可達使用者投資額的計算(Java)
有話要說:
前陣子遇到了一個計算可達使用者投資額的問題,覺得非常有趣,故把它記錄下來。
問題描述:
某產品可被投資,註冊後才可以投資,其註冊可以被邀請(並不是每個人都是被邀請的)。邀請人可以邀請多個人註冊投資,而被邀請人只能有一位邀請人。也就是說邀請人與被邀請人是一對多的關係。
現給定兩組資料:邀請與被邀請的關係;所有使用者的投資額。
如下:
1,2
1,4
2,11
2,10
4,5
5,6
6,8
6,9
6,7
13,14
13,15
13,17
14,20
20,21
15,18
15,19
以上資料是處理過後的邀請關係,前者邀請了後者。
1,1200.00 2,2300.00 4,1500.00 5,7300.00 6,4100.00 7,1100.00 8,9000.00 9,1000.00 10,1100.00 11,100.00 12,1000.00 13,4500.00 14,1100.00 15,1200.00 17,700.00 18,100.00 19,200.00 20,100.00 21,0.00
以上資料是處理過後的所有使用者投資額。
現在根據這兩組資料需要計算每位使用者的“使用者投資金額”,“可達使用者投資金額”,“邀請使用者階數”,“成功邀請使用者數”,“一階推薦使用者投資金額”。
使用者投資金額:即該使用者的投資額,以以上資料舉個例子來說:2的投資金額為2300
可達使用者投資金額:即該使用者的投資額加上該使用者邀請的所有人的投資額(包括該使用者邀請人所邀請的人),假設A邀請了B和C,B邀請了D和E,C、D、E沒有邀請別人,那麼A的可達使用者投資金額就是A、B、C、D、E投資額的總數
邀請使用者階數:即該使用者所邀請人的總數(不包括該使用者邀請人所邀請的人),假設A邀請了B和C,B邀請了D和E,C、D、E沒有邀請別人,那麼A的邀請使用者階數
成功邀請使用者數:在邀請使用者階數的基礎上除去投資額為零的使用者
一階推薦使用者投資金額:即該使用者所邀請人的總投資額(不包括該使用者邀請人所邀請的人),假設A邀請了B和C,B邀請了D和E,C、D、E沒有邀請別人,那麼A的一階推薦使用者投資金額為B、C投資額的總數
大家可以先想想如何處理該資料
思路分析:
首先根據邀請的關係可以分析出邀請人的關係圖可以分解為多棵不相關的樹(反證法可證)。
邀請關係如下圖所示:
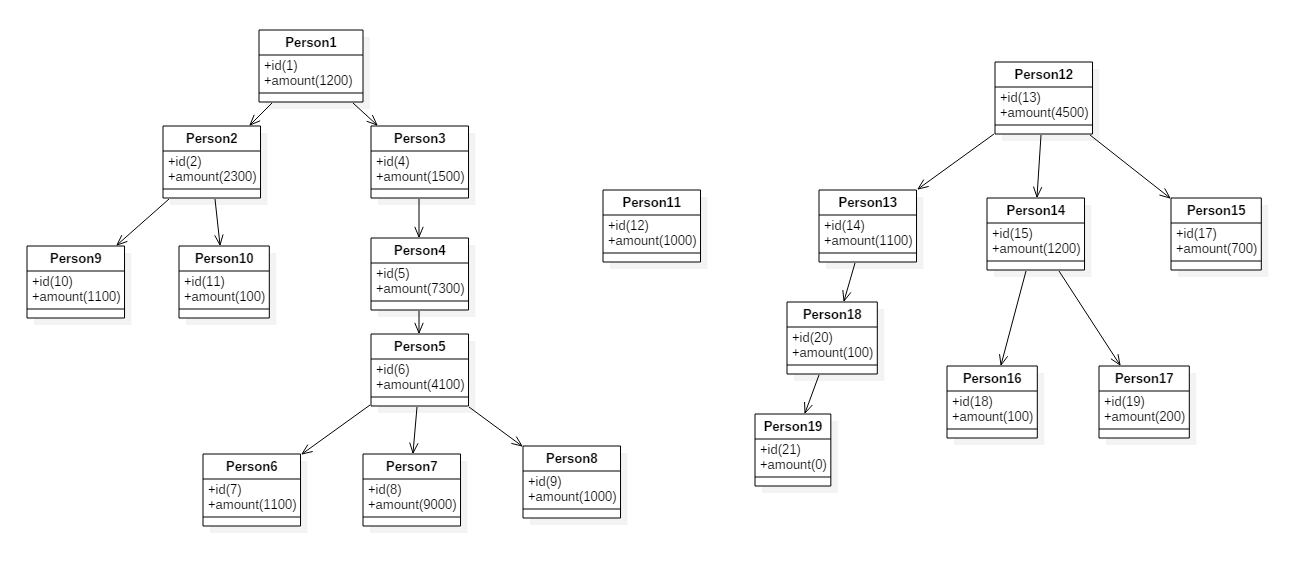
因此可以先將資料生成若干棵樹,然後針對於樹進行遍歷。
對於每棵樹來說,父節點的可達使用者投資金額就是子節點的可達使用者投資金額之和再加上父節點的投資額,根據這一特性,可以對每棵樹從葉子節點網上遍歷。
程式碼實現:
獲取所有使用者的投資額:
直接讀取檔案,並把使用者id與使用者投資額放在Map集合中
1 // 獲取每個人的投資額 2 public static Map<String, Double> getAmount() { 3 Map<String, Double> amounts = new HashMap<String, Double>(); 4 5 File file = new File("D:/amount.txt"); 6 7 try { 8 // 建立輸入流,讀取txt 9 InputStream is = new FileInputStream(file.getAbsolutePath()); 10 InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(is, "UTF-8"); 11 12 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr); 13 String line = ""; 14 while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { 15 String[] amount = line.trim().split(","); 16 amount[0] = amount[0].trim(); 17 amounts.put(amount[0], Double.parseDouble(amount[1])); 18 } 19 20 br.close(); 21 isr.close(); 22 is.close(); 23 24 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 25 e.printStackTrace(); 26 } catch (IOException e) { 27 e.printStackTrace(); 28 } 29 return amounts; 30 }
獲取使用者的邀請關係:
直接讀取檔案,並把使用者的邀請關係放在List集合中
