DSL 系列(2) - 外掛的論述與實現
前言
本文主要探討基於 DSL(domain specific language) 之上的外掛設計,他們是領域的附屬,為領域提供額外的服務,但領域不依賴於他們。

1. 論述
領域應當儘可能地去專注他的核心業務規則,應當儘可能地與其他輔助性的程式碼解耦,一些通用的功能可以耦合進框架或者設計為中介軟體;但還存在有一些是與核心功能無關的,且又與業務邏輯密不可分,譬如特定的監控、特定的埋點、為領域定製的穩定性保障等,把他們定義為外掛再合適不過,其依賴關係如前言所述。
2. 設計方案
暫不討論特定的外掛要實現哪些特定的能力,後續系列中將逐步展開構建一個完整的 DSL 具體需要哪些外掛及其實現方案,這裡我想展開思考的是怎樣設計一個比較通用的 DSL 外掛方案。
論述中對外掛的定義與 AOP 的思想相當吻合,也當首選使用 AOP 來實現,但這其中還存在一個問題,我希望外掛只專注其自身職責的表達,至於哪些節點需要接入哪些外掛應當在 DSL 中配置(即我期望外掛與 DSL 之間只存在配置關係),而配置應當支援動態更新,因此這就導致了 AOP 的代理物件事先是不確定的,需要去動態生成。
最後落到實現上,外掛這塊我需要去攻克兩個核心技術點:
1、怎樣去更新 AOP 的代理及切點表示式?
2、怎樣去更新 IOC 容器?
3. 實現方案
3.1 配置入口
若不考慮動態更新,那麼入口要實現的基本功能有兩個:1、按需引入,這很簡單,用一個 Conditional
@Configuration @ConditionalOnBean(DSL.class) public class PluginConfig { @Bean public AspectJExpressionPointcutAdvisor pluginAdvisor() { AspectJExpressionPointcutAdvisor advisor = new AspectJExpressionPointcutAdvisor(); advisor.setExpression(DSL.getExpression()); advisor.setAdvice(new PluginAdvice()); return advisor; } } public class PluginAdvice implements MethodInterceptor { @Override public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable { System.out.println("do plugin_work start..."); Object resObj = invocation.proceed(); System.out.println("do plugin_work end..."); return resObj; } }
測試:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class DefaultTest {
@ExtensionNode
private Engine engine;
@Test
public void test() {
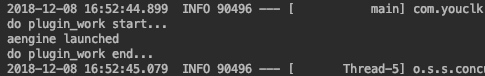
DslUtils.setDslA();
engine.launch();
}
}
3.2 監聽 DLS 變更
怎麼監聽配置的更新是所有的配置中心都需要去深入設計的(後續系列中探討),此處暫用虛擬碼代替:
@Configuration
public class PluginListenerImpl implements DslListener {
@Override
public void refresh(DslContext dslContext) {
// do something...
}
}3.3 更新切點表示式
3.1 中我們已經注入了一個表示式通知器的 Bean:AspectJExpressionPointcutAdvisor,因此僅僅更新表示式的字串非常簡單,但檢視檢視原始碼會發現起匹配作用的是他的內部物件 AspectJExpressionPointcut,而他在首次執行匹配時會構建一個 PointcutExpression 並儲存起來:
private PointcutExpression obtainPointcutExpression() {
if (getExpression() == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Must set property 'expression' before attempting to match");
}
if (this.pointcutExpression == null) {
this.pointcutClassLoader = determinePointcutClassLoader();
this.pointcutExpression = buildPointcutExpression(this.pointcutClassLoader);
}
return this.pointcutExpression;
}因此我們還需要通過反射將這個私有欄位置空,讓 ClassFilter 重新執行構建,示例如下:
@Configuration
public class PluginListenerImpl implements DslListener {
@Autowired
private AspectJExpressionPointcutAdvisor aspectJExpressionPointcutAdvisor;
@Override
public void refresh(DslContext dslContext) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
refreshExpression(dslContext);
// next...
