Redis配置檔案(1)units/includes/GENERAL/SECURITY/LIMITS
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-02
redis.conf檔案
在Linux進行檔案的檢視!
units單位:
8 # Note on units: when memory size is needed, it is possible to specify 9 # it in the usual form of 1k 5GB 4M and so forth: 10 # 11 # 1k => 1000 bytes 12 # 1kb => 1024 bytes 13 # 1m => 1000000 bytes 14 # 1mb => 1024*1024 bytes 15 # 1g => 1000000000bytes 16 # 1gb => 1024*1024*1024 bytes 17 # 18 # units are case insensitive so 1GB 1Gb 1gB are all the same.
1 配置大小單位,開頭定義了一些基本的度量單位,只支援bytes,不支援bit 2 對大小寫不敏感
includes:
20 ################################## INCLUDES ##############################和我們的Struts2配置檔案類似,可以通過includes包含,redis.conf可以作為總閘,包含其他22 # Include one or more other config files here. This is useful if you 23 # have a standard template that goes to all Redis servers but also need 24 # to customize a few per-server settings. Include files can include 25 # other files, so use this wisely. 26 # 27 # Notice option "include" won't be rewritten by command "CONFIG REWRITE" 28 # from admin or Redis Sentinel. Since Redis always uses the last processed 29 # line as value of a configuration directive, you'd better put includes 30 # at the beginning of this file to avoid overwriting config change at runti me. 31 # 32 # If instead you are interested in using includes to override configuration 33 # options, it is better to use include as the last line. 34 # 35 # include /path/to/local.conf
GENERAL
141 # If a pid file is specified, Redis writes it where specified at startup 142 # and removes it at exit. 143 # 144 # When the server runs non daemonized, no pid file is created if none is 145 # specified in the configuration. When the server is daemonized, the pid fi le 146 # is used even if not specified, defaulting to "/var/run/redis.pid". 147 # 148 # Creating a pid file is best effort: if Redis is not able to create it 149 # nothing bad happens, the server will start and run normally. 150 pidfile /var/run/redis_6379.pid
126 # By default Redis does not run as a daemon. Use 'yes' if you need it. 127 # Note that Redis will write a pid file in /var/run/redis.pid when daemoniz ed. 128 daemonize yes
82 # Accept connections on the specified port, default is 6379 (IANA #815344). 83 # If port 0 is specified Redis will not listen on a TCP socket. 84 port 6379
# TCP listen() backlog. # # In high requests-per-second environments you need an high backlog in order # to avoid slow clients connections issues. Note that the Linux kernel # will silently truncate it to the value of /proc/sys/net/core/somaxconn so # make sure to raise both the value of somaxconn and tcp_max_syn_backlog # in order to get the desired effect. tcp-backlog 511 tcp-backlog 設定tcp的backlog,backlog其實是一個連線佇列,backlog佇列總和=未完成三次握手佇列 + 已經完成三次握手佇列。 在高併發環境下你需要一個高backlog值來避免慢客戶端連線問題。注意Linux核心會將這個值減小到 /proc/sys/net/core/somaxconn的值,所以需要確認增大somaxconn和tcp_max_syn_backlog兩個值 來達到想要的效果
# Close the connection after a client is idle for N seconds (0 to disable) timeout 0
# IF YOU ARE SURE YOU WANT YOUR INSTANCE TO LISTEN TO ALL THE INTERFACES # JUST COMMENT THE FOLLOWING LINE. # ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ bind 127.0.0.1
# On Linux, the specified value (in seconds) is the period used to send ACKs. # Note that to close the connection the double of the time is needed. # On other kernels the period depends on the kernel configuration. # # A reasonable value for this option is 300 seconds, which is the new # Redis default starting with Redis 3.2.1. tcp-keepalive 300 單位為秒,如果設定為0,則不會進行Keepalive檢測,建議設定成60
# Specify the server verbosity level. # This can be one of: # debug (a lot of information, useful for development/testing) # verbose (many rarely useful info, but not a mess like the debug level) # notice (moderately verbose, what you want in production probably) # warning (only very important / critical messages are logged) loglevel notice 日誌級別
# Specify the log file name. Also the empty string can be used to force # Redis to log on the standard output. Note that if you use standard # output for logging but daemonize, logs will be sent to /dev/null logfile "" 日誌的名字
# Set the number of databases. The default database is DB 0, you can select # a different one on a per-connection basis using SELECT <dbid> where # dbid is a number between 0 and 'databases'-1 databases 16 系統預設的庫16個 預設使用0庫
# To enable logging to the system logger, just set 'syslog-enabled' to yes, # and optionally update the other syslog parameters to suit your needs. # syslog-enabled no 是否把日誌輸出到syslog中 系統日誌預設時關著 # Specify the syslog identity. # syslog-ident redis 指定syslog裡的日誌標誌 裝置以redis開頭 # Specify the syslog facility. Must be USER or between LOCAL0-LOCAL7. # syslog-facility local0 指定syslog裝置,值可以是USER或LOCAL0-LOCAL7 預設使用local0
SECURITY安全
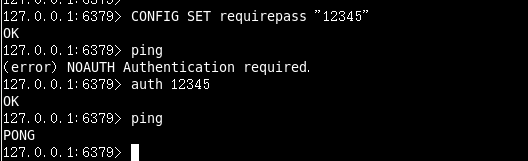
訪問密碼的檢視、設定和取消
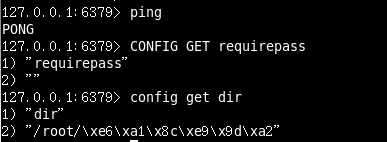
設定密碼:
config set requirepass " "
;
改為空的時候預設沒有密碼!
