輸出n以內互質數對 CodeForce1009D
D. Relatively Prime Graph
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Let's call an undirected graph G=(V,E)G=(V,E) relatively prime if and only if for each edge (v,u)∈E(v,u)∈E GCD(v,u)=1GCD(v,u)=1 (the greatest common divisor of vv and uu is 11). If there is no edge between some pair of vertices vv and uu then the value of GCD(v,u)GCD(v,u) doesn't matter. The vertices are numbered from 11 to |V||V|.
Construct a relatively prime graph with nn vertices and mm edges such that it is connected and it contains neither self-loops nor multiple edges.
If there exists no valid graph with the given number of vertices and edges then output "Impossible".
If there are multiple answers then print any of them.
Input
The only line contains two integers nn and mm (1≤n,m≤1051≤n,m≤105) — the number of vertices and the number of edges.
Output
If there exists no valid graph with the given number of vertices and edges then output "Impossible".
Otherwise print the answer in the following format:
The first line should contain the word "Possible".
The ii-th of the next mm lines should contain the ii-th edge (vi,ui)(vi,ui) of the resulting graph (1≤vi,ui≤n,vi≠ui1≤vi,ui≤n,vi≠ui). For each pair (v,u)(v,u)there can be no more pairs (v,u)(v,u) or (u,v)(u,v). The vertices are numbered from 11 to nn.
If there are multiple answers then print any of them.
Examples
input
Copy
5 6
output
Copy
Possible 2 5 3 2 5 1 3 4 4 1 5 4
input
Copy
6 12
output
Copy
Impossible
Note
Here is the representation of the graph from the first example: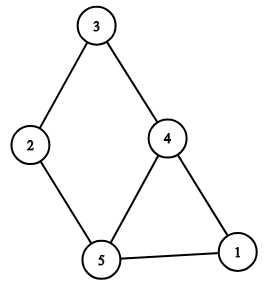
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int mn = 1e5 + 10;
int u[mn], v[mn];
int main()
{
int n, m;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
/// 相鄰兩數互質
if (n - 1 > m) // 不連通
{
printf("Impossible\n");
return 0;
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
u[i] = i, v[i] = i + 1;
int cnt = n - 1;
for (int i = 3; i <= n && cnt != m; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= i - 2 && cnt != m; j++)
{
if (gcd(i, j) == 1)
{
cnt++;
u[cnt] = i, v[cnt] = j;
}
}
}
if (cnt < m)
printf("Impossible\n");
else
{
printf("Possible\n");
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
printf("%d %d\n", u[i], v[i]);
}
return 0;
}