}
private void refreshExpression(DslContext dslContext) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
aspectJExpressionPointcutAdvisor.setExpression(dslContext.getExpression());
AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut = (AspectJExpressionPointcut) aspectJExpressionPointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getClassFilter();
Field f = AspectJExpressionPointcut.class
.getDeclaredField("pointcutExpression");
f.setAccessible(true);
f.set(pointcut, null);
}
}
3.3 更新動態代理
通過翻閱原始碼可得出 Spring AOP 主要通過:AbstractAdvisingBeanPostProcessor 、AbstractAutoProxyCreator 這兩個 processor 來實現動態代理,其對應的例項為:MethodValidationPostProcessor、AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator,前者用於建立代理物件,後者用於標記切面(即織入代理)。由此,若我們需要去更新動態代理,我想到的最簡單的方法就是對指定的節點重新執行以下這兩個 processor(原理簡單,就是一點點扣原始碼,麻煩...),其中還有一個小問題,和 3.2 中的一致,代理結果被快取了,清空再執行即可,示例如下:
@Autowired
private DefaultListableBeanFactory defaultListableBeanFactory;
private void refreshTypes(DslContext dslContext) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
List<Class<?>> refreshTypes = dslContext.getRefreshTypes();
for (Class<?> refreshType : refreshTypes) {
String[] beanNames = defaultListableBeanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(refreshType);
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Object bean = defaultListableBeanFactory.getBean(beanName);
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : defaultListableBeanFactory.getBeanPostProcessors()) {
bean = getProxyBean(bean, beanName, processor);
}
}
}
}
private Object getProxyBean(Object bean, String beanName, BeanPostProcessor processor) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
if (processor instanceof MethodValidationPostProcessor
|| processor instanceof AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator) {
removeAdvisedBeanCache(processor, bean, beanName);
Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);
return current == null ? bean : current;
}
return bean;
}
private void removeAdvisedBeanCache(BeanPostProcessor processor, Object bean, String beanName) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
if (processor instanceof AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator) {
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator annotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator = (AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator) processor;
Field f = AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.class
.getSuperclass()
.getSuperclass()
.getSuperclass()
.getDeclaredField("advisedBeans");
f.setAccessible(true);
Map<Object, Boolean> advisedBeans = (Map<Object, Boolean>) f.get(annotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator);
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
advisedBeans.remove(cacheKey);
}
}
private Object getCacheKey(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName)) {
return (FactoryBean.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) ?
BeanFactory.FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName : beanName);
} else {
return beanClass;
}
}到此可以測試以下新生成的代理類:
public class PluginTest {
@Autowired
private BEngine bEngine;
@Autowired
private DslListener dslListener;
@Test
public void test() throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
System.out.println("--------proxy before-----------");
System.out.println("BEngine.class:" + bEngine.getClass());
bEngine.launch();
DslContext dslContext = new DslContext();
// 初始值為 execution( void com.youclk.et.car.a.AEngine.launch() ),BEngine 並未被代理
dslContext.setExpression("execution( void com.youclk.et.car.b.BEngine.launch() )");
dslContext.setRefreshTypes(Collections.singletonList(BEngine.class));
dslListener.refresh(dslContext);
}
}結果如下:
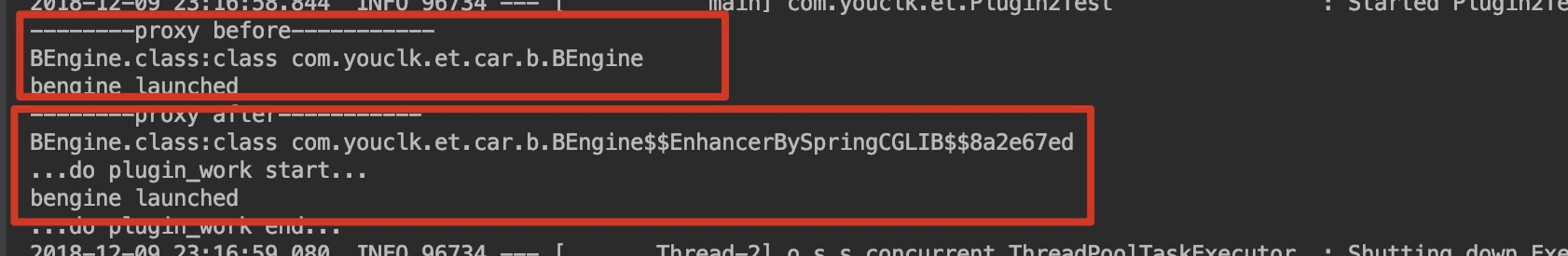
通過這種方式更新可以不用擔心多次重新整理代理物件產生的副作用,因為最終變化的只是代理類所匹配切面通知而已。
3.4 更新 Spring Context
開碼之前我一直認為這一步是難點,刷了一遍原始碼後發覺這一步異常簡單(看原始碼還是很重要...)。DefaultListableBeanFactory 其實有提供 remove 和 register 方法用於更新 Bean,但是這兩步的操作我認為太重了,而且在 remove 和 register 之間用到了這個 Bean 怎麼辦,因此存在極大風險。且看我們上一步做了什麼,從 BeanDefinition 這個維度看我們只更新了 classType,其他的都沒變,因此我考慮只要更新下 BeanDefinition,並清除對應的快取即可,示例如下:
private void refreshTypes(DslContext dslContext) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
