03-樹3 Tree Traversals Again (25 point(s))
03-樹3 Tree Traversals Again (25 point(s))
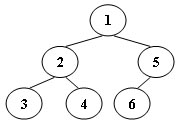
An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recursive way with a stack. For example, suppose that when a 6-node binary tree (with the keys numbered from 1 to 6) is traversed, the stack operations are: push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop(). Then a unique binary tree (shown in Figure 1) can be generated from this sequence of operations. Your task is to give the postorder traversal sequence of this tree.
Figure 1
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤30) which is the total number of nodes in a tree (and hence the nodes are numbered from 1 to N). Then 2N lines follow, each describes a stack operation in the format: "Push X" where X is the index of the node being pushed onto the stack; or "Pop" meaning to pop one node from the stack.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the postorder traversal sequence of the corresponding tree in one line. A solution is guaranteed to exist. All the numbers must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
6 Push 1 Push 2 Push 3 Pop Pop Push 4 Pop Pop Push 5 Push 6 Pop Pop
Sample Output:
3 4 2 6 5 1題意:總結下來就是:用stack模擬了二叉樹的先序和中序,我們要輸出該二叉樹的後序遍歷。 push就是先序,pop就是中序,我們可以建立一個stack容器來儲存。
程式碼如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=100;
struct tree{
int data;
tree *l;
tree *r;
};
int per[maxn],in[maxn];
tree* Buildtree(int pl,int pr,int il,int ir){
if(pl>pr){
return NULL;
}
tree *root = new tree;
root->data=per[pl];
int k;
for(k=il;k<=ir;k++){
if(in[k]==root->data)
break;
}
int lnum=k-il;
root->l=Buildtree(pl+1,pl+lnum,il,k-1);
root->r=Buildtree(pl+lnum+1,pr,k+1,ir);
return root;
}
int flag=0;
void postorder(tree *root){
if(root==NULL)
return;
postorder(root->l);
postorder(root->r);
if(!flag){
cout<<root->data;
flag=1;
}
else
cout<<" "<<root->data; //末尾不能有多餘空格
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
int cnt=0;
string str;
int num,i=0,k=0;
stack <int>s;
while(cnt<n){ //當Pop次數和要輸入的資料相等時不再輸入
cin>>str;
if(str=="Push"){
cin>>num;
per[i++]=num;
s.push(num);
}
if(str=="Pop"){
int res=s.top(); //將stack容器中的元素轉移到中序遍歷陣列中
s.pop();
in[k++]=res;
cnt++;
}
}
tree *root=Buildtree(0,n-1,0,n-1); //根據先序和中序建立二叉樹
postorder(root); //後序遍歷
return 0;
}