Tensorflow學習筆記(五)——卷積神經網路實現
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-11-25
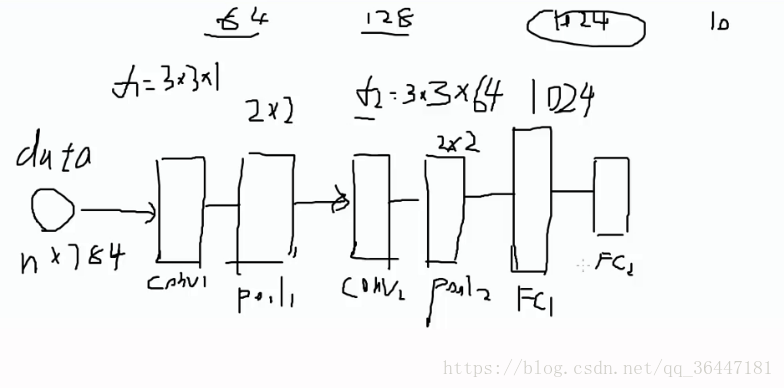
今天來實現tensorflow架構下的卷積神經網路,首先了解清楚我們要構建的網路架構,資料集還是用mnist,所以輸入還是28X28。
建立的卷積神經網路架構是:卷積層->pooling層->卷積層->pooling層->全連線層1->全連線層2。
全連線層的尺寸公式:N = (W − F + 2P )/S+1
引數解釋:
輸入圖片大小 W×W
Filter大小 F×F
步長 S
padding的畫素數
因為定義的filter所以卷積層=(28-3+2X1)/1+1=28,池化選擇2X2,所以經過兩次卷積和pooling層,特徵圖的尺寸大小=7X7,
建完架構和設定好引數就可以開始寫程式碼啦。程式碼如下:
一、匯入好工具包和資料集
import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import input_data mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('data/', one_hot=True) trainimg = mnist.train.images trainlabel = mnist.train.labels testimg = mnist.test.images testlabel = mnist.test.labels print ("MNIST ready")
二、定義各層引數
n_input = 784
n_output = 10
weights = {
'wc1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 1, 64], stddev=0.1)),
'wc2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 64, 128], stddev=0.1)),
'wd1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([7*7*128, 1024], stddev=0.1)),
'wd2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1024, n_output], stddev=0.1))
}
biases = {
'bc1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([64], stddev=0.1)),
'bc2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([128], stddev=0.1)),
'bd1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1024], stddev=0.1)),
'bd2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_output], stddev=0.1))
}


三、定義卷積架構
def conv_basic(_input, _w, _b, _keepratio):
# INPUT
_input_r = tf.reshape(_input, shape=[-1, 28, 28, 1])
# CONV LAYER 1
_conv1 = tf.nn.conv2d(_input_r, _w['wc1'], strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
#_mean, _var = tf.nn.moments(_conv1, [0, 1, 2])
#_conv1 = tf.nn.batch_normalization(_conv1, _mean, _var, 0, 1, 0.0001)
_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(_conv1, _b['bc1']))
_pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(_conv1, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
_pool_dr1 = tf.nn.dropout(_pool1, _keepratio)
# CONV LAYER 2
_conv2 = tf.nn.conv2d(_pool_dr1, _w['wc2'], strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
#_mean, _var = tf.nn.moments(_conv2, [0, 1, 2])
#_conv2 = tf.nn.batch_normalization(_conv2, _mean, _var, 0, 1, 0.0001)
_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(_conv2, _b['bc2']))
_pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(_conv2, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
_pool_dr2 = tf.nn.dropout(_pool2, _keepratio)
# VECTORIZE
_dense1 = tf.reshape(_pool_dr2, [-1, _w['wd1'].get_shape().as_list()[0]])
# FULLY CONNECTED LAYER 1
_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.add(tf.matmul(_dense1, _w['wd1']), _b['bd1']))
_fc_dr1 = tf.nn.dropout(_fc1, _keepratio)
# FULLY CONNECTED LAYER 2
_out = tf.add(tf.matmul(_fc_dr1, _w['wd2']), _b['bd2'])
# RETURN
out = { 'input_r': _input_r, 'conv1': _conv1, 'pool1': _pool1, 'pool1_dr1': _pool_dr1,
'conv2': _conv2, 'pool2': _pool2, 'pool_dr2': _pool_dr2, 'dense1': _dense1,
'fc1': _fc1, 'fc_dr1': _fc_dr1, 'out': _out
}
return out
print ("CNN READY")tf.nn.max_pool(value, ksize, strides, padding, data_format='NHWC', name=None)中四個數值的解釋:
value是一個四維的輸入:batch, height, width, channels。輸入經過卷積和relu層的_conv1,
_fc_dr1 = tf.nn.dropout(_fc1, _keepratio):是隨機殺死一些節點,_keepratio是比例的意思
ksize[1,2,2,1]:batchsize維度,height,width,步行strides
四、在mnist資料集上驗證一下準確率
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(init)
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_input])
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_output])
keepratio = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
# FUNCTIONS
_pred = conv_basic(x, weights, biases, keepratio)['out']
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(_pred, y))
optm = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=0.001).minimize(cost)
_corr = tf.equal(tf.argmax(_pred,1), tf.argmax(y,1))
accr = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(_corr, tf.float32))
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# SAVER
print ("GRAPH READY")
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(init)
training_epochs = 15
batch_size = 16
display_step = 1
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
avg_cost = 0.
#total_batch = int(mnist.train.num_examples/batch_size)
total_batch = 10
# Loop over all batches
for i in range(total_batch):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
# Fit training using batch data
sess.run(optm, feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y: batch_ys, keepratio:0.7})
# Compute average loss
avg_cost += sess.run(cost, feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y: batch_ys, keepratio:1.})/total_batch
# Display logs per epoch step
if epoch % display_step == 0:
print ("Epoch: %03d/%03d cost: %.9f" % (epoch, training_epochs, avg_cost))
train_acc = sess.run(accr, feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y: batch_ys, keepratio:1.})
print (" Training accuracy: %.3f" % (train_acc))
#test_acc = sess.run(accr, feed_dict={x: testimg, y: testlabel, keepratio:1.})
#print (" Test accuracy: %.3f" % (test_acc))
print ("OPTIMIZATION FINISHED")得出結果:
Epoch: 000/015 cost: 30.928401661 Training accuracy: 0.500 Epoch: 001/015 cost: 12.954609606 Training accuracy: 0.700 Epoch: 002/015 cost: 10.392489696 Training accuracy: 0.700 Epoch: 003/015 cost: 7.254891634 Training accuracy: 0.800 Epoch: 004/015 cost: 4.977767670 Training accuracy: 0.900 Epoch: 005/015 cost: 5.414173813 Training accuracy: 0.600 Epoch: 006/015 cost: 3.057567777 Training accuracy: 0.700 Epoch: 007/015 cost: 4.929724103 Training accuracy: 0.600 Epoch: 008/015 cost: 3.192437538 Training accuracy: 0.600 Epoch: 009/015 cost: 3.224479928 Training accuracy: 0.800 Epoch: 010/015 cost: 2.720530389 Training accuracy: 0.400 Epoch: 011/015 cost: 3.000342276 Training accuracy: 0.800 Epoch: 012/015 cost: 0.639763238 Training accuracy: 1.000 Epoch: 013/015 cost: 1.897303332 Training accuracy: 0.900 Epoch: 014/015 cost: 2.295500937 Training accuracy: 0.800 OPTIMIZATION FINISHED