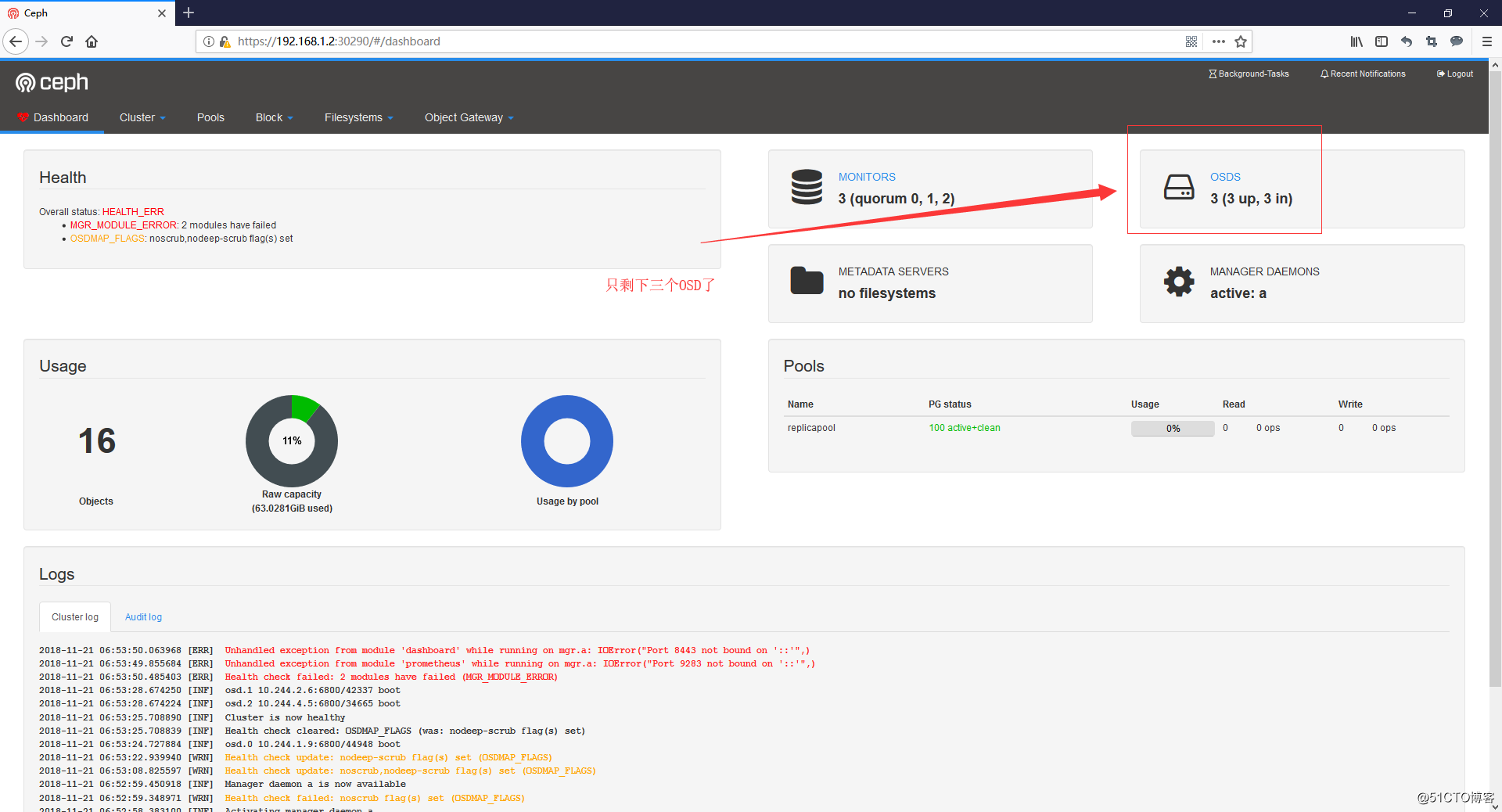
- 再打開dashboard看一眼
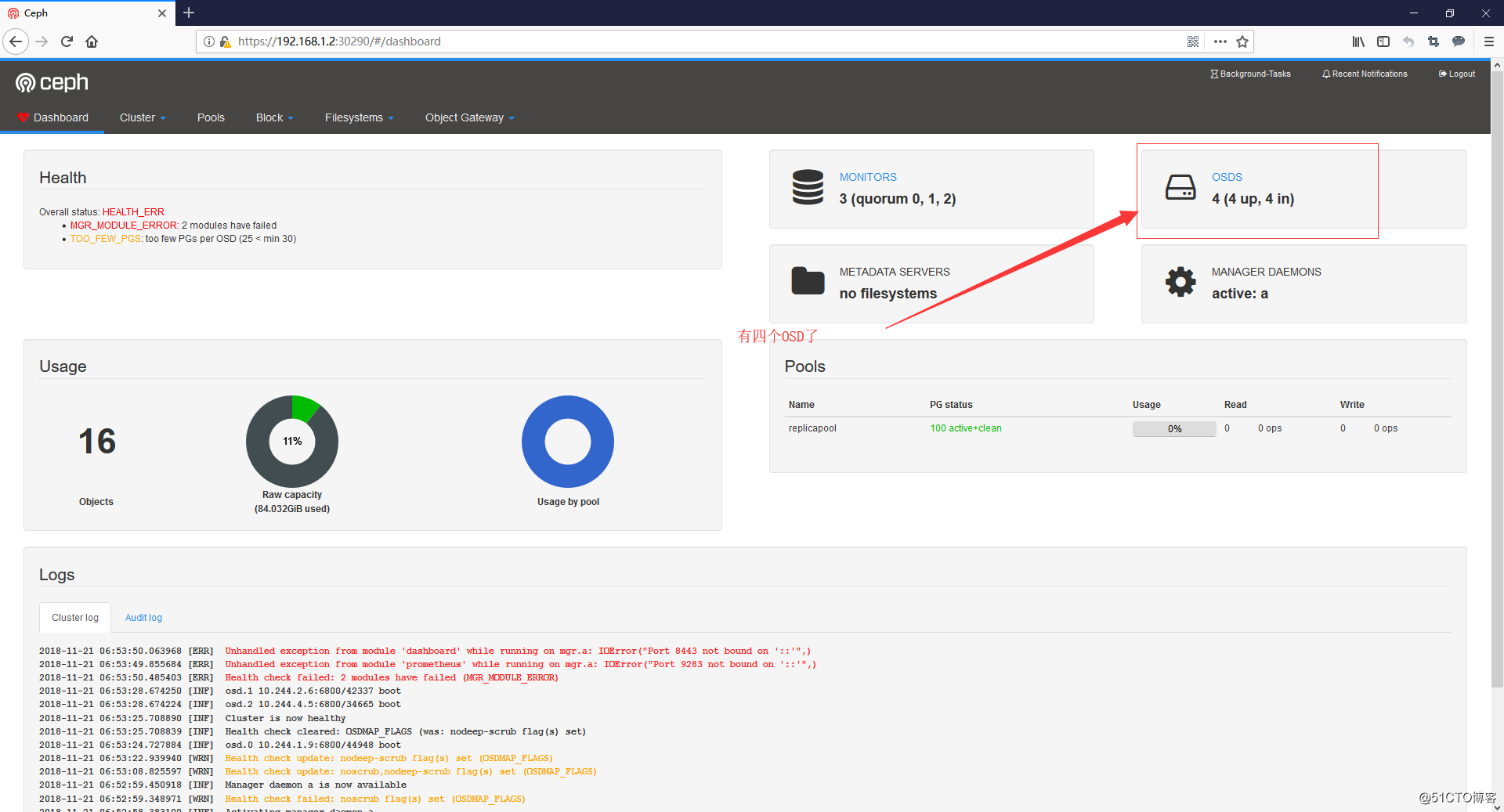
刪除一個節點
- 去掉node3的標簽
kubectl label nodes kube-node3 ceph-osd-
- 重新編輯cluster.yaml文件