List<Class<?>> refreshTypes = dslContext.getRefreshTypes();
for (Class<?> refreshType : refreshTypes) {
String[] beanNames = defaultListableBeanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(refreshType);
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Object bean = defaultListableBeanFactory.getBean(beanName);
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : defaultListableBeanFactory.getBeanPostProcessors()) {
bean = getProxyBean(bean, beanName, processor);
}
refreshBeanDefinition(beanName, bean.getClass());
}
}
}
private void refreshBeanDefinition(String beanName, Class<?> classType) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
RootBeanDefinition rootBeanDefinition = (RootBeanDefinition) defaultListableBeanFactory.getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName);
rootBeanDefinition.setBeanClass(classType);
ScannedGenericBeanDefinition scannedGenericBeanDefinition = (ScannedGenericBeanDefinition) defaultListableBeanFactory.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
scannedGenericBeanDefinition.setBeanClass(classType);
removeBeanDefinitionCache(beanName);
}
private void removeBeanDefinitionCache(String beanName) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
Field factoryBeanObjectCache_f = DefaultListableBeanFactory.class
.getSuperclass()
.getSuperclass()
.getSuperclass()
.getDeclaredField("factoryBeanObjectCache");
factoryBeanObjectCache_f.setAccessible(true);
Map<String, Object> factoryBeanObjectCache = (Map<String, Object>) factoryBeanObjectCache_f.get(defaultListableBeanFactory);
factoryBeanObjectCache.remove(beanName);
Field singletonObjects_f = DefaultListableBeanFactory.class
.getSuperclass()
.getSuperclass()
.getSuperclass()
.getSuperclass()
.getDeclaredField("singletonObjects");
singletonObjects_f.setAccessible(true);
Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = (Map<String, Object>) singletonObjects_f.get(defaultListableBeanFactory);
singletonObjects.remove(beanName);
Field singletonFactories_f = DefaultListableBeanFactory.class
.getSuperclass()
.getSuperclass()
.getSuperclass()
.getSuperclass()
.getDeclaredField("singletonFactories");
singletonFactories_f.setAccessible(true);
Map<String, Object> singletonFactories = (Map<String, Object>) singletonFactories_f.get(defaultListableBeanFactory);
singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
Field earlySingletonObjects_f = DefaultListableBeanFactory.class
.getSuperclass()
.getSuperclass()
.getSuperclass()
.getSuperclass()
.getDeclaredField("earlySingletonObjects");
earlySingletonObjects_f.setAccessible(true);
Map<String, Object> earlySingletonObjects = (Map<String, Object>) earlySingletonObjects_f.get(defaultListableBeanFactory);
earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
}測試下是否完成了我的預期:
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Test
public void testRefreshBeanDefinition() throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
System.out.println("--------refresh before-----------");
System.out.println("BEngine.class:" + applicationContext.getBean(bEngine.getClass()).getClass());
refresh();
System.out.println("--------refresh after-----------");
System.out.println("BEngine.class:" + applicationContext.getBean(bEngine.getClass()).getClass());
}
private void refresh() throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
DslContext dslContext = new DslContext();
//初始值為 execution( void com.youclk.et.car.a.AEngine.launch() ),BEngine 並未被代理
dslContext.setExpression("execution( void com.youclk.et.car.b.BEngine.launch() )");
dslContext.setRefreshTypes(Collections.singletonList(BEngine.class));
dslListener.refresh(dslContext);
}結果如下:
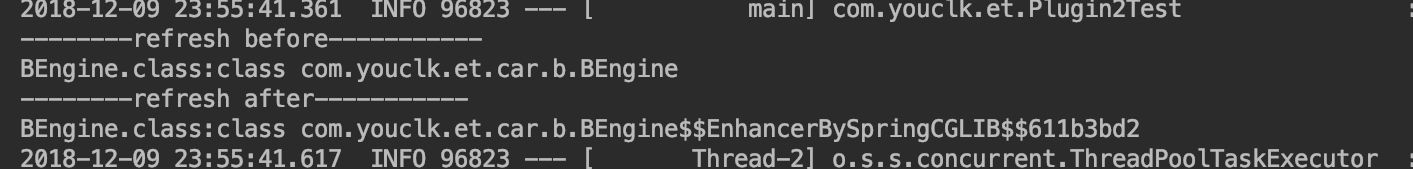
兩次獲取到的 classType 不同,說明更新成功。
3.5 更新 IOC 容器
這是最關鍵的一步,從運算元量上來看也是最重的一步,我們來回顧下,到此我們已經重新整理了代理、重新整理了切面通知、並將變更提交到了 Spring Context 中,我們還缺最後一步:更新目標物件所有的依賴注入。
因為我們需要將修改後的 Bean 重新注入所有依賴他的 Bean 中,這其中可能涉及到眾多的修改操作,因此第一步我們要獲取所有的依賴注入關係,他們維護在:AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.injectionMetadataCache 中;由於一次提交可能涉及到多個目標物件的更新,他們之間又有存在依賴的可能性,因此第二步先把那一堆新的 bean 刷到 metadataCache,最後篩選出所有與更新相關的依賴,重新注入一遍,示例如下:
private AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor autowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor;
