子字串查詢
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-11-29
1 暴力破解
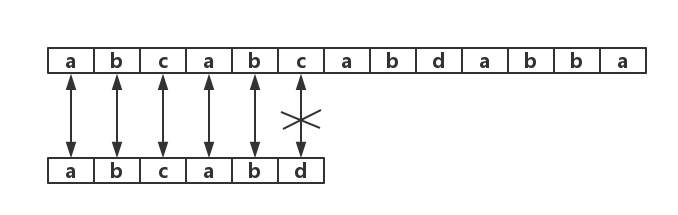
java實現如下:
1 public class Naive { 2 3 /** 4 * 暴力破解 5 * 6 * @param pat 7 * @param txt 8 * @return 9 */ 10 private static int search(String pat, String txt) { 11 int m = pat.length(); 12 int n = txt.length(); 13 for(int i = 0; i <= n - m; i++) { 14 int j; 15 for (j = 0; j < m; j++) { 16 if (txt.charAt(i + j) != pat.charAt(j)) { 17 break; 18 } 19 } 20 if (j == m) { 21 return i; 22 }23 } 24 return n; 25 } 26 27 public static void main(String[] args) { 28 int pos = search("abcabd", "abcabcabdabba"); 29 System.out.println(pos); 30 } 31 32 }
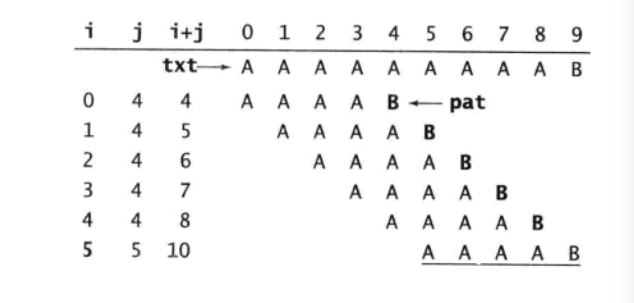
最壞的情況是:

常見的是二進位制情況下的匹配:
2 KMP演算法
如果用暴力方法解決的話就會有大量的回溯,每次只移動一位,若是不匹配,移動到下一位接著判斷,浪費了大量的時間:
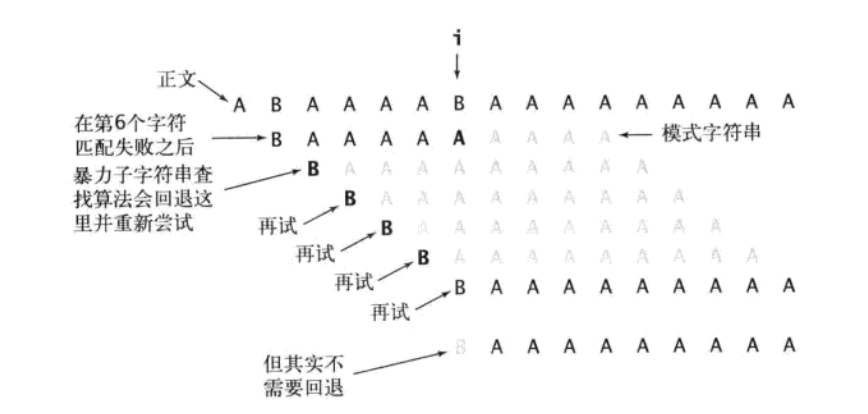
所以,kmp方法演算法就利用之前判斷過資訊,通過一個next陣列,儲存模式串中前後最長公共子序列的長度,每次回溯時,通過next陣列找到,前面匹配過的位置,省去了大量的計算時間。
1 public class KMP { 2 public static int KMP(String pat, String txt) { 3 char[] t = pat.toCharArray(); 4 char[] p = txt.toCharArray(); 5 6 int i = 0; // 主串的位置 7 int j = 0; // 模式串的位置 8 int[] next = getNext(txt); 9 10 while (i < t.length && j < p.length) { 11 if (j == -1 || t[i] == p[j]) { // 當j為-1時,要移動的是i,當然j也要歸0 12 i++; 13 j++; 14 } else { 15 // i不需要回溯了 16 // i = i - j + 1; 17 j = next[j]; // j回到指定位置 18 } 19 } 20 21 if (j == p.length) { 22 return i - j; 23 } else { 24 return -1; 25 } 26 } 27 28 public static int[] getNext(String ps) { 29 char[] p = ps.toCharArray(); 30 int[] next = new int[p.length]; 31 next[0] = -1; 32 33 int j = 0; 34 int k = -1; 35 while (j < p.length - 1) { 36 if (k == -1 || p[j] == p[k]) { 37 next[++j] = ++k; 38 } else { 39 k = next[k]; 40 } 41 } 42 return next; 43 } 44 45 public static void main(String[] args) { 46 String pat = "abcabd"; 47 String txt = "abcabcabdabba"; 48 int pos = KMP(pat, txt); 49 System.out.println(pos); 50 } 51 52 }
kmp演算法的核心時間複雜度就是O(m+n)
