深入理解Android Gradle
深入理解Android Gradle
標籤(空格分隔): 未分類
原作者真的寫的很棒附上鍊接
新的android開發工具引用了Gradle構建工具,方便了開發者進行構建不同的應用版本以完成不同的需求。(從此多版本不再痛苦)
1. gradle基本語法
新建專案把預設的配置檔案貼上來
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
android {
compileSdkVersion 22
buildToolsVersion "19.1.0"
defaultConfig {
applicationId "org.guf.mediagesturedetector" apply plugin:
我的理解為構建版本,當你作為一個普通的安卓應用程式的時候為
apply plugin: ‘com.android.application’
當你作為安卓modle形式為apply plugin: ‘com.android.library’
當然最簡單的只是java專案則為 apply plugin: ‘java’
android
這個標籤下主要包含了應用程式編譯的sdkapi版本,sdkbuildTools的版本
defaultConfig 裡包含了manifests裡的編譯屬性
buildTypes 裡包含了輸出版本的型別
當然這些是可擴充的,這個下面會說到
dependencies
android studio的依賴庫配置
開發工具給我們提供了三種方式新增依賴包,這就是gradle帶來的好處
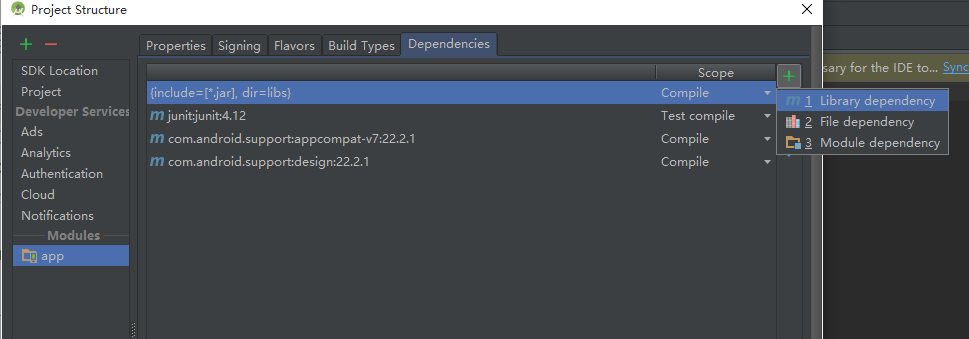
第一種是通過maven倉庫下載線上的依賴庫,比較依賴網路,但是更新編輯,後期只需要修改版本號即可
第二種是以檔案的方式引入jar檔案,如果你是eclipse轉過來的話就用的是這種方式,當然如果你已經配置了
compile fileTree(dir: ‘libs’, include: [‘*.jar’])
那麼就無需手動的新增,它自動載入libs裡的jar包
第三種就是引入專案中的modle專案,這個無需多講,跟eclipse中新增library類似
2. 通過gradle替換AndroidManifest中的佔位符
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="${APP_NAME}"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
現在我需要在AndroidManifest中新增佔位符’APP_NAME’,通過gradle編譯的過程中,通過bulid.gradle修改它,
manifestPlaceholders=[佔位符:需要修改的值]
buildTypes {
release {
manifestPlaceholders = [APP_NAME: 'test']
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}3. 獨立配置簽名信息
對於簽名相關的資訊,直接寫在gradle當然不好,特別是一些開源專案,可以新增到gradle.properties:
RELEASE_KEY_PASSWORD=xxxx
RELEASE_KEY_ALIAS=xxx
RELEASE_STORE_PASSWORD=xxx
RELEASE_STORE_FILE=../.keystore/xxx.jks
然後在build.gradle中引用即可:
android {
signingConfigs {
release {
storeFile file(RELEASE_STORE_FILE)
storePassword RELEASE_STORE_PASSWORD
keyAlias RELEASE_KEY_ALIAS
keyPassword RELEASE_KEY_PASSWORD
}
}
}4. 多版本生產環境
版本釋出的流程分為:
所以,我們的版本可以分為三種版本
debug-開發測試版
preview-測試預覽版
release-正式版
每個版本都會有不同的要求,測試版不能影響生產環境,不用通過改程式碼來切換測試環境和生產環境,可以增加自定義Build Type完成此類版本需求
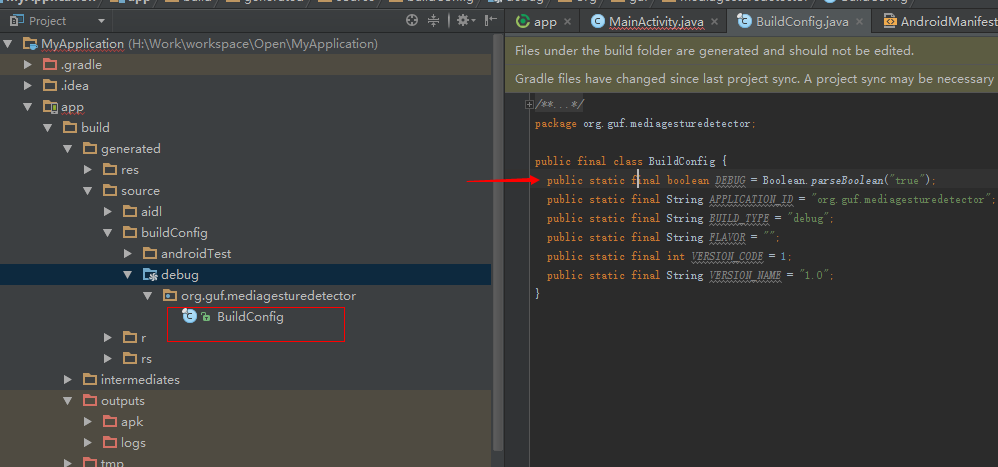
在這個目錄下會有個BuildConfig,我們可以用配置這裡面的值來切換全域性log的開關,保證生產環境不會洩漏log日誌
buildTypes {
debug {
buildConfigField "boolean", "DEBUG", "true"
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
release {
buildConfigField "boolean", "DEBUG", "false"
minifyEnabled true
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}5. build type中的定製引數
我這裡列幾個我在工作中用到的:
android {
debug {
manifestPlaceholders = [app_label:"@string/app_name_debug"]
applicationIdSuffix ".debug"
minifyEnabled false
signingConfig signingConfigs.debug
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
release {
manifestPlaceholders = [app_label:"@string/app_name"]
minifyEnabled true
shrinkResources true
signingConfig signingConfigs.release
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
preview{
manifestPlaceholders = [app_label:"@string/app_name_preview"]
applicationIdSuffix ".preview"
debuggable true // 保留debug資訊
minifyEnabled true
shrinkResources true
signingConfig signingConfigs.preview
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
}這些都用的太多了,稍微解釋一下:
// minifyEnabled 混淆處理
// shrinkResources 去除無用資源
// signingConfig 簽名
// proguardFiles 混淆配置
// applicationIdSuffix 增加APP ID的字尾
// debuggable 是否保留除錯資訊
// ... ...
6. 多工程全域性配置
隨著產品渠道的鋪開,往往一套程式碼需要支援多個產品形態,這就需要抽象出主要程式碼到一個Library,然後基於Library擴充套件幾個App Module。
相信每個module的build.gradle都會有這個程式碼:
android {
compileSdkVersion 22
buildToolsVersion "23.0.1"
defaultConfig {
minSdkVersion 10
targetSdkVersion 22
versionCode 34
versionName "v2.6.1"
}
}當升級sdk、build tool、target sdk等,幾個module都要更改,非常的麻煩。最重要的是,很容易忘記,最終導致app module之間的差異不統一,也不可控。
強大的gradle外掛在1.1.0支援全域性變數設定,一舉解決了這個問題。
先在project的根目錄下的build.gradle定義ext全域性變數:
ext {
compileSdkVersion = 22
buildToolsVersion = "23.0.1"
minSdkVersion = 10
targetSdkVersion = 22
versionCode = 34
versionName = "v2.6.1"
}然後在各module的build.gradle中引用如下:
android {
compileSdkVersion rootProject.ext.compileSdkVersion
buildToolsVersion rootProject.ext.buildToolsVersion
defaultConfig {
applicationId "com.xxx.xxx"
minSdkVersion rootProject.ext.minSdkVersion
targetSdkVersion rootProject.ext.targetSdkVersion
versionCode rootProject.ext.versionCode
versionName rootProject.ext.versionName
}
}然後每次修改project級別的build.gradle即可實現全域性統一配置。
7. 自定義匯出的APK名稱
預設android studio生成的apk名稱為app-debug.apk或者app-release.apk,當有多個渠道的時候,需要同時編出50個渠道包的時候,就麻煩了,不知道誰是誰了。
這個時候,就需要自定義匯出的APK名稱了,不同的渠道編出的APK的檔名應該是不一樣的。
android {
// rename the apk with the version name
applicationVariants.all { variant ->
variant.outputs.each { output ->
output.outputFile = new File(
output.outputFile.parent,
"ganchai-${variant.buildType.name}-${variant.versionName}-${variant.productFlavors[0].name}.apk".toLowerCase())
}
}
}當apk太多時,如果能把apk按debug,release,preview分一下類就更好了(事實上,對於我這樣經常發版的人,一編往往就要編四五十個版本的人,debug和release版本全混在一起沒法看,必須分類),簡單:
android {
// rename the apk with the version name
// add output file sub folder by build type
applicationVariants.all { variant ->
variant.outputs.each { output ->
output.outputFile = new File(
output.outputFile.parent + "/${variant.buildType.name}",
"ganchai-${variant.buildType.name}-${variant.versionName}-${variant.productFlavors[0].name}.apk".toLowerCase())
}
}
}現在生成了類似於ganchai-dev-preview-v2.4.0.0.apk這樣格式的包了,preview的包自然就放在preview的資料夾下,清晰明瞭。
8. 多渠道打包
多渠道打包的關鍵之處在於,定義不同的product flavor, 並把AndroiManifest中的channel渠道編號替換為對應的flavor標識:
android {
productFlavors {
dev{
manifestPlaceholders = [channel:"dev"]
}
official{
manifestPlaceholders = [channel:"official"]
}
// ... ...
wandoujia{
manifestPlaceholders = [channel:"wandoujia"]
}
xiaomi{
manifestPlaceholders = [channel:"xiaomi"]
}
"360"{
manifestPlaceholders = [channel:"360"]
}
}注意一點,這裡的flavor名如果是數字開頭,必須用引號引起來。
構建一下,就能生成一系列的Build Variant了:
devDebug
devRelease
officialDebug
officialRelease
wandoujiaDebug
wandoujiaRelease
xiaomiDebug
xiaomiRelease
360Debug
360Release
其中debug, release是gradle預設自帶的兩個build type, 下一節還會繼續說明。
選擇一個,就能編譯出對應渠道的apk了。
9. 動態設定一些額外資訊
假如想把當前的編譯時間、編譯的機器、最新的commit版本新增到apk,而這些資訊又不好寫在程式碼裡,強大的gradle給了我創造可能的自信:
android {
defaultConfig {
resValue "string", "build_time", buildTime()
resValue "string", "build_host", hostName()
resValue "string", "build_revision", revision()
}
}
def buildTime() {
return new Date().format("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
}
def hostName() {
return System.getProperty("user.name") + "@" + InetAddress.localHost.hostName
}
def revision() {
def code = new ByteArrayOutputStream()
exec {
commandLine 'git', 'rev-parse', '--short', 'HEAD'
standardOutput = code
}
return code.toString()
}上述程式碼實現了動態的添加了3個字串資源: build_time、build_host、build_revision, 然後在其他地方可像如引用字串一樣