467 ################################## SECURITY ################################### 468 469 # Require clients to issue AUTH <PASSWORD> before processing any other 470 # commands. This might be useful in environments in which you do not trust 471 # others with access to the host running redis-server.
要求必須auth + password 在任何命令之前
LIMITS限制 maxclients:
設定redis同時可以與多少個客戶端進行連線。預設情況下為10000個客戶端。當你
無法設定程序檔案控制代碼限制時,redis會設定為當前的檔案控制代碼限制值減去32,因為redis會為自
身內部處理邏輯留一些控制代碼出來。如果達到了此限制,redis則會拒絕新的連線請求,並且向這
些連線請求方發出“max number of clients reached”以作迴應。
509 # Once the limit is reached Redis will close all the new connections sending
510 # an error 'max number of clients reached'.
511 #
512 # maxclients 10000
預設情況下為10000個客戶端
maxmemory
設定redis可以使用的記憶體量。一旦到達記憶體使用上限,redis將會試圖移除內部資料,移除規則可以通過maxmemory-policy來指定。533 # In short... if you have slaves attached it is suggested that you set a lower 534 # limit for maxmemory so that there is some free RAM on the system for slave 535 # output buffers (but this is not needed if the policy is 'noeviction'). 537 # maxmemory <bytes> maxmemory-policy: 最大快取清楚策略
如果redis無法根據移除規則來移除記憶體中的資料,或者設定了“不允許移除”, 那麼redis則會針對那些需要申請記憶體的指令返回錯誤資訊,比如SET、LPUSH等。 但是對於無記憶體申請的指令,仍然會正常響應,比如GET等。如果你的redis是主redis(說明你的redis有從redis),
那麼在設定記憶體使用上限時,需要在系統中留出一些記憶體空間給同步佇列快取,只有在你設定的是“不移除”的情況下,才不用考慮這個因素
(1)volatile-lru:使用LRU演算法移除key,只對設定了過期時間的鍵 (2)allkeys-lru:使用LRU演算法移除key (3)volatile-random:在過期集合中移除隨機的key,只對設定了過期時間的鍵 (4)allkeys-random:移除隨機的key (5)volatile-ttl:移除那些TTL值最小的key,即那些最近要過期的key (6)noeviction:不進行移除。針對寫操作,只是返回錯誤資訊 LRU 演算法或者 TTL 演算法都是不是很精確演算法,而是 個近似演算法。539 # MAXMEMORY POLICY: how Redis will select what to remove when maxmemory 540 # is reached. You can select among five behaviors: 541 # 542 # volatile-lru -> remove the key with an expire set using an LRU algorithm 543 # allkeys-lru -> remove any key according to the LRU algorithm 544 # volatile-random -> remove a random key with an expire set 545 # allkeys-random -> remove a random key, any key 546 # volatile-ttl -> remove the key with the nearest expire time (minor TTL) 547 # noeviction -> don't expire at all, just return an error on write operations

maxmemory-samples
設定樣本數量,LRU演算法和最小TTL演算法都並非是精確的演算法,而是估算值,所以你可以設定樣本的大小,
redis預設會檢查這麼多個key並選擇其中LRU的那個
562 # LRU and minimal TTL algorithms are not precise algorithms but approximated
563 # algorithms (in order to save memory), so you can tune it for speed or
564 # accuracy. For default Redis will check five keys and pick the one that was
565 # used less recently, you can change the sample size using the following
566 # configuration directive.
568 # The default of 5 produces good enough results. 10 Approximates very closely
569 # true LRU but costs a bit more CPU. 3 is very fast but not very accurate.
571 #
maxmemory-samples 5