private void refreshTypes(DslContext dslContext) throws Exception {
List<Class<?>> refreshTypes = dslContext.getRefreshTypes();
HashMap<String, String> refreshBeans = new HashMap<>();
for (Class<?> refreshType : refreshTypes) {
String[] beanNames = defaultListableBeanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(refreshType);
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Object bean = defaultListableBeanFactory.getBean(beanName);
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : defaultListableBeanFactory.getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (processor instanceof AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor) {
autowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor = (AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor) processor;
continue;
}
bean = getProxyBean(bean, beanName, processor);
}
refreshBeanDefinition(beanName, bean.getClass());
refreshBeans.put(beanName, getRealName(bean.getClass().getName()));
}
}
refreshIoc(refreshBeans);
}
private void refreshIoc(HashMap<String, String> refreshBeans) throws Exception {
for (String refreshBeanName : refreshBeans.keySet()) {
resetInjectionMetadataCache(refreshBeanName);
}
Set<Object> beans = getReInjectionBeans(refreshBeans);
for (Object bean : beans) {
defaultListableBeanFactory.autowireBeanProperties(bean, 0, false);
}
}
private void resetInjectionMetadataCache(String refreshBeanName) {
autowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.resetBeanDefinition(refreshBeanName);
autowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.determineCandidateConstructors(refreshBeanName.getClass(), refreshBeanName);
RootBeanDefinition rootBeanDefinition = (RootBeanDefinition) defaultListableBeanFactory.getMergedBeanDefinition(refreshBeanName);
Object bean = defaultListableBeanFactory.getBean(refreshBeanName);
autowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(rootBeanDefinition, bean.getClass(), refreshBeanName);
}
private Set<Object> getReInjectionBeans(HashMap<String, String> refreshBeans) throws Exception {
Field injectionMetadataCache_f = AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class.getDeclaredField("injectionMetadataCache");
injectionMetadataCache_f.setAccessible(true);
Map<String, InjectionMetadata> factoryBeanObjectCache = (Map<String, InjectionMetadata>) injectionMetadataCache_f.get(autowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor);
Set<Object> injectedBeanNames = new HashSet<>();
for (String beanName : factoryBeanObjectCache.keySet()) {
Collection<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> injectedElements = getInjectedElements(factoryBeanObjectCache.get(beanName));
if (injectedElements == null) {
continue;
}
for (InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement injectedElement : injectedElements) {
if (refreshBeans.values().contains(getRealName(getResourceType(injectedElement).getName()))) {
injectedBeanNames.add(defaultListableBeanFactory.getBean(beanName));
}
}
}
return injectedBeanNames;
}
private Collection<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> getInjectedElements(InjectionMetadata injectionMetadata) throws Exception {
Field injectedElements_f = InjectionMetadata.class.getDeclaredField("injectedElements");
injectedElements_f.setAccessible(true);
Collection<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> injectedElements = (Collection<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement>) injectedElements_f.get(injectionMetadata);
return injectedElements;
}
private Class<?> getResourceType(InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement injectedElement) throws Exception {
Method getResourceType_m = InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement.class.getDeclaredMethod("getResourceType");
getResourceType_m.setAccessible(true);
return (Class<?>) getResourceType_m.invoke(injectedElement);
}
private String getRealName(String instanceName) {
int index = instanceName.indexOf("$");
if (index > 0) {
instanceName = instanceName.substring(0, index);
}
return instanceName;
}最後再來測試一波:
@Test
public void test() throws Exception {
bEngine.launch();
refresh();
bEngine.launch();
}正如預期效果:
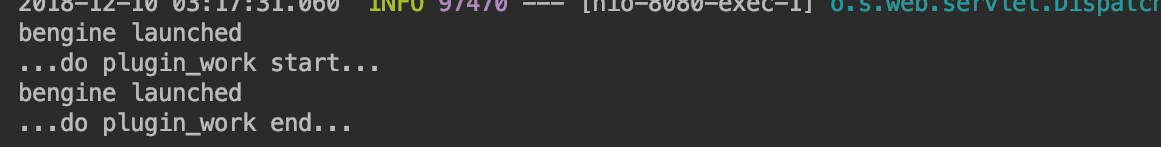
結語
靈明無著,物來順應,未來不迎,當下不雜,既過不戀~ 請關注公眾號:

