Java集合---CopyOnWriteArrayList(5)
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-04
用途與特點
可用於多讀取,寫入需要執行緒安全的情況使用。
實現演算法
該集合如其名字一樣,是先建立一個新的陣列,然後將舊的陣列copy到新陣列中,再切換陣列引用。並且該陣列是在每次新增時都會執行以上流程,所以不建議在多寫入的場景使用。
該集合在多併發時使用ReentrantLock鎖來處理併發問題,比Vector中synchronized的效率會高一些,但在並法過程中可能會出現髒讀問題,如兩個執行緒一個執行讀取陣列數量,一個在做寫入操作,如在寫入操作之前,還沒做size++操作前,另外一個執行緒讀取size值,此時還時未增加的數量,會產生髒讀。
新增

/** * Appends the specified element to the end of this list. * * @param e element to be appended to this list * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add}) */ public boolean add(E e) { final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; lock.lock(); try { Object[] elements = getArray(); int len = elements.length; Object[] newElements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, len + 1); newElements[len] = e; setArray(newElements); return true; } finally { lock.unlock(); } }
刪除
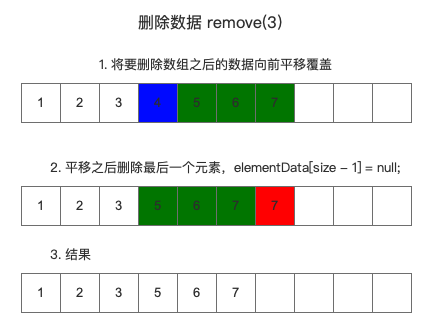
這裡說明一下,之前的幾個集合在刪除操作時都是不會對object[]陣列進行操作,但這個集合會重新生成-1的新陣列。所以可以說該集合的陣列長度與集合的實際資料佔用長度是相同的。
/** * Removes the element at the specified position in this list. * Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their * indices). Returns the element that was removed from the list. * * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public E remove(int index) { final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; lock.lock(); try { Object[] elements = getArray(); int len = elements.length; E oldValue = get(elements, index); int numMoved = len - index - 1; if (numMoved == 0) setArray(Arrays.copyOf(elements, len - 1)); else { Object[] newElements = new Object[len - 1]; System.arraycopy(elements, 0, newElements, 0, index); System.arraycopy(elements, index + 1, newElements, index, numMoved); setArray(newElements); } return oldValue; } finally { lock.unlock(); } }
擴容機制
擴容時機:在增加資料時,沒增加一個擴容一個
是否執行緒安全,為什麼?
執行緒安全,在原始碼中對資料操作使用ReentrantLock方法,保證了併發鎖。
具體ReentrantLock的使用詳解與synchronized有何區別,會在之後詳細檢視併發時做補充。
根據jdk1.8版本原始碼解讀