1 // 獲取關係資料集合 2 public static List<String[]> getRelationship() { 3 List<String[]> list = new ArrayList<String[]>(); 4 5 File file = new File("D:/relationship.txt"); 6 7 try { 8 // 建立輸入流,讀取txt 9 InputStream is = new FileInputStream(file.getAbsolutePath()); 10 InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(is, "UTF-8"); 11 12 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr); 13 String line = ""; 14 while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { 15 String[] relation = line.trim().split(","); 16 relation[0] = relation[0].trim(); 17 relation[1] = relation[1].trim(); 18 list.add(relation); 19 } 20 21 br.close(); 22 isr.close(); 23 is.close(); 24 25 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 26 e.printStackTrace(); 27 } catch (IOException e) { 28 e.printStackTrace(); 29 } 30 return list; 31 }
構造Person物件:
1 // 使用者邀請關係(前者邀請了後者) 2 List<String[]> relationships = new ArrayList<>(); 3 relationships = getRelationship(); 4 5 // 每個使用者投資額 6 Map<String, Double> amounts = new HashMap<String, Double>(); 7 amounts = getAmount(); 8 9 // 構造使用者資訊 10 Map<String, Person> persons = new HashMap<String, Person>(); 11 Iterator<String> it = amounts.keySet().iterator(); 12 while (it.hasNext()) { 13 String key = it.next(); 14 15 Person temp = new Person(); 16 temp.setId(key); 17 temp.setAmount(amounts.get(key)); 18 19 persons.put(key, temp); 20 }
其中Person類為:
1 class Person { 2 3 /** 4 * 使用者id 5 */ 6 private String id; 7 8 /** 9 * 邀請人列表 10 */ 11 private List<Person> invitedPersons = new ArrayList<Person>(); 12 13 /** 14 * 投資額 15 */ 16 private double amount; 17 18 /** 19 * 所有下線投資額總額(包括自身) 20 */ 21 private double allAmount; 22 23 public String getId() { 24 return id; 25 } 26 27 public void setId(String id) { 28 this.id = id; 29 } 30 31 public double getAmount() { 32 return amount; 33 } 34 35 public void setAmount(double amount) { 36 this.amount = amount; 37 } 38 39 public List<Person> getInvitedPersons() { 40 return invitedPersons; 41 } 42 43 public void setInvitedPersons(List<Person> invitedPersons) { 44 this.invitedPersons = invitedPersons; 45 } 46 47 public double getAllAmount() { 48 return allAmount; 49 } 50 51 public void setAllAmount(double allAmount) { 52 this.allAmount = allAmount; 53 } 54 55 }
構建邀請關係:
1 for (int i = 0; i < relationships.size(); i++) { 2 String[] relationship = relationships.get(i); 3 4 // 獲取邀請人 5 Person person1 = persons.get(relationship[0]); 6 // 獲取被邀請人 7 Person person2 = persons.get(relationship[1]); 8 // 加上關聯關係 9 person1.getInvitedPersons().add(person2); 10 }
根據以上的構造,已經針對於每個使用者都生成了一棵樹。