# 刪除node3的信息
cd $HOME/rook/cluster/examples/kubernetes/ceph/
vi cluster.yam
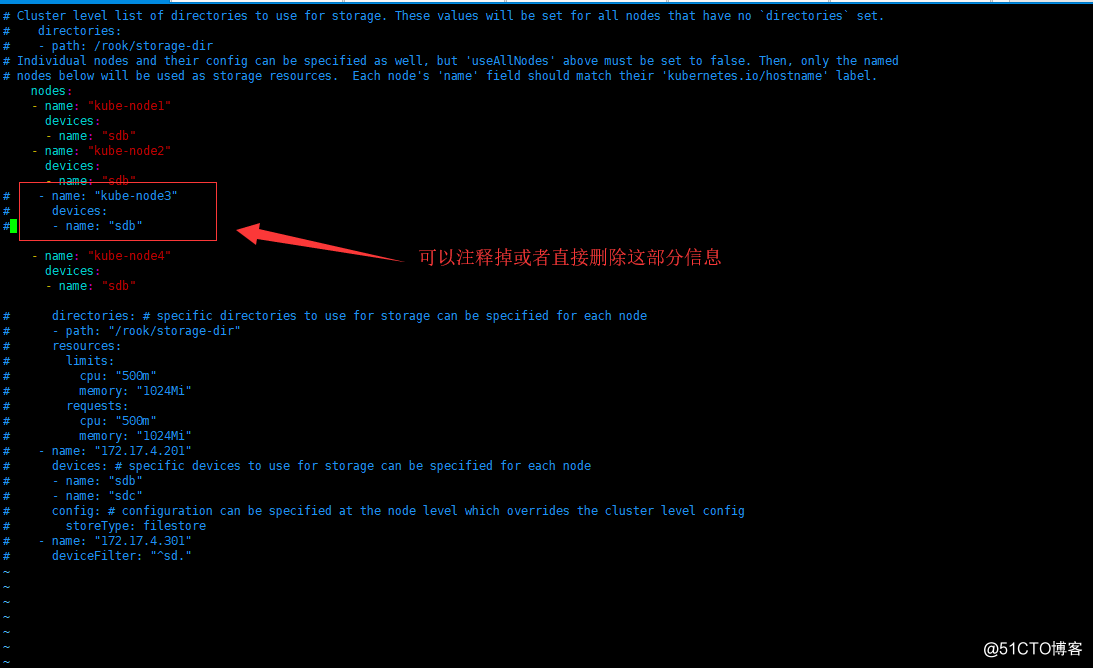
- apply一下cluster.yaml文件
kubectl apply -f cluster.yaml
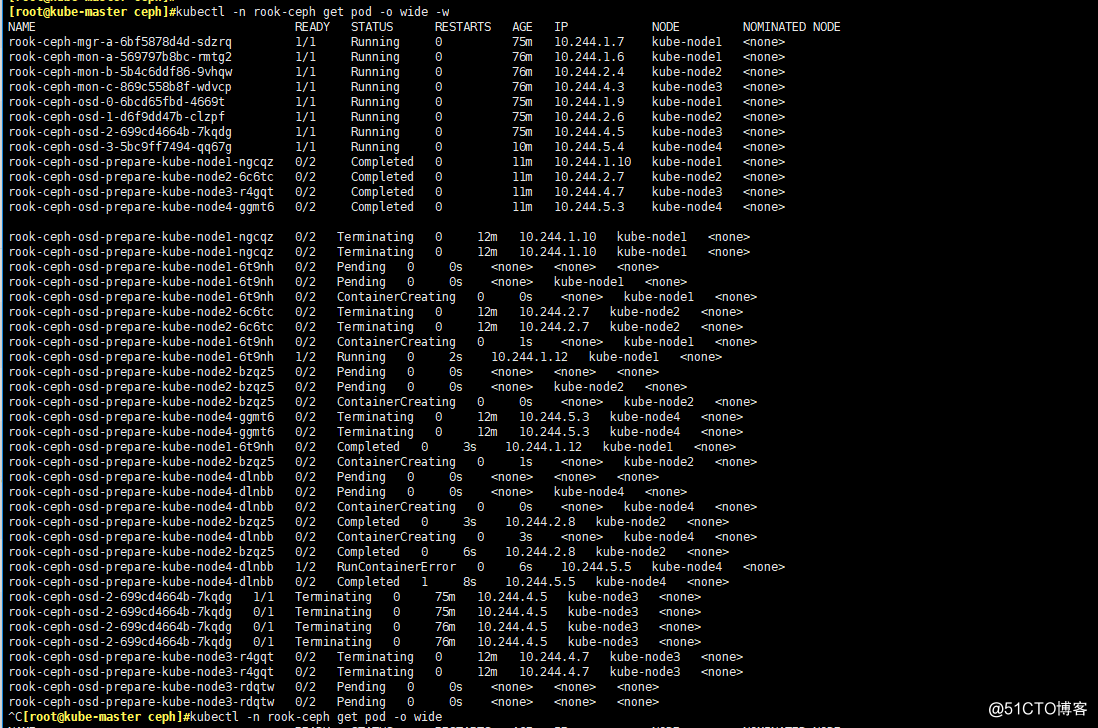
# 盯著rook-ceph名稱空間
kubectl -n rook-ceph get pod -o wide -w
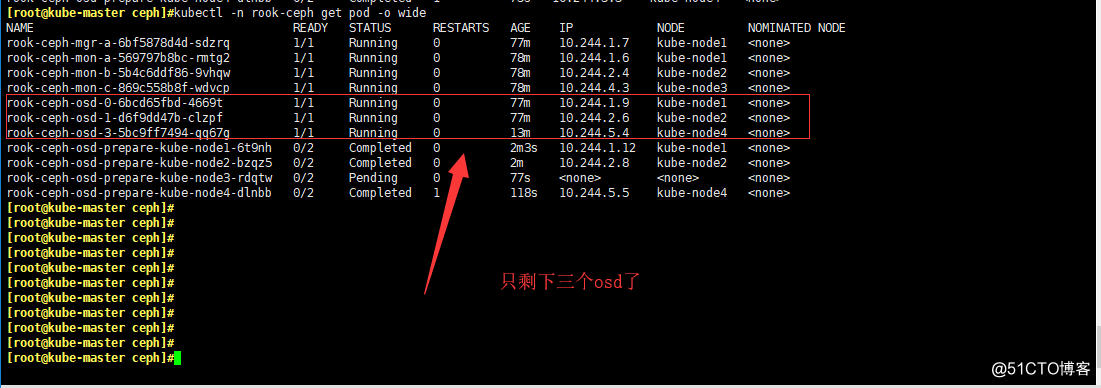
kubectl -n rook-ceph get pod -o wide
# 最後記得刪除宿主機的/var/lib/rook文件夾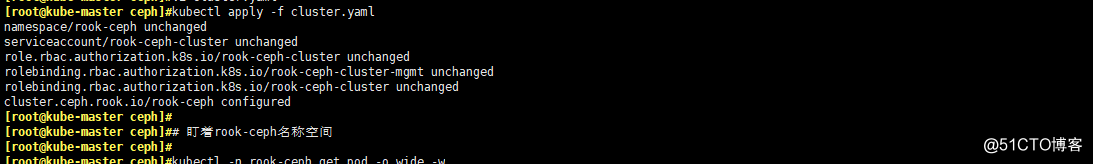
常見問題
-
官方解答:https://rook.io/docs/rook/v0.8/common-issues.html
- 當機器重啟之後,osd無法正常的Running,無限重啟
#解決辦法:
# 標記節點為 drain 狀態
kubectl drain <node-name> --ignore-daemonsets --delete-local-data
# 然後再恢復
kubectl uncordon <node-name>
kubernetes搭建rook-ceph
