排序演算法(三):簡單選擇排序(Simple Selection Sort)
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-11-26
基本思想:
在要排序的一組數中,選出最小(或者最大)的一個數與第1個位置的數交換;然後在剩下的數當中再找最小(或者最大)的與第2個位置的數交換,依次類推,直到第n-1個元素(倒數第二個數)和第n個元素(最後一個數)比較為止。
簡單選擇排序的示例:
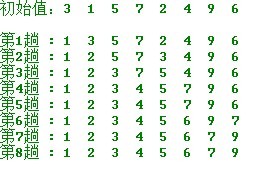
操作方法:
第一趟,從n 個記錄中找出關鍵碼最小的記錄與第一個記錄交換;
第二趟,從第二個記錄開始的n-1 個記錄中再選出關鍵碼最小的記錄與第二個記錄交換;
以此類推.....
第i 趟,則從第i 個記錄開始的n-i+1 個記錄中選出關鍵碼最小的記錄與第i 個記錄交換,
直到整個序列按關鍵碼有序。
演算法實現:
#include <stdio.h> #include <iostream> using namespace std; void print(int a[],int i) { cout<<i <<" : "; for(int j= 0; j<8; j++) { cout<<a[j] <<" "; } cout<<endl; } void selection_sort (int a[], int n) { int i,j,pos,tmp; for (i=0; i<n-1; i++) { //尋找最小值的下標 for (pos=i, j=i+1; j<n; j++) if (a[pos]>a[j]) pos=j; if (pos != i) { tmp=a[i]; a[i]=a[pos]; a[pos]=tmp; } print(a, i); } } int main(){ int a[8] = {3,1,5,7,2,4,8,6}; selection_sort(a,8); return 0; }
執行結果:
0 : 1 3 5 7 2 4 8 6
1 : 1 2 5 7 3 4 8 6
2 : 1 2 3 7 5 4 8 6
3 : 1 2 3 4 5 7 8 6
4 : 1 2 3 4 5 7 8 6
5 : 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 7
6 : 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
演算法優化(一):最大值和最小值同時查詢
#include <stdio.h> #include <iostream> using namespace std; void print(int a[],int i) { cout<<i <<" : "; for(int j= 0; j<8; j++) { cout<<a[j] <<" "; } cout<<endl; } void selection_sort (int a[], int n) { int i,j,max, min,tmp; for (i=0; i<n/2; i++) { //尋找最小值的下標 min = i; max = n - i - 1; for (j = i+1; j < n - i; j++) { if (a[max] < a[j]){ max = j; continue; } if (a[min] > a[j]) min = j; } if (max != n - i - 1) { tmp = a[n - i - 1]; a[n - i - 1] = a[max]; a[max] = tmp; } if (min != i) { tmp = a[i]; a[i] = a[min]; a[min] = tmp; } printf("max = %d, min = %d\n", max, min); print(a, i); } } int main(){ int a[8] = {3,1,5,7,2,4,8,6}; selection_sort(a,8); return 0; }
執行結果:
max = 6, min = 1
0 : 1 3 5 7 2 4 6 8
max = 3, min = 4
1 : 1 2 5 6 3 4 7 8
max = 3, min = 4
2 : 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
max = 4, min = 3
3 : 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