但事實上這些樹有大量的重合,如果逐一遍歷的話會導致不必要的浪費。
於是準備找出所有的根樹,遍歷根數即可。
找到所有的根樹:
1 // 所有person集合 2 List<Person> allPerson = new ArrayList<>(); 3 allPerson.addAll(persons.values()); 4 5 // 找到根節點,去除非根節點 6 for (int i = 0; i < relationships.size(); i++) { 7 String[] relationship = relationships.get(i); 8 9 // 如果是被邀請人,則去除 10 persons.remove(relationship[1]); 11 }
根據以上精簡,persons集合裡只有根節點。
遍歷根數,找出所有人的可達使用者投資金額:
Iterator<Person> it4 = persons.values().iterator(); while (it4.hasNext()) { Person person = it4.next(); addAllChildren(person); }
其中addAllChildren為
1 // 可達使用者投資金額 2 public static double addAllChildren(Person person) { 3 double childrenAmount = 0; 4 5 // 先加自己的 6 childrenAmount += person.getAmount(); 7 8 // 再加孩子的 9 for (int i = 0; i < person.getInvitedPersons().size(); i++) { 10 Person child = person.getInvitedPersons().get(i); 11 12 if (child.getInvitedPersons().size() > 0) { 13 childrenAmount += addAllChildren(child); 14 } else { 15 childrenAmount += child.getAmount(); 16 } 17 } 18 19 person.setAllAmount(childrenAmount); 20 21 return childrenAmount; 22 }
通過此遍歷,每個person物件的可達使用者投資金額均已被算出,又因為java是值傳遞的,所以allPerson內的person物件的值都已經被計算出來了。
接下來就可以遍歷所有的person物件了。
遍歷person集合,算出需要的所有資料:
1 try { 2 String path = "D:/result.txt"; 3 File file = new File(path); 4 if (!file.exists()) { 5 file.getParentFile().mkdirs(); 6 } 7 file.createNewFile(); 8 9 // write 10 FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(file, true); 11 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(fw); 12 13 Iterator<Person> it3 = allPerson.iterator(); 14 15 while (it3.hasNext()) { 16 Person person = it3.next(); 17 18 if (person.getAllAmount() == 0) { 19 bw.write("可達使用者投資總額:" + person.getAmount() + ";"); 20 } else { 21 bw.write("可達使用者投資總額:" + person.getAllAmount() + ";"); 22 } 23 24 bw.write("邀請使用者階數:" + person.getInvitedPersons().size() + ";"); 25 26 int count = 0; 27 double sum = 0; 28 for (Person temp : person.getInvitedPersons()) { 29 if (temp.getAmount() != 0) { 30 sum += temp.getAmount(); 31 count++; 32 } 33 } 34 35 bw.write("成功邀請使用者數:" + count + ";"); 36 bw.write("一階推薦使用者投資金額:" + sum + ";\n"); 37 } 38 39 bw.flush(); 40 bw.close(); 41 fw.close(); 42 } catch (Exception e) { 43 e.printStackTrace(); 44 }
結束語:
以上便是我這次遇到問題的解決思路以及解決過程,對於樹的構造以及java值傳遞的應用值得學習。
本題的解決思路以及解決過程比較倉促,只用了一下午的時間,可能會有更好的解決辦法,如果大家有什麼更好的解決辦法歡迎留言~
大家如果有什麼疑問或者建議可以通過評論或者郵件的方式聯絡我,歡迎大家的評論~
